SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Kong Yi Ru Kaelyn
Background of Study Area
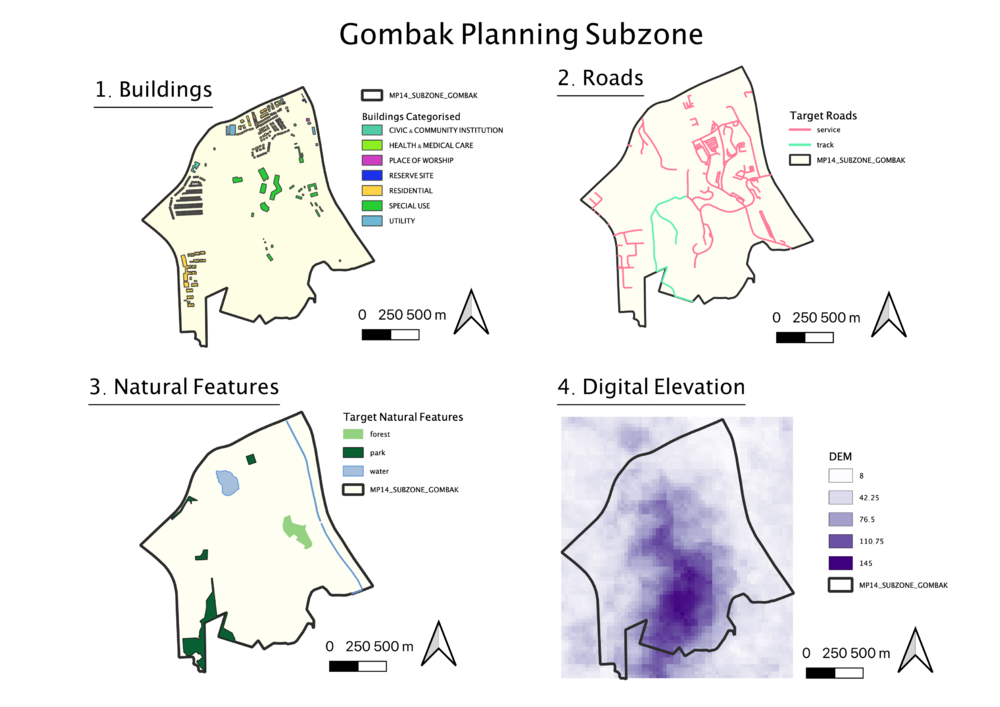
Gombak Planning Subzone, or Bukit Gombak, is located in Bukit Batok Planning Area, in the central-west part of Singapore. In order to identify the most suitable location for building a national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre, we will be studying both natural and man-made features present and weighing each feature’s importance in deciding where is most suitable.
Initial Analysis of Study Area
We will be analyzing four features, the buildings, roads, natural features, and elevation of the subzone. Each of these features contribute as a decision factor in the following ways.
| Decision Factor | Feature Analysed |
|---|---|
| 1. Health Risk Factor | Buildings |
| 2. Accessibility Factor | Roads |
| 3. Natural Conservation Factor | Natural Features |
| 4. Economic Factor | Slope |
1. Health Risk Factor (Buildings)
Due to the nature of a Disease Quarantine Centre, it is important that the selected site should be away from residential and working areas, i.e. located away from buildings. In the Buildings data from OpenStreetMap, it was null for most of the values in attribute ‘Type’. Therefore, I clipped the 2014 Masterplan Landuse layer with the buildings layer, to get a better idea of the type of buildings. This shows that the buildings in Gombak Planning Subzone consist of mostly special use and residential buildings. Therefore, the selected site should be situated far away from any of these buildings.
2. Accessibility Factor (Roads)
In order for ease of construction and transportation of goods, the selected site should be near service roads and tracks. The Roads layer from OpenStreetMap also contained information on other types of roads, such as residential roads or footways. Therefore, service roads and tracks were selected, and categorized as shown, using different colours to represent the different roads.
3. Natural Conservation Factor (Natural Features)
The selected site should be away from natural features, namely forests, parks and water. Several of these natural features can be found in Gombak Planning Subzone, as shown, where several parks, forests and water features are found. They are categorized into those respective categories, and represented by using colours representing the nature of the feature, for easy differentiation between features. Dark green is used to represent parks, light green for forests, and light blue for water features.
4. Economic Factor (Slope)
The selected site should avoid steep slope due to the high cost of construction on such areas. To study the slope in Gombak Planning Subzone, ASTER GDEM raster data was imported, clipped, and categorized as shown. A graduated model is used, to show the range of elevation above sea level in the subzone. The elevation ranges from 8 to 145 metres above sea level. The greatest elevation in the subzone is situated near the centre to southern area of the Subzone, and the areas near the subzone boundary have lower elevations.
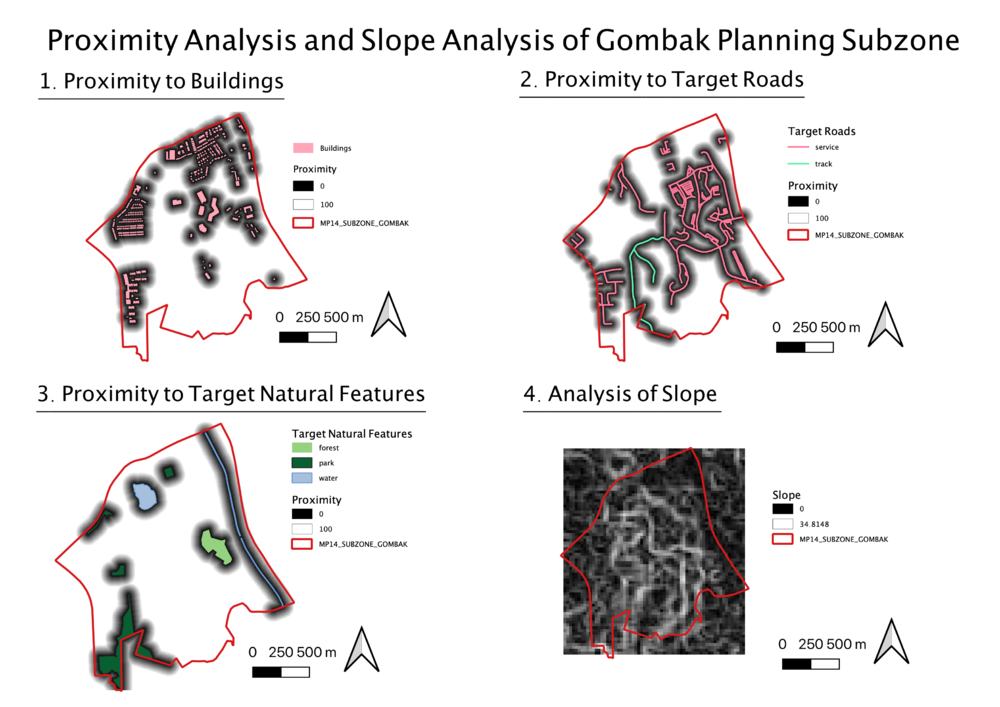
Proximity and Slope Analysis
To study the proximity to the different features, the different vector layers were rasterized before carrying out proximity analysis. This was done by first creating a new column, POI code, then converting it using to a raster layer, using georeferenced units as the output raster size units. For ease of comparison, the largest distance studied was from 0 – 100 metres for the 3 target features. The proximity to the features is represented as shown, where the darker the areas, the closer they are to the target features.
1. Proximity to Buildings
The furthest distance from the buildings is 100m, represented by the black areas.
2. Proximity to Target Roads
The furthest distance from service roads and tracks is 100m, represented by the black areas.
3. Proximity to Natural Features
The furthest distance from the forests, parks and water is 100m, represented by the black areas.
4.Analysis of Slope
The legend shows that the minimum and maximum values of the slope values are 0 and 34.8148 degrees, represented by the colours black and white respectively. Dark grey areas on the map are indicative of a gentle slope, while light grey areas are indicative of a steeper slope.