ISSS608 2018-19 T1 Assign Arief Sulistio Task2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Task 2: Spatio-temporal Analysis of Citizen Science Air Quality Measurements
In this page, we are going to analyze our secondary data source which come from Citizen Science Air Quality Measurements.
Data Exploratory
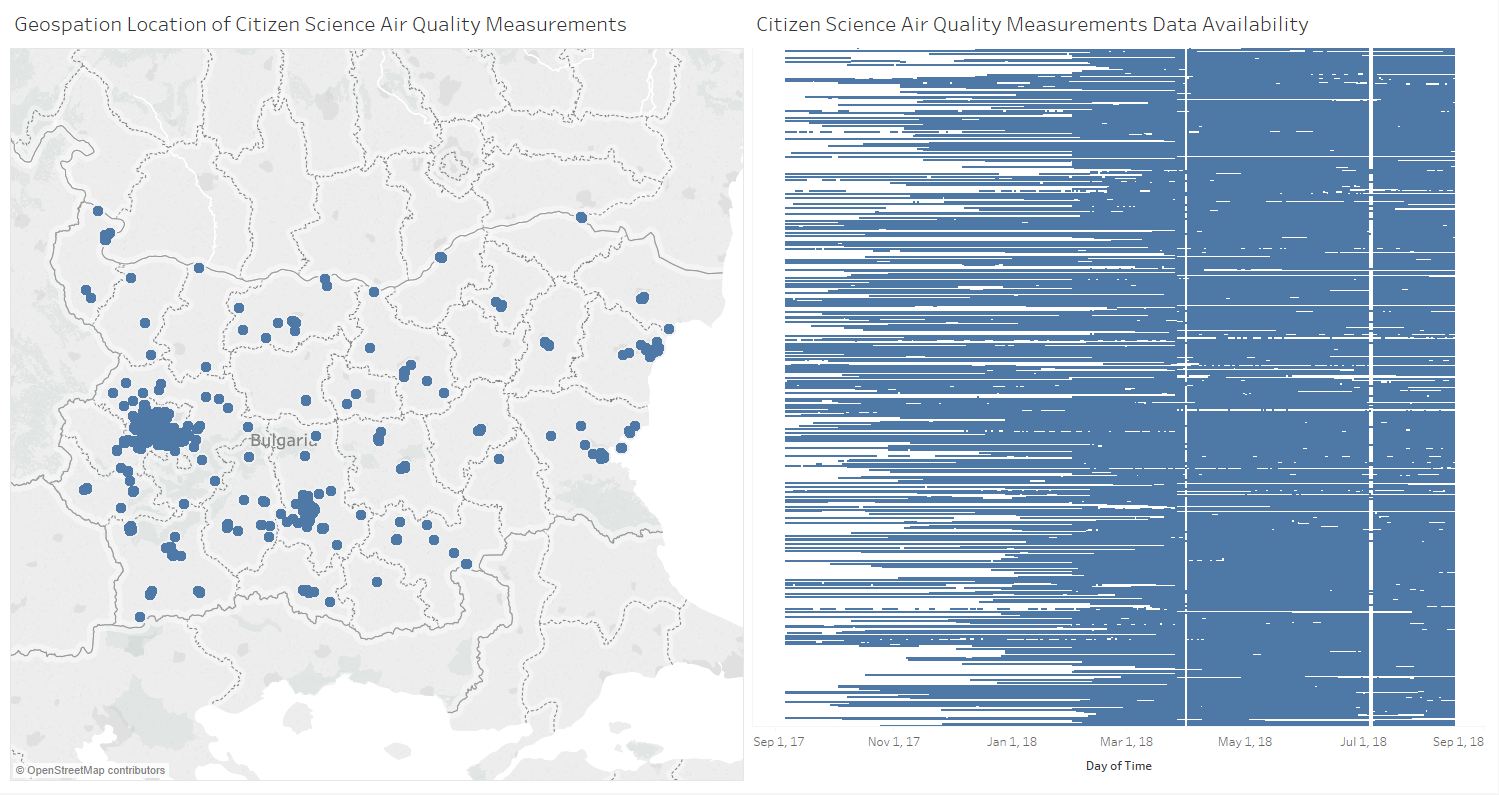
Figure 1 (Top). Top left: was geo-spatial location of Citizen Science's station. Top right: was data availability in chronological order, each rows represent a single station. From the data we had, Citizen Science's data was better distributed across country with 1980 different station points as compare with 6 goverment's stations in which all located in Sofia. Majority of these stations was located in capital city of Sofia. on the Top right we can see that there is increase in number of station along the year which shows a good progress of obtaining a more data measurement. From data quality stand point, there are multiple missing data across all stations and there are few particular days where no data available from all stations. We also identify 1 abnormal coordinate which we excluded in our analysis.
Since all goverment's station was located only in Sofia's city, we limit our analysis to only stations in proximity with goverment's as we need to compare both stations performance.
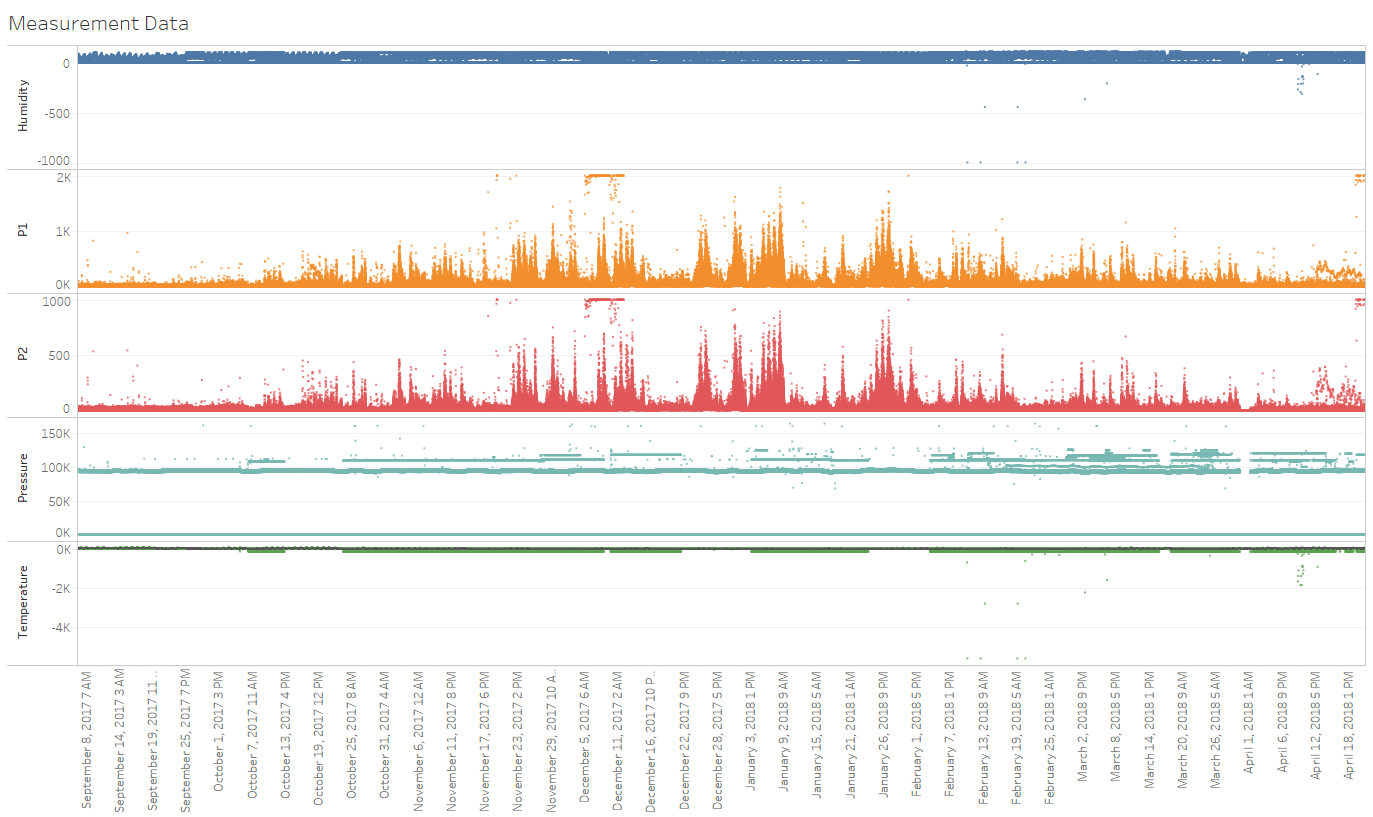
Figure 2(Top)show the measurement result from 556 stations located near goverment's stations in Sofia. as we can see from the result, there are few abnormalities observed from multiple stations such as: 2 stations reporting temperature at lower than -2000C, 20 stations reported 0 P1 and P2 measurement and 31 stations are reporting more than 1k P1 value, 25 stations reporting 0 value for Temperature/Humidity/Pressure, no differentiation between "no data" and data with 0 value, multiple stations reporting flat unchanged measurement result, and so on. These issue was most likely due to no regulation with regards to all these stations, causing its capability and accuracy was varied across different device. All these tools was never calibrated which each other as well, causing potential systematic error during measurement. For these reason, we will filter out these stations and using aggregate value of measurement reading to minimize the inconsistency.
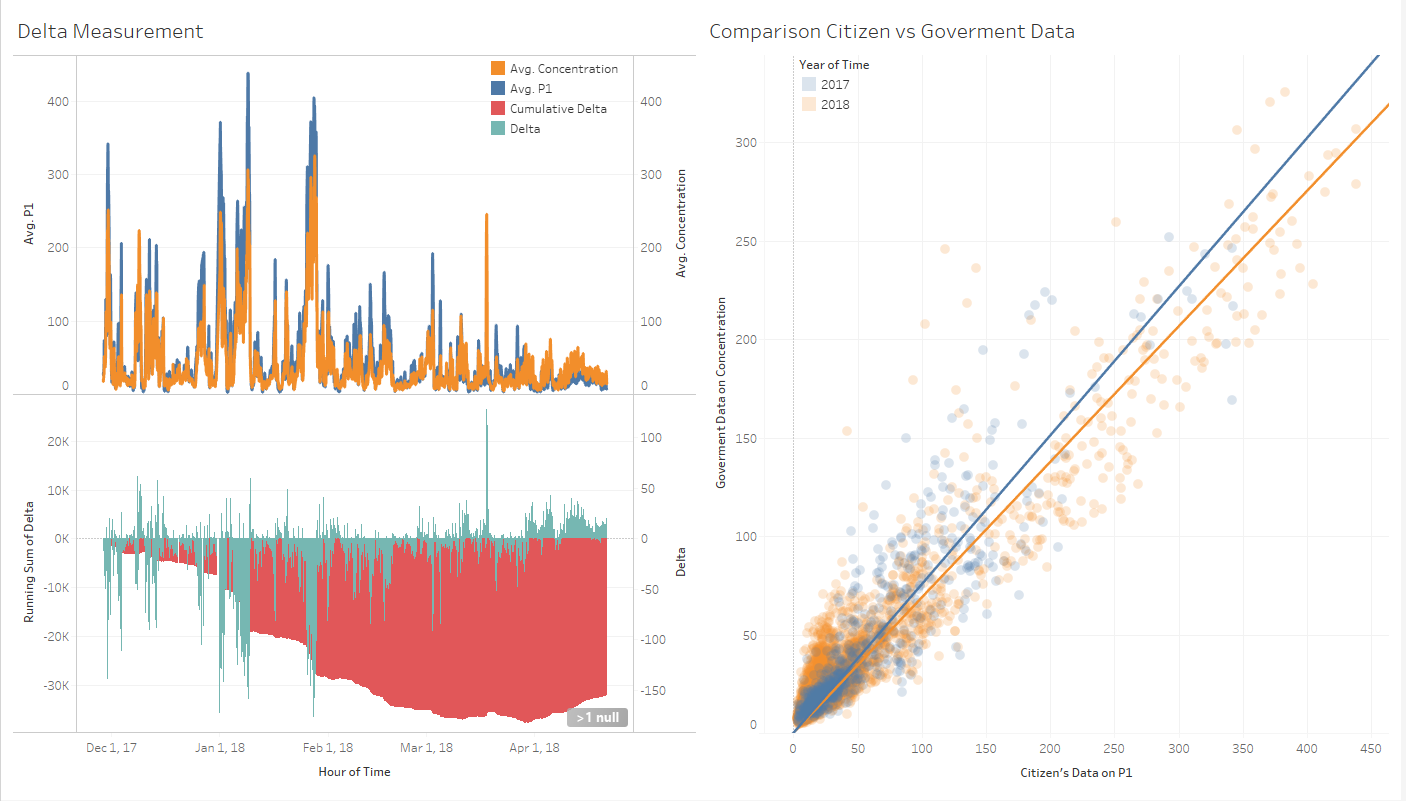
According to datasource from AirTube [1] the P1 in the data was measuring average of P10 particle, which suppose to be the same with government measurement result. Therefore we will need to compare these 2 measurement result for reliability check.
Air Pollution Consentration
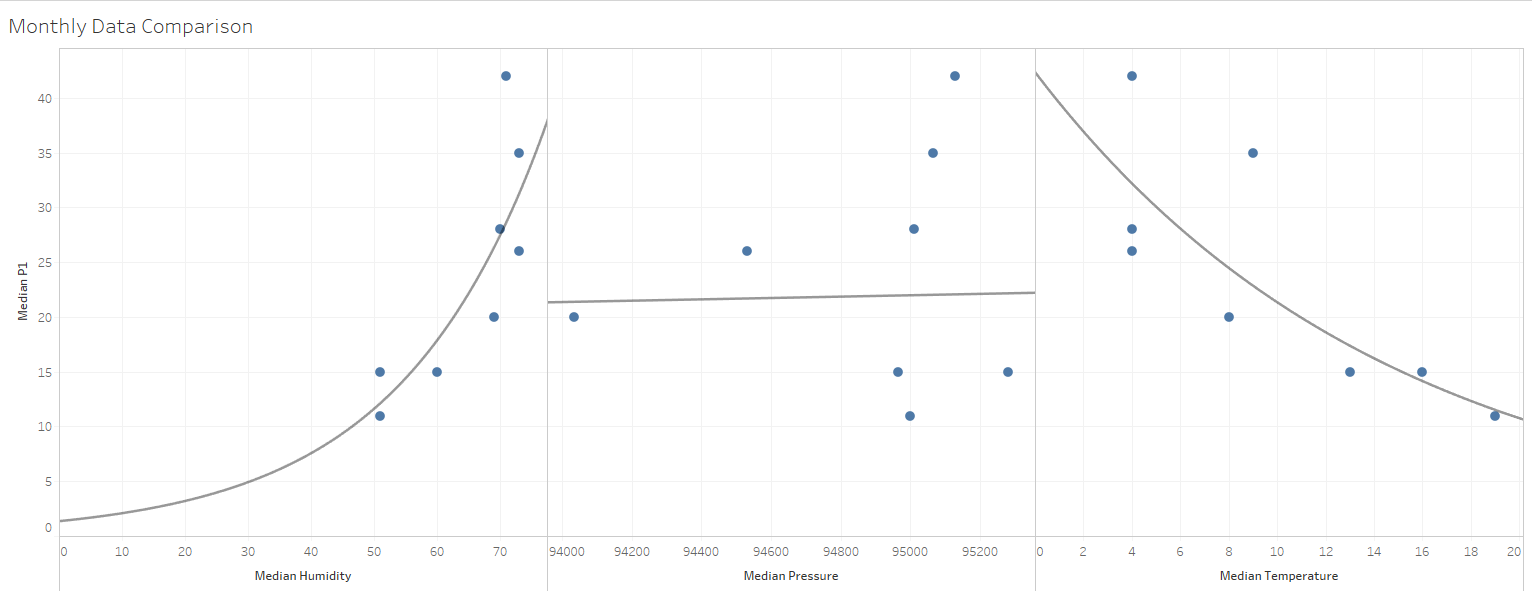
We return back to initial objective, which was to analyze the air pollution contamination. We have show that both government and civilian data are aligned, now we are using additional information we have from civilian's data to understand more on the distribution of air pollution across Sophia. We will first try to identify relationship between Temperature, Pressure, and Humidity with P1 measurement. We will look at monthly aggregate data as comparison to minimize and data abnormality.
From figure 4 (Top), we observe that there is positive quadratic relationship between humidity and P1, and negative relationship between temperature and P1 reading. No significant relationship between Pressure value and P1. This increase in P1 due to drop in temperature may be attributed due to increase in pollution coming from heater. For next analysis, we will focus more on temperature vs P1 as it is easier to relate to and interpreted.
Next is we are using civilian data to mapped the air pollution and temperature pattern across the city to see if there is any time-depended pattern. we will observe monthly data first and followed by hourly breakdown for specific month.
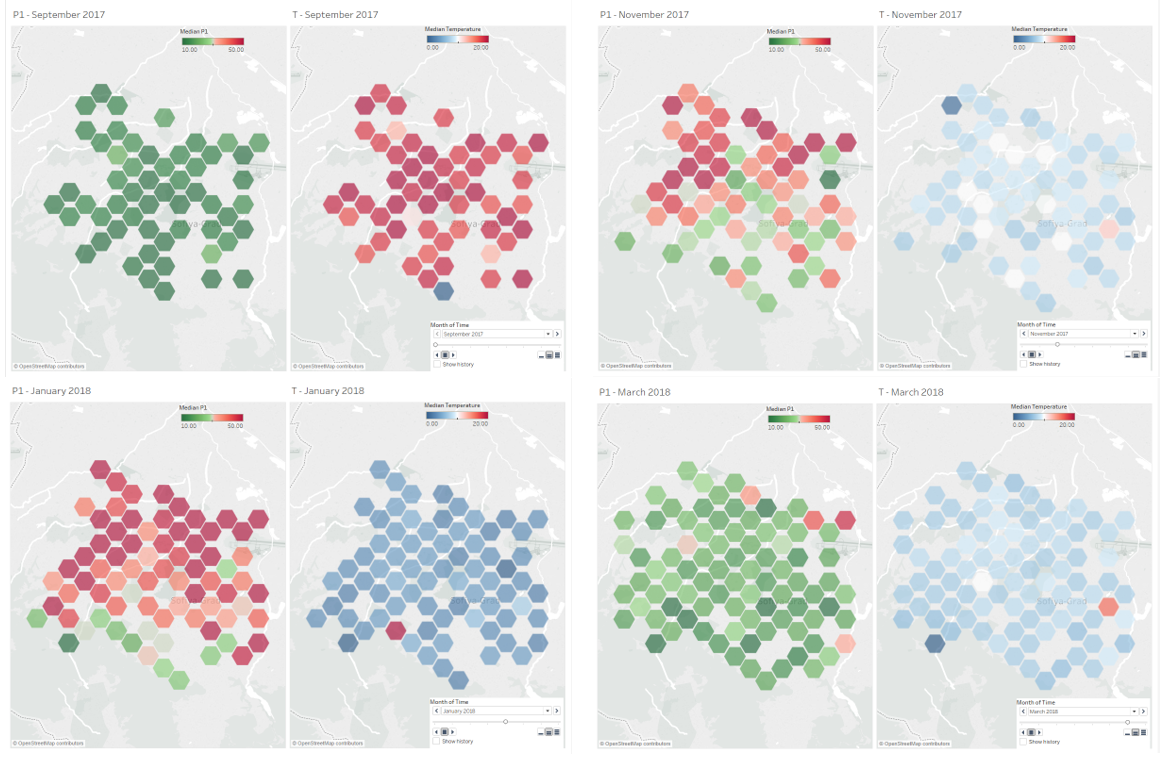
From figure 5 (Top), we are comparing the air pollutant reading and temperature across Sofia in 4 different snapshot month.
- Sep'17 (Top left): Higher temperature at around 19C. Low air pollutant at about 11µg/m3.
- Nov'17 (Top right): Average temperature drop to around 9C. Increase in air pollutant to 35µg/m3. Some area on the north have breach 50µg/m3 limit.
- Jan'18 (Bottom left): Average temperature continue to drop to 4C. Average air pollutant increase to 42µg/m3. Some area has air pollutant concentration as high as 91µg/m3.
- Mar'18 (Bottom right): Average temperature start to increase to 8C. Average air pollutant reduce to 20µg/m3
Besides, we also can see few other observation:
- Temperature distribution across Sofia was quite evenly distributed
- Air Pollutant start to increased from northern side to the south.
- When temperature start to climb up, air pollution was ceased across all city together.
- This pattern indicates that temperature may not be the sole contribution of air pollutant. Further study are required to analyze the impact of other parameter such as altitude, geography, wind, etc.
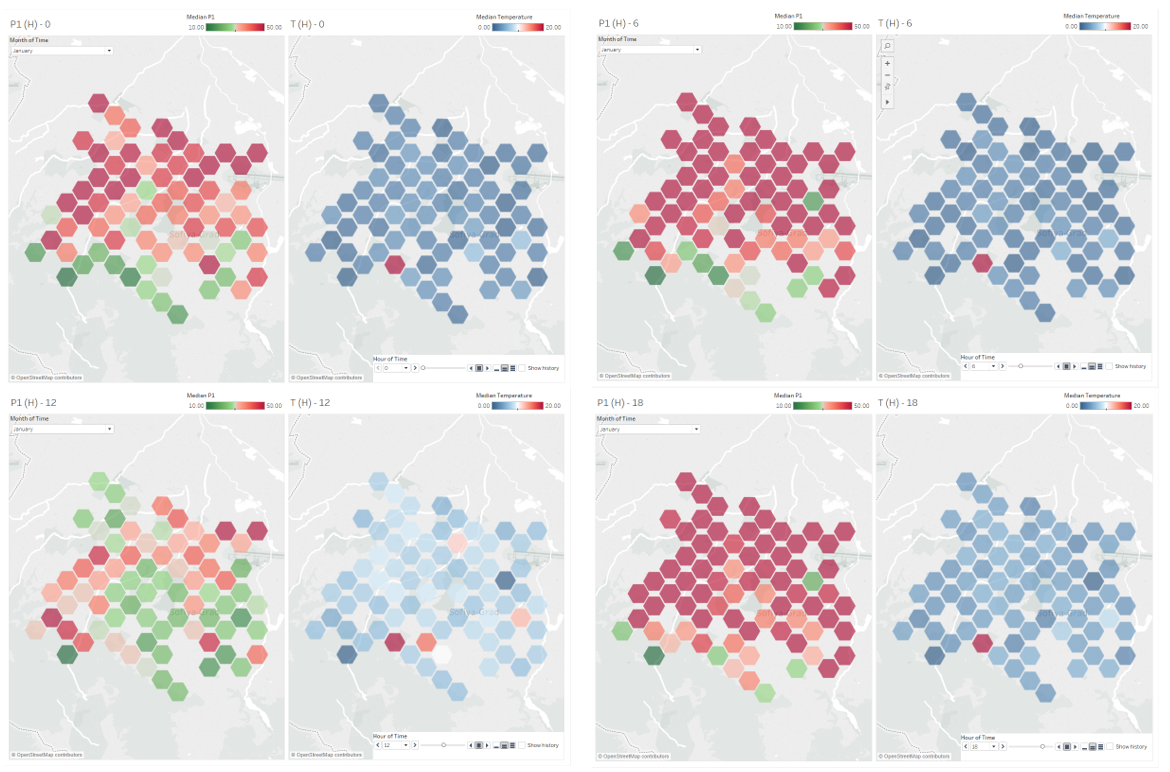
For next analysis, we are looking at hourly Spatio-temporal analysis on the month of Jan.
From figure 6 (Top), we are comparing the air pollutant reading and temperature in the month of January. There is 1 outlier data for temperature (highlighted red), showing unchangeable measurement reading of 23C.
- 00:00 Midnight (Top left): Average temperature at 2C, High air pollutant concentration at 37µg/m3 which mainly from the northern part.
- 06:00 (Top right): Average temperature still at 2C. Increase in average air pollutant to 50µg/m3. Some area reported to reach 130µg/m3.
- 12:00 (Bottom left): Average temperature reach its peak at 7C. Average air pollutant drop to 30µg/m3.
- 18:00 (Bottom right): Average temperature start to drop to 4C. Average air pollutant increase back to 54µg/m3.
From here, we can see similar pattern of air pollution and temperature across Sofia, which is higher air pollutant from the north side while temperature was well distributed across the city.