Difference between revisions of "1718t1is428T3"
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
| | | | ||
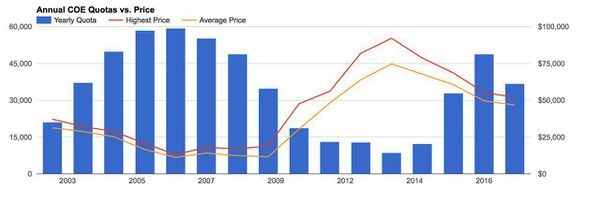
<p><center>'''COE Price Data''' </center></p> | <p><center>'''COE Price Data''' </center></p> | ||
| + | <p><center>https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1Ma8dm_rdtdfNp8ONUG5ykFHwrEg1GFC3ObOMualMVBM/edit#gid=0</center></p> | ||
[[File:Car_prices_ceic_dataset.PNG|center|300px]] | [[File:Car_prices_ceic_dataset.PNG|center|300px]] | ||
|| | || | ||
| Line 223: | Line 224: | ||
Our team has decided to focus on the following tools and libraries to create the visualisations and analysis | Our team has decided to focus on the following tools and libraries to create the visualisations and analysis | ||
*D3.js | *D3.js | ||
| − | |||
*Tableau | *Tableau | ||
*Notepad++ | *Notepad++ | ||
Revision as of 00:08, 27 November 2017
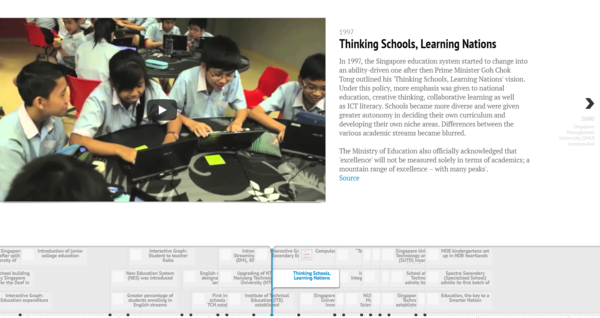
A recent news article highlights Singapore's struggle between owning cars and taking public transportation. "The Big Read: Despite push for public transport, a love for cars endures" The government has been making a conscientious effort to promote the utilization of the public transport and dissuade the public from driving. Apart from improving the transport system, there are deterrent measures such as a Certificate of Entitlement (COE) bidding system, high carpark rates, high taxes and the dreaded ERPs.
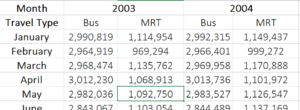
Out of these factors, the COE not only takes up the largest proportion of income spent on cars, its significant fluctuations are discussed the most frequently with a bid occurring every twice a month. Data Autolytics serves to explore the relationship between the existing COE prices and public transport. With our current infrastructure, are people really be dissuaded by even higher COE prices? Or does the government need to have more pull factors to woo people to using the public transport?
The push for more quantifiable analysis in Singapore have made current resources data-rich but information poor. Presently, there are many sources of fragmented datasets on the vehicle population. There is a need for policy makers, industry professionals and the everyday Singaporean to be able to easily access understand the transport landscape before they make informed decisions on policies or drive for change. To be able to do so, they need to be able to access the data from a central location and have the numbers tell a story in a way which they can easily understand and analyse. By piecing the parts together, we hope to give a more complete picture and help our audiences make more informed decisions.
We aim to deliver an interactive web application that allows someone to easily access and navigate a large amount of time-series data.
Our intended audiences are:
- Car suppliers dealers to make better forecasts
- Prospective car buyers
- Government and policy makers regarding vehicle overpopulation
In this project, we will be focusing on the following:
- Different price sensitivities of car buyers
- The market share of car brands
- The proportion of transport expenditure to the transport tax revenue collected
- The effectiveness of COE prices in encouraging public transport ridership
| Related Works | Relevant and Useful Features |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Proposed Visualization | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Visualising the Car Market Market Share of Car Brands |
The overview of the Singapore's private vehicle market will be shown in "Visualising the Car Market" and the "Market Share of Car Brands" these two time series visualisations will give an overview of the customer demand of car brands and the varying car brand market share over time. User interactivity include: Playing the visualization to show the different car brand quantities changing over time. We can focus on car brands and learn about their COE price elasticity and changing market share. |
|
Tax Expenditure Public and Private Transport |
The next two visualisations will explore the relationship between expenditure of the COE as transport tax and whether the transport policies which are implemented with the COE tax revenue are effective. User interactivity includes: brushing over specific timeframes to zoom in on the trends. |
| Dataset/Source | Data Attribute | Rationale of Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
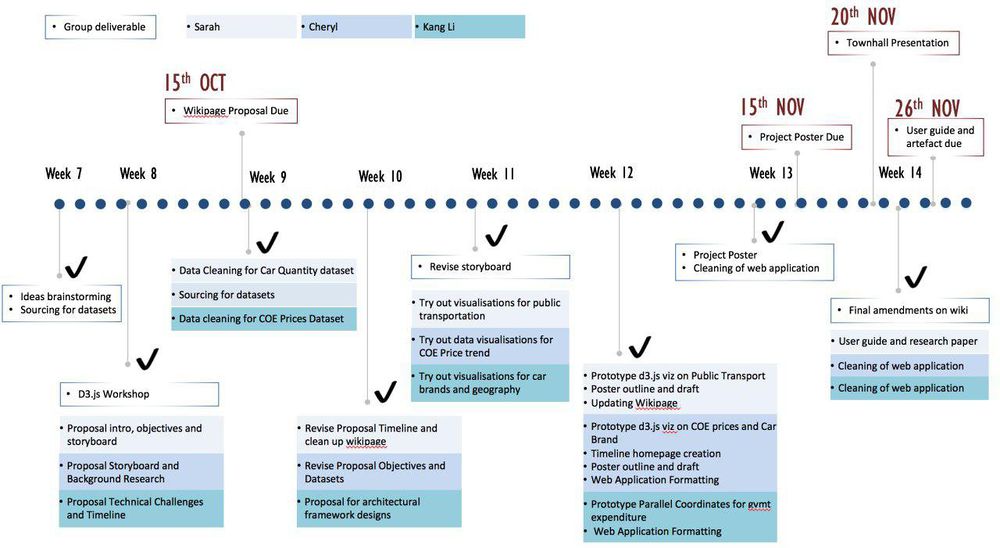
| Technical Challenges | Mitigation Plan |
|---|---|
| Obtaining datasets |
|
| Acquiring Data, Data Cleaning |
|
| Using d3.js and Highchart to display the visualisations which we want |
|
| Unfamiliarity in Implementing Interactivity and Animation Tools/Techniques in Visualization App |
|
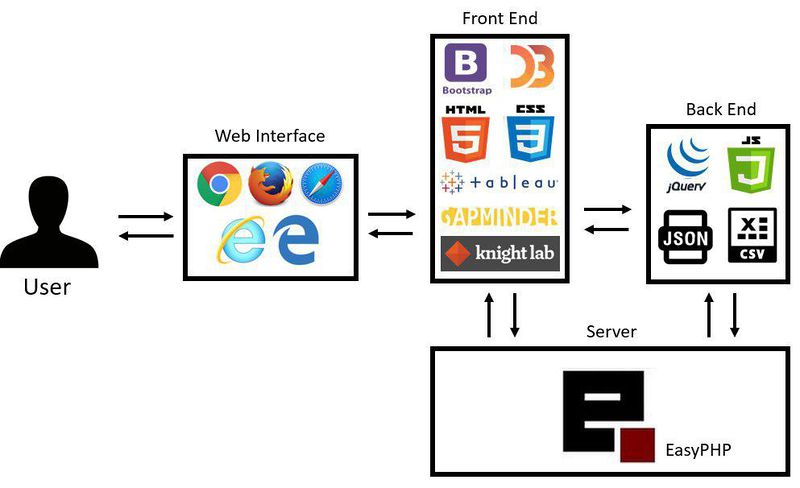
Our team has decided to focus on the following tools and libraries to create the visualisations and analysis
- D3.js
- Tableau
- Notepad++
- Adobe PhotoShop
- What influences COE prices?: https://www.gov.sg/factually/content/what-influences-coe-prices
- D3.js: https://d3js.org/
- CEIC Database: https://www.ceicdata.com/en
Please share with us your feedback! :)
Prof In class review: Project intro and motivation need review, get a full appreciation of data, data rich - information poor, need effort to consolidate. Technically this data is someone who collected through various sources to put it through LTA, consolidated info in LTA repo, one of this web data service provider, they actually subscribe to LTA, they distribute through their paid portal, unless you know a query search for vertical form. Need effort to organize it to do a proper analysis. Understand how the structure of data looks like, to create data visualization. The current data structure of what you download from CEIC, dont have hierarchical structure, so need to reorganize the data in hierarchy ways to have hierarchical structure. Organize data to be in line with visualization else cant realise it. Be more specific in the motivation. Data sets are generic cant see the real data, need provide screenshot to see how it looks like. Reviewing diff is good. Timeline need to be updated. Tech and tools need review.