Difference between revisions of "1718t1is428T15"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
=== Data Source === | === Data Source === | ||
| − | The analysis will be based on | + | The analysis will be based on EMA dataset<ref>https://www.ema.gov.sg/Statistics.aspx EMA dataset</ref>: |
* Public housing's average monthly household electricity consumption (kwh) (2013 - 2015) | * Public housing's average monthly household electricity consumption (kwh) (2013 - 2015) | ||
* Private apartment's average monthly household electricity consumption (kwh) (2013 - 2015) | * Private apartment's average monthly household electricity consumption (kwh) (2013 - 2015) | ||
Revision as of 21:26, 12 October 2017
|
PROJECT PROPOSAL |
Contents
Project Motivation
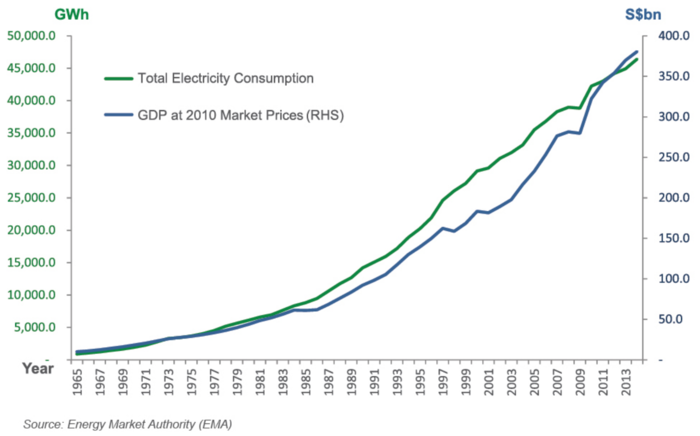
Experts have warned that power demand is set to double by 2030 globally despite authoritative control. High power consumption can already be observed locally. According Energy Market Authority (EMA), Singapore has faced increasing power consumption from 1965 to 2013 [1].
As Singapore is land-scarce and does not have significant renewable energy options such as hydro-power, wave, or sufficient land for mass solar energy production, energy has been a top concern in the urban nation[2]. It is thus important to promote energy saving concepts to the public as well as deploying energy saving solution island wide. However, the usual analysis tools are not enough to provide a different perspective to facilitate the deployment of the solution. Information about the energy consumption levels of residents in Singapore are often not conveyed adequately enough in data visualisation. While EMA and Singstat provide annual data and reports on energy usage in Singapore, a powerful visualisation technique should be used to gain insights effectively.
Project Objective
Our team aims to create a visualisation that leverages on energy datasets provided by EMA to perform spatial analysis to identify energy usage clusters with hexagonal binning.
Dataset
Data Source
The analysis will be based on EMA dataset[3]:
- Public housing's average monthly household electricity consumption (kwh) (2013 - 2015)
- Private apartment's average monthly household electricity consumption (kwh) (2013 - 2015)
Data Attributes
Public Housing
- Postal code
- 1-room
- 2-room
- 3-room
- 4-room
- 5-room/executive
Private Apartment
- Postal code
- Jan
- Feb
- Mar
- Apr
- May
- Jun
- Jul
- Aug
- Sep
- Oct
- Nov
- Dec
Related Works
Much of the relevant prior work on residential energy consumption levels in Singapore revolve around the motivations and barriers towards energy efficiency.
In 2013, the Ministry of the Environment and Water Resources (MEWR) interviewed 2,500 residents on their extent of energy efficiency practice at home, level of awareness of energy efficiency, and barriers towards being energy efficient. It found that 41.3% of the respondents are more encouraged to conserve electricity if the government were to provide monetary incentives or voucher rewards/rebates, and 36.5% are motivated by advertisements on various media platforms. The findings also concluded that residents generally perceived the high cost of energy-efficient appliances and inconvenience of energy-saving practices as barriers to energy efficiency in households.
Another research by Energy Efficient Singapore (E2 Singapore) indicated that when residents in other countries are allowed to compare their utility bills against that of their neighbours, they can potentially achieve 4 to 12% energy savings. This is because it leverages on the power of social norms to provide direct feedback to the residents – residents are likely to bring their behavior closer to the norm when they are informed of what the norm is.
A third by Xu and Ang from NUS analyzes the root cause of high energy consumption using the index decomposition analysis (IDA). The IDA model studies changes in energy consumption over time and is often used in major energy consuming sectors such as the transport industry. To fit the model for use on the residential sector, Xu and Ang applied a hybrid IDA model that divides the residential sector into various subsectors, each with a different key factor driving energy consumption. For instance, energy consumption in a subsector may be driven by floor area (for air cooling and heating). The paper found that environment control and household appliances are the main factors for energy consumption by households, and each of these is greatly affected by population growth and decreases in residents per household.
By using our proposed work jointly with the first two papers, users can visually identify clusters with high energy usage where efficient energy consumption measures can be implemented. With the last paper, we can trace the root cause for high energy usage.
Inspirations
EMA publishes energy statistics on an annual basis to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the Singapore energy landscape through a detailed coverage of various energy-related topics. As project Enerlyst focuses on analysing households' energy consumption, only private and public households data will be used. This study will be based on EMA dataset from 2013 to 2015. 2013 data will be prepared manually whereas 2014 and 2015 data will be uploaded to the application and process on the fly.
Proposed Storyboard
Technical Challenges
Timeline
| Week No(s). | Task | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Prepares Project Proposal | Completed | |
| Attend D3.js workshop, research on technologies/tools and project wiki | Completed | |
| Clean data, start visualisation | Incomplete | |
| Continue with visualisation | Incomplete | |
| Prepare poster, final report and wiki page | Incomplete | |
| Poster submission and final deliverables | Incomplete |
Technologies/Tools
The following are technologies and tools which we used:
- Microsoft Excel (data cleaning)
- D3.js (visualisation)
- Leaflet (overlaying of map)
- Github (version control)
Reference
Comments