From Visual Analytics for Business Intelligence
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
|
| Line 94: |
Line 94: |
| | || | | || |
| | <center> | | <center> |
| − | [[File:1.png|700px|frameless|center]] | + | [[File:1 - Graduates.png|700px|frameless|center]] |
| | || | | || |
| | * Undergraduates generally have equal weightage in terms of performance and importance level of the four groups of questions posed under these criterias. | | * Undergraduates generally have equal weightage in terms of performance and importance level of the four groups of questions posed under these criterias. |
Revision as of 20:23, 15 March 2020
Overview
Every two years, SMU Libraries conduct a comprehensive survey in which faculty, students and staff have the opportunity to rate various aspects of SMU library's services. The survey provides SMU libraries with input to help enhance existing services and to anticipate emerging needs of SMU faculty, students and staff. The latest survey is currently on going and will be ended by 17th February 2020.
The past reports are mainly made-up of pages of tables, which are very difficult to comprehend. In view of this, your task is to apply appropriate data visualisation to transform these tables into visual representation that allow SMU libraries to gain useful insights.
Data Cleaning & Preparation
About
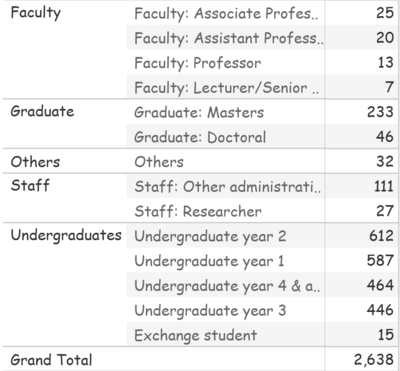
An overview of the library 2018 survey results found that there are 2638 respondents in total that responded to various parts of the 83 survey questions with respect to the performance and importance level of the library and other general questions to understand the patron's sentiments of the SMU Library. Here is the breakdown of the users that frequent the SMU library
Figure 1
As seen from figure 1, predominantly, most of the survey respondents comes from undergraduates with some from other areas such as graduates, faculty, staff and others. In order to gain more insights from the survey results, we will first do some pre-processing and cleaning of the data.
Cleaning
| Step
|
Screen shot
|
Explanation
|
| 1
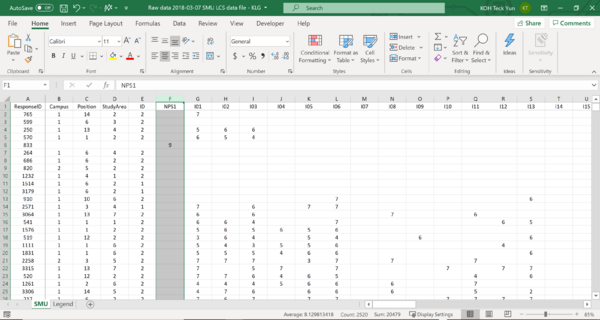
|
Img 1
Img 2
|
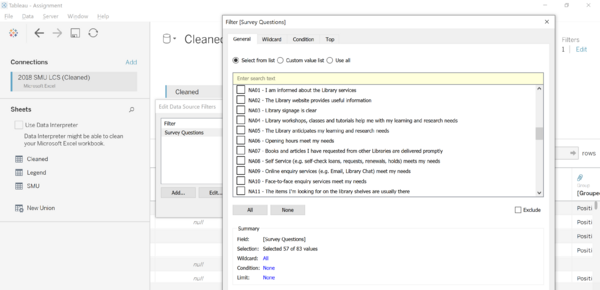
- Based on the initial dataset given, the datset is aggregated by values for various fields as seen from img 1. The column names are labelled by its code number and there is no name given in the raw data. The given names are represented in img 2 where the labelling of each code are given in the legend.
- To re-label the data into a readable dataset for users to further analyse, we will then process the data and labelling through excel.
|
| 2
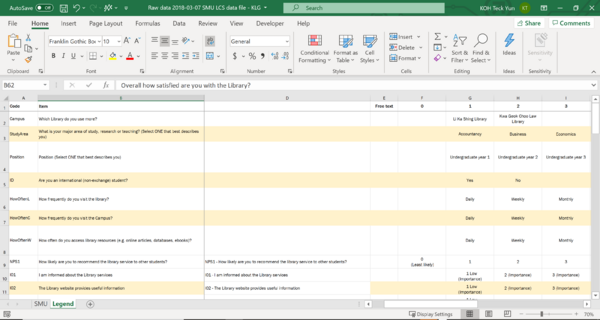
|
Img 3
|
- Through using lookup and concatenate function, we can combine the id code and the name into the column headers. We then transfer the values into a new sheet and re-arrange the values such that the general questions are in front as seen in Img 3.
|
| 3
|
|
- After further inspection of the survey questions, there is 26 survey questions that are irrelevant towards the insights that will be generated later on. The survey questions that fall under the ID code 'NA' to filtered and removed under the 'Datasource' tab.
|
Findings
From the word cloud generated by RStudio, the common words that appear consistently are study, seats, can, find, good, seats, like and many more.
| No.
|
Finding
|
Description
|
|
1.
|
|
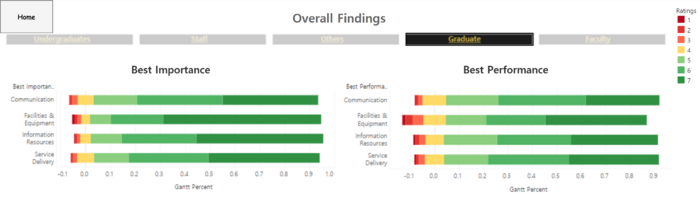
- Undergraduates generally have equal weightage in terms of performance and importance level of the four groups of questions posed under these criterias.
- The only disparity spotted is that undergraduates find that the facilities & equipment are not up to standard as seen by the greater negative sentiment as denoted by the red to yellow area that contrasts between importance and performance.
|
|
2.
|
|
Accountancy
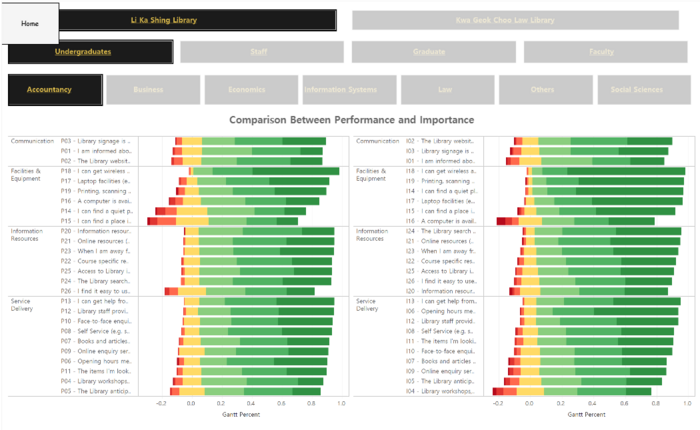
1. Similarity
- In the perspective of the accountancy students, the library performed well when they render services to users at either libraries as seen by code P13 and I13 under Service Delivery
- Interestingly, the mobile access under Information resource to library resources for I26 and P26 fared the worst comparatively for both LKS and KGC.
2. Differences
|
|
3.
|
|
Accountancy
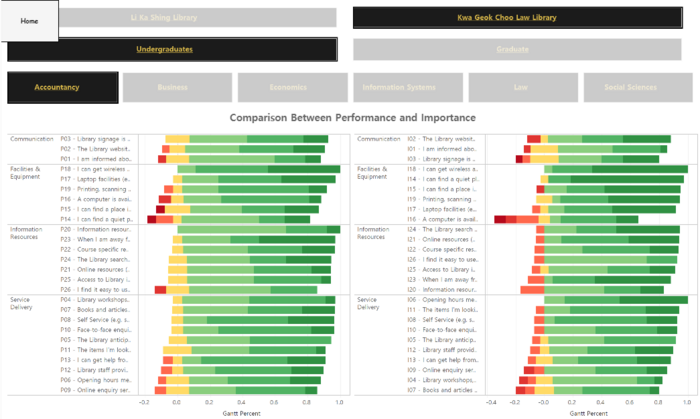
1. Similarity
- In the perspective of the accountancy students, the library performed well when they render services to users at either libraries as seen by code P13 and I13 under Service Delivery
- Interestingly, the mobile access under Information resource to library resources for I26 and P26 fared the worst comparatively for both LKS and KGC.
2. Differences
|
|
4.
|
|
Accountancy
1. Similarity
- In the perspective of the accountancy students, the library performed well when they render services to users at either libraries as seen by code P13 and I13 under Service Delivery
- Interestingly, the mobile access under Information resource to library resources for I26 and P26 fared the worst comparatively for both LKS and KGC.
2. Differences
|
|
5.
|
|
Accountancy
1. Similarity
- In the perspective of the accountancy students, the library performed well when they render services to users at either libraries as seen by code P13 and I13 under Service Delivery
- Interestingly, the mobile access under Information resource to library resources for I26 and P26 fared the worst comparatively for both LKS and KGC.
2. Differences
|
Revealed Insights
Report