ISSS608 2018-19 T1 Assign Kateryna Mazurenko
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
Introduction into Problem and Goal definition
Air pollution harms human health and the environment. Particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide and ground-level ozone, are now generally recognised as the three pollutants that most significantly affect human health.
Particulate matter (PM) is made up of small airborne particles like dust, soot, and drops of liquids. The majority of PM in urban areas is formed directly from burning of fossil fuels by power plants, automobiles, non-road equipment, and industrial facilities.
Coarse particulate matter (PM10, particles < 10 microns in diameter) is known to cause nasal and upper respiratory tract health problems. Fine particles (PM2.5, particles < 2.5 microns in diameter; Ultra Fine Particles) penetrate deeper into the lungs and cause heart attacks, strokes, asthma, and bronchitis, as well as premature death from heart ailments, lung disease, and cancer.
Air Pollution is a major Problem in Bulgaria. Bulgaria ranked eighth in terms of most premature deaths caused by PM2.5 in all of Europe with a total of 12,280 in 2014. When compared to their total population, Bulgaria finds itself first on the list with the highest ratio of premature deaths caused by PM2.5, a pollutant stemming from fuel combustion, heating, transportation, waste incineration, agriculture, and other anthropogenic sources.
The goal of this assignment is to prepare interactive visualisation to help understand the real picture of air quality in Sofia city (capital of Bulgaria) as well as discuss reliability and performance of pollution measurements taken.
Scope of the Work
Typical day in Sofia city
Task: Spatio-temporal Analysis of Official Air Quality Characterize the past and most recent situation with respect to air quality measures in Sofia City. What does a typical day look like for Sofia city? Do you see any trends of possible interest in this investigation? What anomalies do you find in the official air quality dataset? How do these affect your analysis of potential problems to the environment?
Air pollution measurements analysis
Task: Spatio-temporal Analysis of Citizen Science Air Quality Measurements Using appropriate data visualisation, you are required will be asked to answer the following types of questions:
Characterize the sensors’ coverage, performance and operation. Are they well distributed over the entire city? Are they all working properly at all times? Can you detect any unexpected behaviors of the sensors through analyzing the readings they capture? Limit your response to no more than 4 images and 600 words. Now turn your attention to the air pollution measurements themselves. Which part of the city shows relatively higher readings than others? Are these differences time dependent?
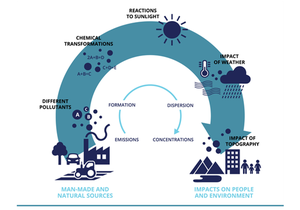
Factors potentially involved into causing polluting
Task Urban air pollution is a complex issue. There are many factors affecting the air quality of a city. Some of the possible causes are:
Local energy sources. For example, according to Unmask My City, a global initiative by doctors, nurses, public health practitioners, and allied health professionals dedicated to improving air quality and reducing emissions in our cities, Bulgaria’s main sources of PM10, and fine particle pollution PM2.5 (particles 2.5 microns or smaller) are household burning of fossil fuels or biomass, and transport. Local meteorology such as temperature, pressure, rainfall, humidity, wind etc Local topography Complex interactions between local topography and meteorological characteristics. Transboundary pollution for example the haze that intruded into Singapore from our neighbours.
Data source
- Official air quality measurements (5 stations in the city)(EEA Data.zip) – as per EU guidelines on air quality monitoring
- Citizen science air quality measurements (Air Tube.zip) , incl. temperature, humidity and pressure (many stations) and topography (gridded data).
- Meteorological measurements (1 station)(METEO-data.zip): Temperature; Humidity; Wind speed; Pressure; Rainfall; Visibility
- Topography data (TOPO-DATA)
Software Used in Analysis
Data preparation:
- RStudio: tidyverse, geohash
- SAS JMP Pro 13
Visualisation, building dashboards:
- Tableau Desktop 2018.3 Professional Edition