Difference between revisions of "Mandi Assignment Final Answer"
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
<td align='justify'> | <td align='justify'> | ||
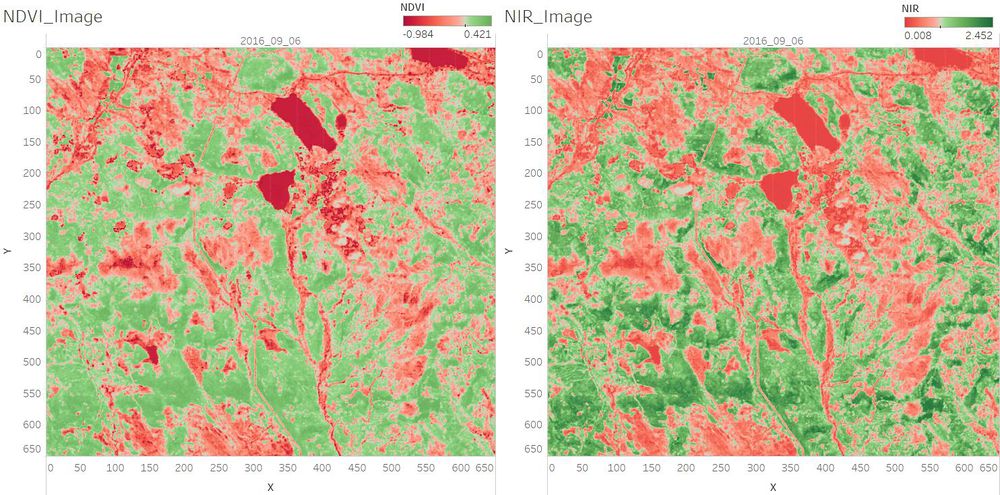
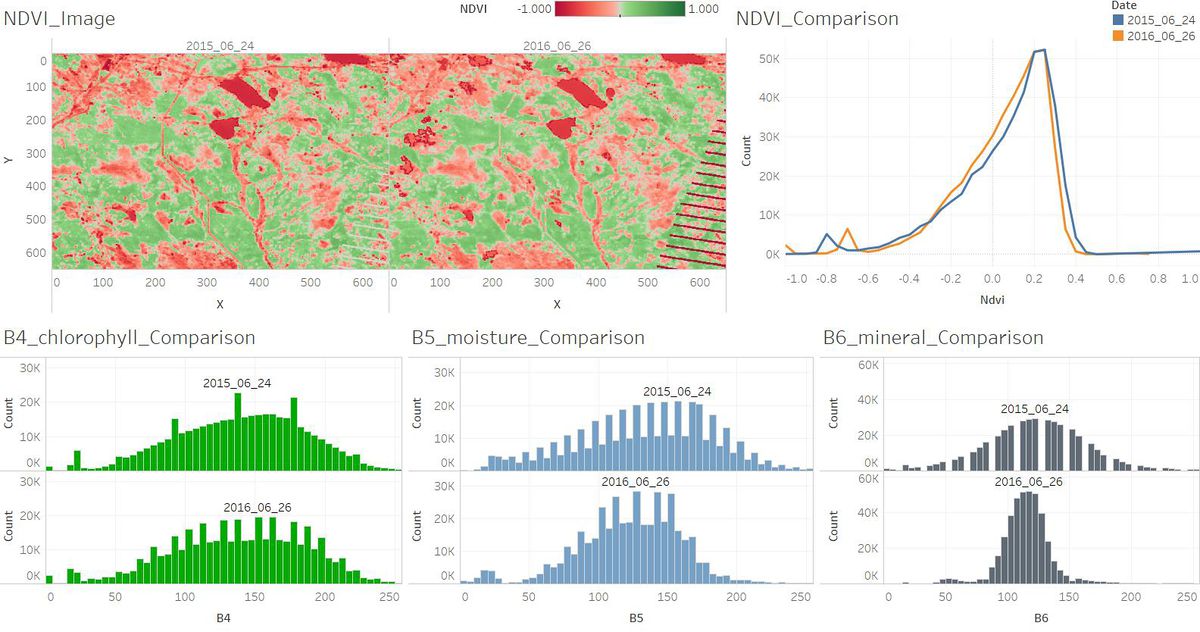
With the NDVI and RVI Value, we can identify the different vegetation. <br /> | With the NDVI and RVI Value, we can identify the different vegetation. <br /> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
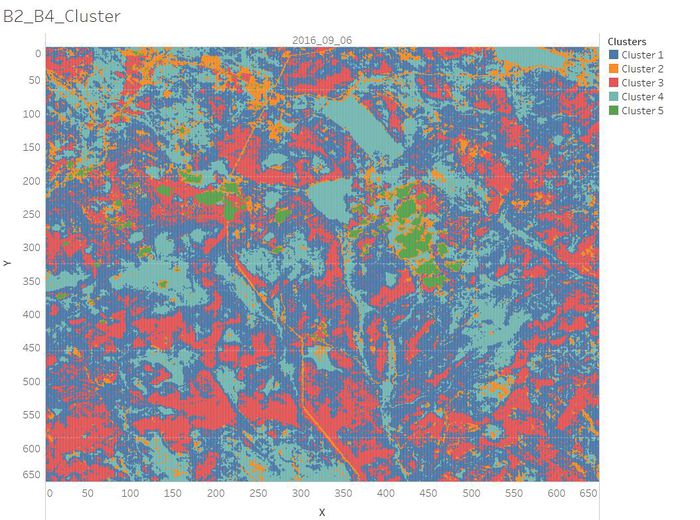
| + | <td width=60% align='center'>[[File:B2 B4 Cluster.jpg|700px]]</td> | ||
| + | <td align='justify'> | ||
* Cluster 1: Common vegetation with lower chlorophyll content. | * Cluster 1: Common vegetation with lower chlorophyll content. | ||
* Cluster 2: Road/Newly Land/Soil. | * Cluster 2: Road/Newly Land/Soil. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 59: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | + | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 00:04, 8 July 2017
Questions:
1. The scale and orientation of the supplied satellite images.
Identified the location and coordinates of the Boonsong Lake in the satellite image as below:
The orientation of the satellite image is the same with that of the Boonsong Lake.
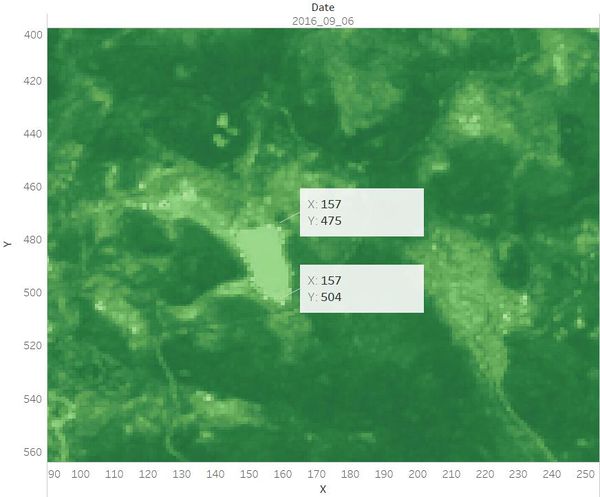
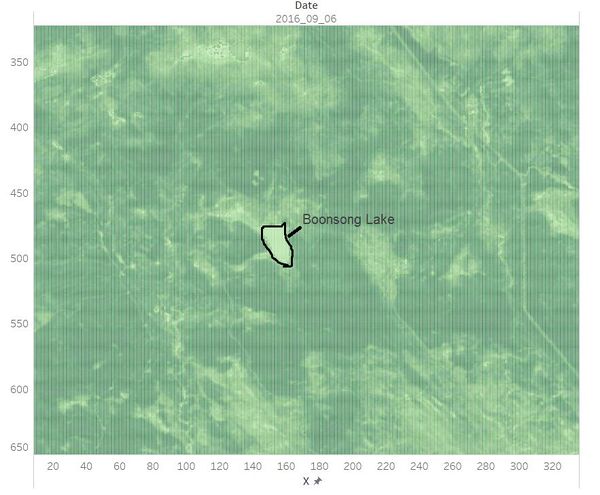

Hence, the length of a pixel is 3000/(504 - 475+1) ft, equals to 100 ft. Then the area of one pixel is 100 * 100 = 10000 square ft.
As the satellite image has 651*651 pixels, the actual scale of the region is 651*651*10000 square ft = 4,238,010,000 square ft.
The orientation of the satellite image is oriented north-south.
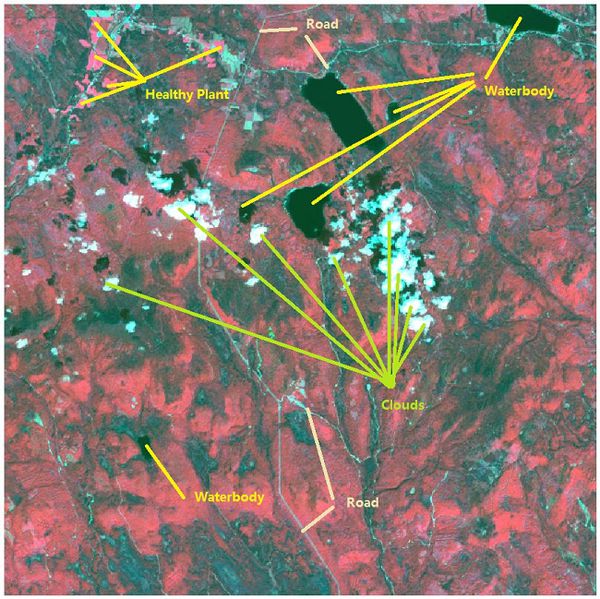
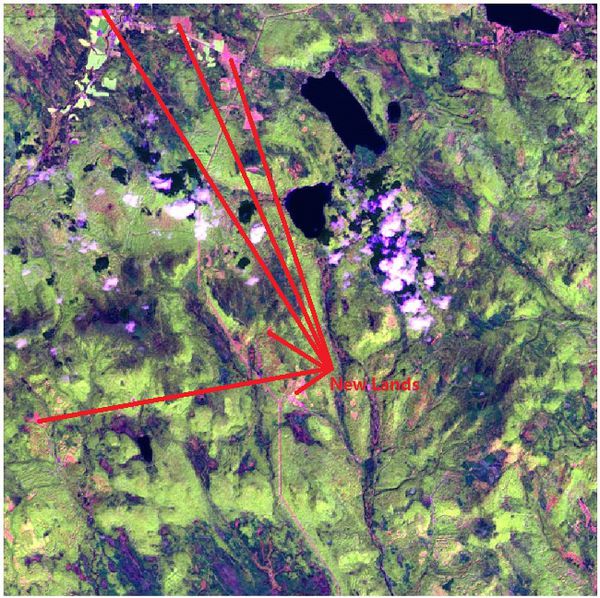
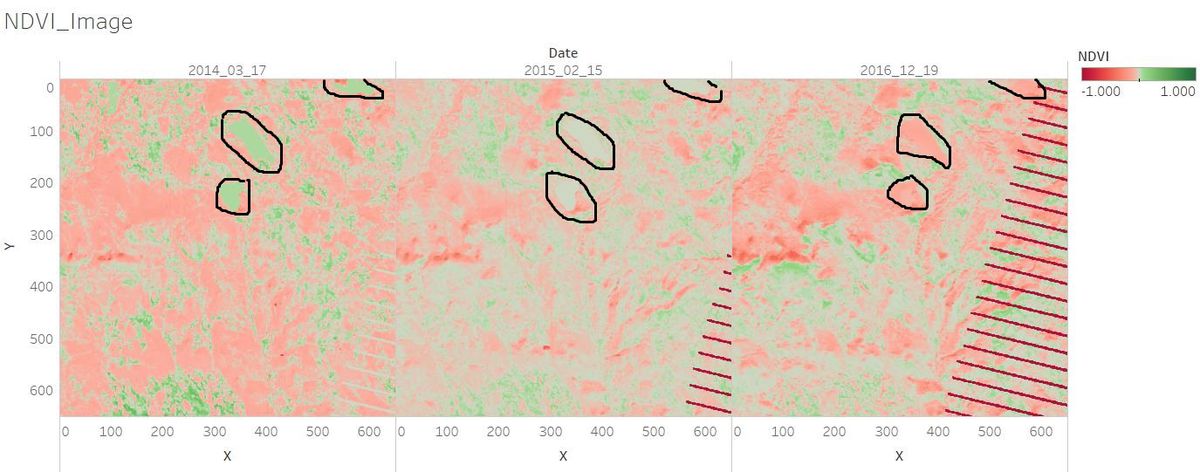
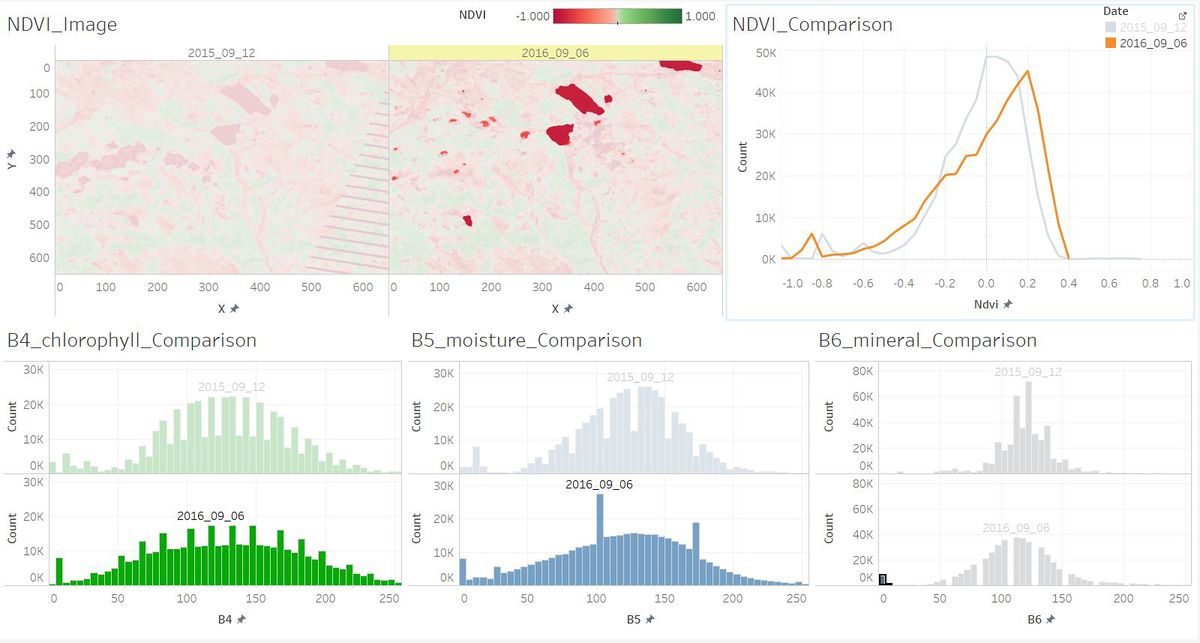
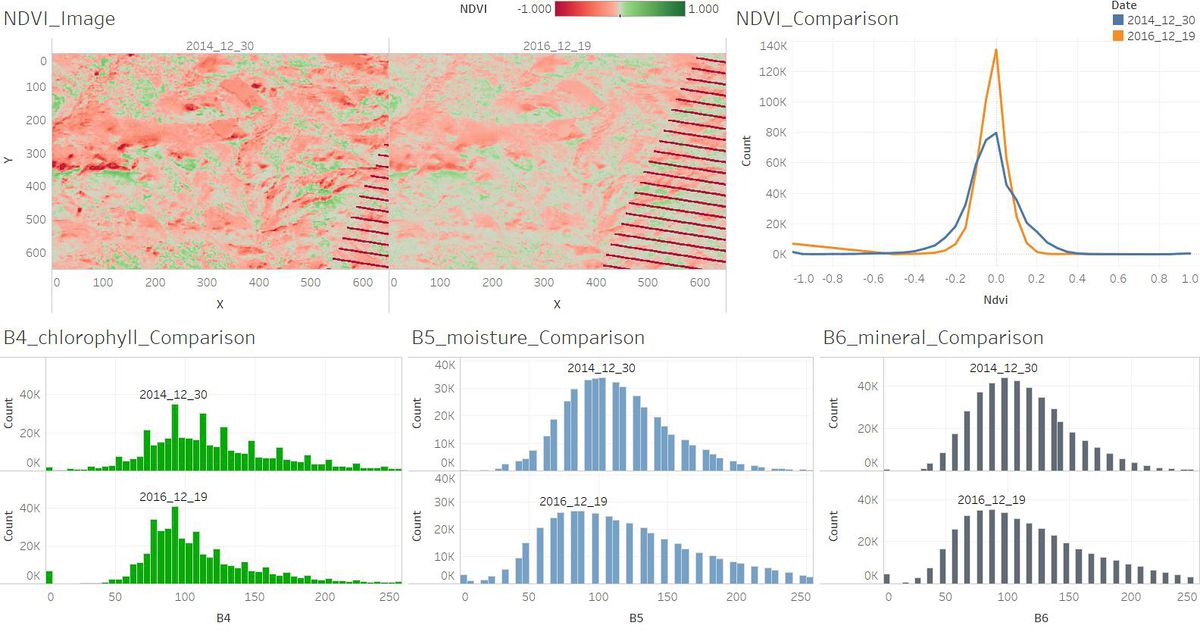
2. Features in the Preserve area as captured in the imagery.
Most of the images have sensor artifacts at the bottom right corner.
To identify the features in the Preserve Area, I picked the image which is generated from the data [image11_2016_09_06.csv]. It has no sensor artifacts at all.