IS428 2017 18T1 Group05
Contents
Problem Statement and Motivation
In 2017, The Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) collected tax revenue amounting to S$47 billion, a 5% increase from the amount collected in the fiscal year 2016 [1].
Taxes are compulsory contributions made to the government by citizens and firms residing in the nation to fund government operations on certain categories of products and services. According to a report by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Singapore was ranked as one of the lowest-taxed economies in South-East Asia and amongst other economically developed countries[2]. Tax revenue in Singapore serves to fund government operations and promote social and economic goals. In doing so, the government aims to ensure competitive tax rates to both corporations and individuals to ensure a healthy economy.
In essence, governments are able to sustain themselves via tax revenue, and we believe that there is an underlying reason why certain taxes continue to make up a huge portion of Singapore's portfolio over the years despite the shift in tax compositions that has been trending globally[3]. Hence, we hope to allow users to explore trends and patterns in the composition of Singapore’s tax revenue over the years through this project. Furthermore, we hope that the interactive visualization will aid the public in understanding the key components of Singapore’s tax revenue and the share of their contribution to tax revenue.
Objectives
In this project, we are interested to create a visualization that helps analyst perform the following:
- Understanding the trend and patterns in the composition of Singapore's tax revenue over the years.
- Analyzing the effect of taxes on certain products and services within the specific tax segment.
- Understanding of their contributions to Singapore's tax revenue
- Evaluating their investment/purchase decisions on big ticket items that are taxable (e.g. cars)
By conducting the analysis, it allows the government or policy makers to better identify potential linkages between tax collection and the potential impact if they were to raise/lower tax rates. If a link between tax collection and the effect on products and services within that segment can be identified, the government and policy makers can be made aware of how they could potentially increase their tax revenue and/or influence the market's movements. On the other hand, individuals and businesses may also better understand the impact of tax within a specific industry. Furthermore, individuals may also evaluate certain trends in the market to get a feel for how the market may move in a few years, as influenced by the government's taxation decisions.
Description of Dataset
In this project, we will be examining the key components that make up government tax revenue. Data used in this project will be obtained from open data published by the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore [4] and Data.gov.sg [5]. We will be looking at the following areas of tax revenue in Singapore.
| Type of Tax Revenue | Description | Breakdown |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Income Tax | Revenue from the progressive tax rate imposed on individuals based on their chargeable income status | Based on individual income groups from S$20,000 to S$1,000,000 with a bin of S$5,000 |
| Corporate Tax | Revenue from the direct tax imposed on the income of business entities | Based on corporate income groups from S$10,000 to S$5,000,000 with a bin of S$10,000 |
| Property Tax | Revenue from the progressive tax rate is applied on owner-occupied and non-owner occupied residential properties. All other properties in Singapore are taxed at a fixed rate of the Annual Value | Based on Property type (e.g. Land, HDB) |
| Estate Duty | Revenue from tax imposed on wealth left by those who have died while residing in Singapore. It should be noted that estate duty is no longer imposed on deaths on and after 15th February 2008 upon the abolishment of this duty | No breakdown of data available hence visualization will depict estate duty as a whole |
| Motor Vehicle Tax | Revenue from the taxes imposed on motor vehicles (e.g. registration fees, road tax) curb car ownership and road congestion. It should be noted that Motor Vehicle Tax exclde excise duties on motor vehicle which are classified under Customs and Excise Duties | No breakdown of data available, hence visualization will depict motor vehicle tax as a whole |
| Customs and Excise Duties | Revenue from duties imposed on motor vehicles, tobacco, liquor and petroleum products | Based on product type |
| Goods and Services Tax | Revenue from the value added tax imposed on most good and services for domestic consumption | Based on economic sector & based on entity type |
| Betting Tax | Revenue from the fixed tax rate imposed on a person or organization receiving bets based on type of betting schemes available in Singapore (e.g. 4D, Toto, Big Sweep, Sports Betting). It should be noted that Betting Tax includes Casino Tax with effect from March 2010, under Section 146 of the Casino Control Act | No breakdown of data available hence visualization will depict betting tax as a whole |
| Stamp Duties | Revenue from tax levied on documents | Based on types of duties (e.g. Sale & Purchase Agreement, Lease Agreement, Mortgage Agreement) |
| Others | Revenue mainly comprising Foreign Worker Levy and Airport Passenger Service charge |
Background of Survey and Research on Related Work
Our group has done prior research on related work on tax composition and pattern visualizations. While there has not been an interactive visualization to depict Singapore's tax revenue composition and patterns over the years, the following work are current visualizations related to Singapore Tax composition and of other countries' tax revenue.
| Related Works | Comments |
|---|---|
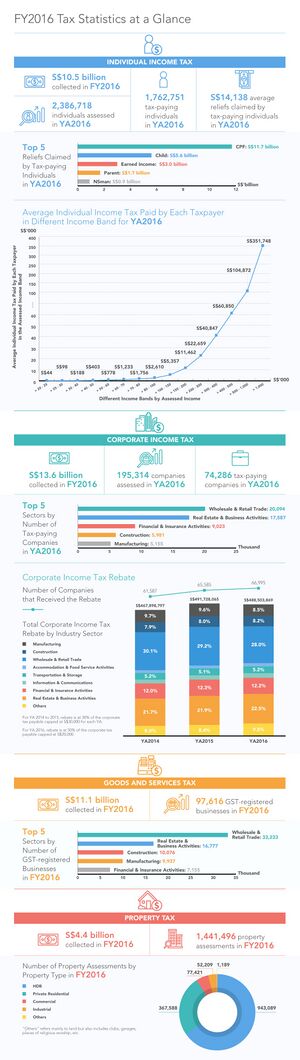
| Data Visualization by Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore for the Public
Link: https://www.iras.gov.sg/IRASHome/Publications/Statistics-and-Papers/Tax-Statistics/ |
Simple and intuitive design that reveals key insights on each component of tax revenue. However, the visualization is not interactive and does not allow users to see the overall composition of tax revenue and observe patterns or changes in tax revenue components. |
| Interactive Graph on Texas Tax Revenue | Interactive visualization allows users to filter and select according to the components needed. Upon selecting the components and year, users are able to see the relevant tax figures and the updated total revenue with a detailed breakdown of the components. |
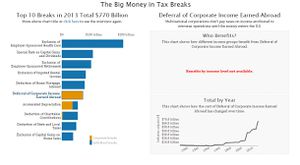
| Interactive visualization of Tax Breaks in the US
Link: https://www.nationalpriorities.org/interactive-data/taxbreaks/2014/visualization/ |
Users are able to analyze the total cost of each tax reduction scheme (also known as tax break) in the US over time and the number of people in each income group who benefit from it. |
In addition, our project will be looking at prior work on various type of visualizations to add value in building the new visualization - Treemap - http://bl.ocks.org/Rnhatch/1820583 - Sunburst - - Line - - Bar -
Technical Challenges
| Key Technical Challenges | Proposed Solution |
|---|---|
| Unfamiliarity in Javascript Programming & the use of D3 Libraries |
|
| Data Cleaning & Data Transformation |
|
| Data Storage & Rendering |
|
| Identifying Optimal Interactive Elements |
|