Difference between revisions of "IS428 AY2019-20T1 Assign Foo Yong Long:R&R"
Ylfoo.2017 (talk | contribs) |
Ylfoo.2017 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
<div style="background: #364558; padding: 15px; font-weight: bold; line-height: 0.3em; text-indent: 0px;font-size:20px"><font face="Arial" color=#fbfcfd><center>'''Contamination Control'''</center></font></div> | <div style="background: #364558; padding: 15px; font-weight: bold; line-height: 0.3em; text-indent: 0px;font-size:20px"><font face="Arial" color=#fbfcfd><center>'''Contamination Control'''</center></font></div> | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="background-color:#FFFFFF;" width="100%" | {| class="wikitable" style="background-color:#FFFFFF;" width="100%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
1 | 1 | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:EndState.jpg| 900px |center]] | ||
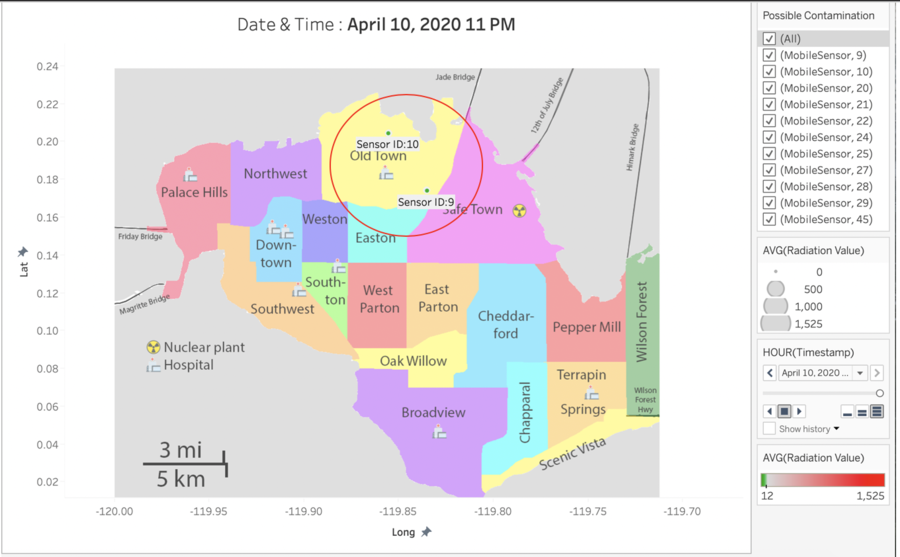
| + | Highly likely contaminated cars with sensor IDs 20,21,22,24,25,27,28,29 and 45 has left the country. The government should issue a warning to search for these 9 vehicles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
2 | 2 | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | + | [[File:EndState6Hrs.jpg| 900px |center]] | |
| − | | | ||
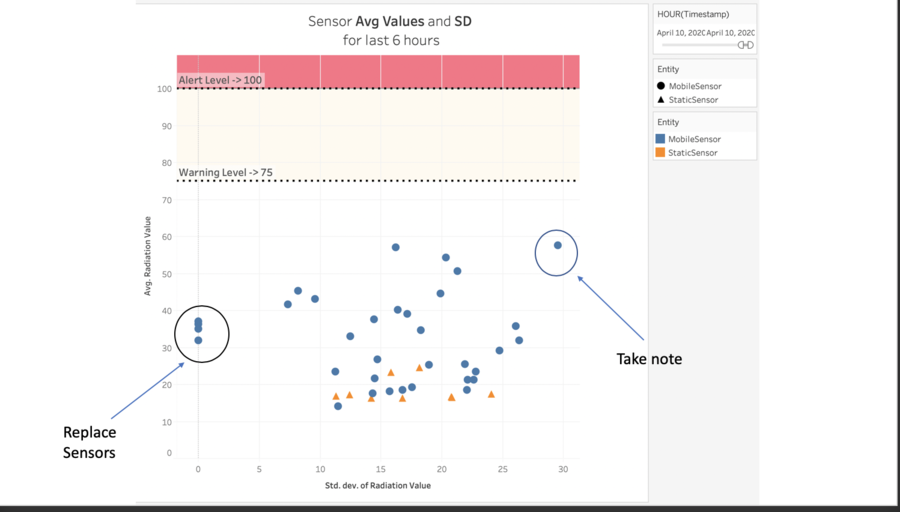
| − | + | The graph above shows the standard deviation and average value of sensor readings for the last 6 hours that are still in the city. Sensor 1,26,35 and 47 has to be checked and replaced as they may be faulty with 0 standard deviations in readings for the last 6 hours. The government will have to Monitor mobile sensor 32 carefully as it has a high variability of sensor readings and its average value is reaching the warning level. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
===Use visual analytics to compare the static sensor network to the mobile sensor network. What are the strengths and weaknesses of each approach? How do they support each other?=== | ===Use visual analytics to compare the static sensor network to the mobile sensor network. What are the strengths and weaknesses of each approach? How do they support each other?=== | ||
Revision as of 21:17, 13 October 2019
Contents
- 1 Question 4
- 1.1 Summarize the state of radiation measurements at the end of the available period. Use your novel visualizations and analysis approaches to suggest a course of action for the city.
- 1.2 Use visual analytics to compare the static sensor network to the mobile sensor network. What are the strengths and weaknesses of each approach? How do they support each other?
- 2 Question 5
Question 4
Summarize the state of radiation measurements at the end of the available period. Use your novel visualizations and analysis approaches to suggest a course of action for the city.
| No. | Description | |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Highly likely contaminated cars with sensor IDs 20,21,22,24,25,27,28,29 and 45 has left the country. The government should issue a warning to search for these 9 vehicles. |
|
|
2 |
The graph above shows the standard deviation and average value of sensor readings for the last 6 hours that are still in the city. Sensor 1,26,35 and 47 has to be checked and replaced as they may be faulty with 0 standard deviations in readings for the last 6 hours. The government will have to Monitor mobile sensor 32 carefully as it has a high variability of sensor readings and its average value is reaching the warning level. |
Use visual analytics to compare the static sensor network to the mobile sensor network. What are the strengths and weaknesses of each approach? How do they support each other?
| No. | Description |
|---|---|
|
4 |
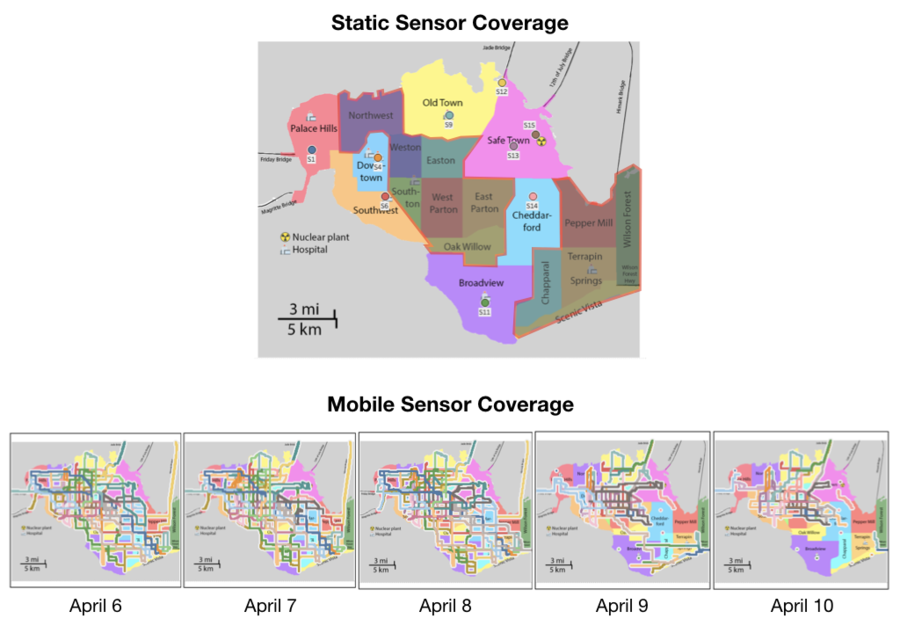
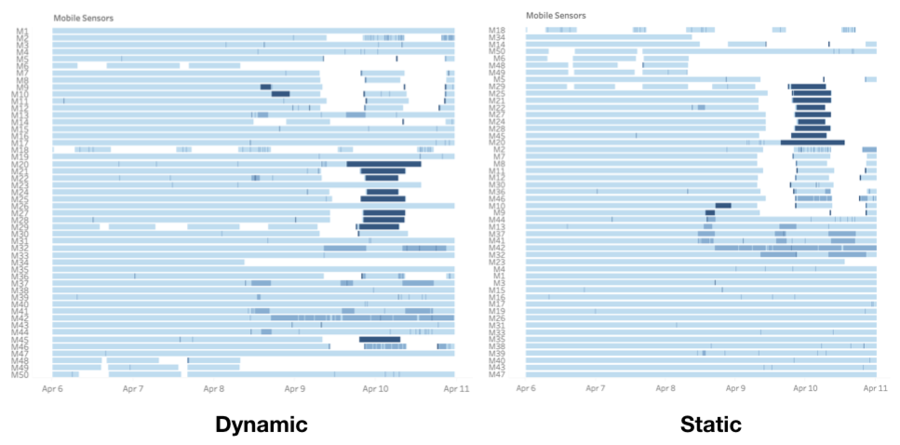
The 9 static sensors are only cover 7 out of the 19 neighbourhoods, leaving many neighbourhoods in Central and Southeast St.Himark uncovered. The range of the static sensors also do not seem to be sufficient to detect radiation over an entire neighbourhood given their relatively low readings, with the occasional spike. |
|
5 |
The mobile sensors provided much better coverage of the city, with the 50 sensors covering pretty much the entire island on a day to day basis. However, in the aftermath of an earthquake or major event (April 9 – 10) the mobility of cars can become restricted due to infrastructure damage. Citizens may also avoid travelling in the aftermath, resulting in lesser ground covered. |
Question 5
The data for this challenge can be analyzed either as a static collection or as a dynamic stream of data, as it would occur in a real emergency. Describe how you analyzed the data - as a static collection or a stream.
| No. | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
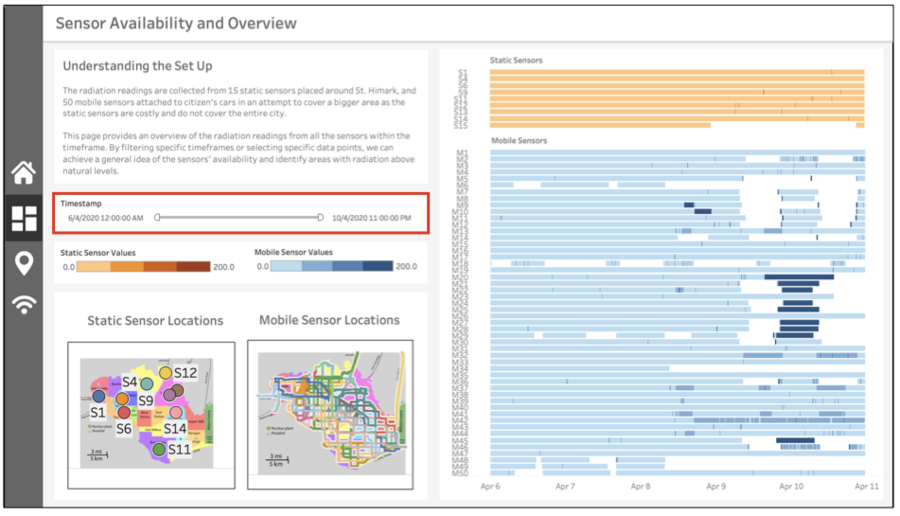
In the process of designing the dashboard, I ensured that all the visualizations could be filtered by date. This is so that static analysis can be done on the entire dataset, as well as dynamic analysis by working on a sliding window of data. |
How do you think this choice affected your analysis?
| No. | Description |
|---|---|
|
2 |
While most of the analysis could be done dynamically, static analysis is especially helpful when trying to identify clusters or patterns in the data. When viewing a stream of dynamic sensor data, it is very difficult to immediately identify patterns or gaps at a glance. However, when viewed statically, it is possible to sort them in a manner where visible clusters and patterns can be found to make meaningful analysis. |