Version 1 | Version 2
INTRODUCTION
Blockchain, artificial intelligence, data science, edtech and internet-of-things are all buzzwords today in this new innovation era. More and more founders and investors begin to see the potential of innovation in Asia today. Meanwhile, local governments in the region have introduced new policies and initiatives to explore new technological innovation frontiers in order to boost the competitiveness of various knowledge-based industries. In recent years, both Hong Kong and Singapore government has pumped in resources including start-up clusters, grants and funding to boost its start-up Ecosystem.
The two Asian-Tigers, Singapore and Hong Kong, will be the main contexts for this project. They are two high-growth metropolitan city-states in Asia that share many characteristics in common in terms of GDP per capita and population density. Beyond that, both Hong Kong and Singapore offers a comprehensive financial and technical infrastructure and has attracted a considerable amount of foreign investment. It is commendable that both countries have achieved stellar economic performance despite the lack of natural resources and large land size. Unicorn Ventures strives to study the current start-up ecosystem in these two city-based regions and hope to generate new insights for policy-makers, founders and investors.
MOTIVATION
Our research is motivated by the lack of comprehensive comparison between these two countries’ startup ecosystem. Currently, there are many sources of fragmented datasets on different aspects of the startup ecosystem such as top-funded companies, industry breakdown and funding analysis. Our project aims to consolidate the data sources and study the two different startup ecosystems through a centralized interactive web application.
This project will focus on start-up companies and funding organizations in the tech ecosystem. The insights generated could help:
- Hong Kong and Singapore policy makers improve its existing infrastructures or policies to cultivate a more robust startup ecosystem
- Potential and current founders to understand the growing industries, competitor landscape and investors
- Potential investors to identify the growing industries and dominant players
OBJECTIVES
Our project aims to explore and compare the following aspects for the startup
ecosystem in Singapore and Hong Kong by considering the startups founded after
2000.
Ecosystem Index Analysis:
- What is the difference of Hong Kong and Singapore in terms of Global Entrepreneurship Index and Global Competitiveness Index?
Startup Analysis:
- Time-series analysis for startups that has formed/exited across the years by different industries
- What is the current breakdown of startups by industries, key industries, team size, funding stage, age and gender of founders?
Funding Analysis:
- What are top funded startups and their funding stages and industries?
- Time-series analysis of the disclosed funding over the years by industries
- Where does the investors originate from and what are the investor types?
SELECTED DATASET
| Dataset
|
Global Entrepreneurship Index Score in Singapore and Hong Kong in 2018
- Description: The GEI measures both the quality of entrepreneurship in a country and the extent and depth of the supporting entrepreneurial ecosystem. The GEI consistsof 3 sub-indices including entrepreneurial attitudes, entrepreneurial abilities and entrepreneurial aspirations.
- Source: Global Entrepreneurship and Development Institute
- Dateset
- Components:
| Sub-index
|
Attributes
|
| Attitudes Sub-index
|
- Opportunity Perception
- Startup Skills
- Risk Acceptance
- Networking
- Cultural Support
|
| Abilities Sub-index
|
- Opportunity Perception
- Technology Absorption
- Human Capital
- Competition
|
| Aspiration Sub-index
|
- Product Innovation
- Process Innovation
- High Growth
- Internationalization
- Risk Capital
|
|
Global Competitiveness Index 2017-2018 for Singapore and Hong Kong
- Description: It measures national competitiveness which is defined as the set of institutions, policies and factors that determine the level of productivity.
- Source: World Economic Forum
- Dataset
- Components:
| Sub-index
|
Attributes
|
| Basic Requirements Sub-index
|
- Institutions
- Infrastructure
- Macroeconomic environment
- Health and primary education
|
| Efficiency Enhancers Sub-index
|
- Higher education and training
- Goods market efficiency
- Labour market efficiency
- Financial market development
- Technological readiness
- Market Size
|
| Innovation and Sophistication Factors Sub-index
|
- Business sophistication
- Innovation
|
|
Startup Information in Singapore and Hong Kong
- Description: This dataset includes various key attributes on startups in Singapore and Hong Kong that was founded after 2000.
- Source: Crunchbase
- Dataset
- Components:
| Information Type
|
Attributes
|
| Basic Information
|
- Organization Name
- Categories
- Category Groups
- Headquarters Location
- Operating Status
- Founded Date
- Exit Date
- Closed Date
|
| Team
|
- Number of Founders
- Female_Founder
- Founders
- Number of Employees
|
| Funding
|
- Number of Funding Rounds
- Funding Status
- Last Funding Date
- Last Funding Amount Currency (in USD)
- Last Funding Type
- Last Equity Funding Amount Currency (in USD)
- Last Equity Funding Type
- Total Equity Funding Amount Currency (in USD)
- Total Funding Amount Currency (in USD)
- Number of Lead Investors
- Number of Investors
- Number of Acquisition
- Acquisition Status
|
| IPO and Stock Price
|
- IPO Status
- IPO Date
- Stock Symbol
- Stock Exchange
|
|
Investment and Funding Information in Singapore and Hong Kong
- Description: This dataset details the individual disclosed funding transactions that are public and are published in crunchbase.
- Source: Crunchbase
- Dataset
- Components:
| Information Type
|
Attributes
|
| Deal Information
|
- Transaction Name
- startup Organization Name
- Funding Type
- Money Raised Currency (in USD)
- Announced Date
- Funding Stage
- Equity Only Funding
|
| Investors
|
- Number of Investors
- Number of Partner Investors
|
|
Investor Information in Singapore and Hong Kong
- Description: This dataset shows the current breakdown of the profile of the investors that had invested in Singapore/Hong Kong startups. However, this data set does not disclose the individual transaction due to privacy policy .
| Information Type
|
Attributes
|
| Basic Information
|
- Organization/Person Name
- Location
- Region
- Primary Job Title
- Number of Organizations Founded
- Primary Organization
|
| Investment
|
- Number of Investments
- Number of Portfolio Organizations
- Number of Partner Investments
- Number of Lead Investments
- Number of Exits
- Number of Exits (IPO)
- Investment Stage
- Investor Type
- Investor’s Category Group
- Investor’s Category
|
|
BACKGROUND SURVEY OF RELATED WORKS
| Related Works
|
What We Can Learn
|
| Spider Chart
|
- A spider chart helps compare two objects in multiple dimensions. By comparing the shapes of different objects, It is easier for user to identify the similarity and differences between them.
- Contrasting colours used can represent different categories.
- When the user hovers to one area, the corresponding category will be shaded and other category will be unshaded. It also helps user to focus on the details of chart.
- Tooltips can also be added to show more details of each sub-index.
|
| Heat Map
|
- A heat map can display time series data for multiple dimensions across a fixed set of categories and this provides more information in one single chart.
- By looking at the overview of color intensity, user are able to identify the overall pattern of the data and highlight any exceptions/outliers.
- The color intensity displays the quantity while tooltip enables users to hover over the individual shaded area and understand the exact quantity.
|
| Cleveland Dot Plot
|
- Cleveland Dot Plot is effective in comparing data of two parties on a single chart. It can easily communicate the huge gaps between two objects to the user.
- Unlike bar chart, this dot plot reduce the clutter and maximize the data-ink ratio.
|
| Grouped Bar Chart
|
- Unlike the traditional bar chart, grouped bar chart shows more information with high dimension in one chart.
- The filtering function provides more interactive features and user can customize the bar charts based on his/her preference.
- The cons of this chart is that the data-ink ratio is too high and the choice of red and green colours is disadvantageous for colour blind users.
|
| Connection Map
|
- Connection Map is useful to show the flow of traffic from one region to another.
- The lines in the chart are all with same thickness and color. However, we can use different thickness of the graphs to show the quantity of connections while the colour intensity shows different dimensions.
|
SKETCHES STORYBOARD
| Sketches
|
How Analyst Can Conduct Analysis
|
|
|
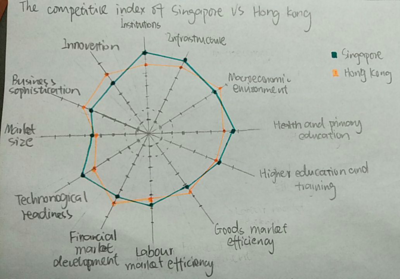
Spider Charts
- Allows users to compare the Global Entrepreneurship Index and Global Competitiveness Index between Singapore and Hong Kong
- Enables users to see the performance of different index when hover on top of the index
|
|
|
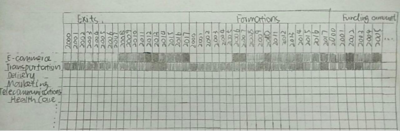
Heat Map:
- Shows time-series analysis for startups that has formed or exited and their funding amount across the years according different industries
- AllowS the user to identify the growing industries as well as the trend in start-up formation and funding amount
|
|
|
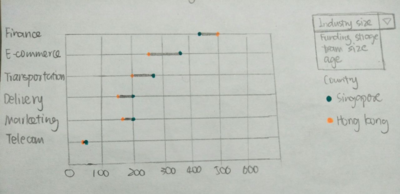
Cleveland Dot Plot with Filters:
- Presents current breakdown of startups by industries, team size, funding stage, age and gender of founders
- Colour of the dots represent the region
|
|
|
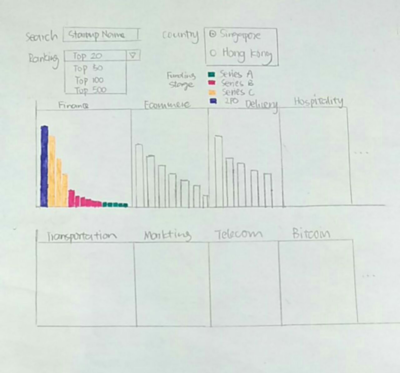
Grouped Bar Chart with filters:
- Displays startups ordered by funding amount in various industries
- Users can search for a startup or choose the ranking range and country.
- Color intensity shows the funding stage of the startups.
|
|
|
Connection Map:
- Paths Illustrates investor’s locations
- Colour density shows investor type and line thickness shows number of investors.
|
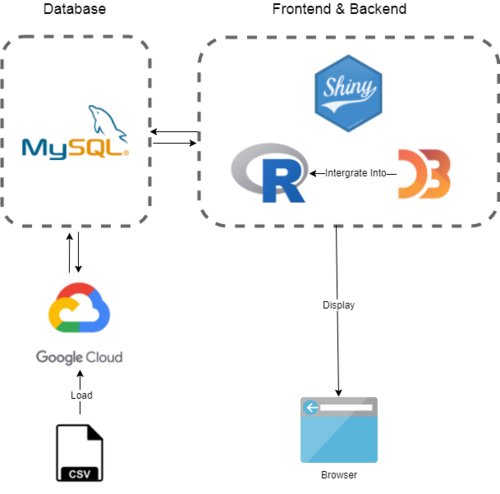
ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAM
KEY TECHNICAL CHALLENGES
Domain Knowledge Understanding:
- As the datasets involves many technical terms in the startup ecosystem, the group has to study more in-depth on the terminologies used in the ecosystem in order to draw meaningful insights. This includes the definition of different funding stages, types of fundings, types of investors, startup industries categories and etc.
Data Preprocessing:
- Missing data: how to deal with missing values
- Data integration and calculation: understanding the column attributes and perform meaningful summation or calculation
- Multiple values for certain observations: how to deal with such attributes and ensure that the visualizations take into account of start-ups that has attributes with multiple values
Technological Expertise:
- Learning relevant packages under R such as ggplot2, tidyverse, shiny and plotly
- Learning how to integrate D3.js with R to achieve both advanced analytics functions as well as interactive visualization
- Learning integration of different charts and enhance the interactivity and animation techniques of the storyboard
PROJECT TIMELINE
REFERENCES
COMMENTS
Feel free to comments, suggestions and feedbacks to help us improve our project!:D