Group09 proposal
| Proposal | Poster | Application | Research Paper |
Contents
Motivation
Our primary motivation for doing this project would be to provide a useful visualization for the effectiveness of environmental policy implementation, as well as showing the relationship of GDP per Capita versus air quality. This visualisation will help us evaluate which countries are both thriving financially and active in managing air pollution. We are very motivated by this problem because one of our team members worked closely with the founder of Nomadlist.com, the No. 1 website for digital nomads. While working on it, he noticed that Air Quality Information (AQI) heavily affected the way people looked at cities – if they were worth living and working in. We believe that as climate change unfolds, AQI, in addition to economic measures like GDP per Capita, will be one of the key indicators that helps anyone decide if economic development in that country is happening at the expense of air quality and thus, the livability of the nation.
Problem
Currently, NomadList which uses a variant of the dataset we have, and displays everything in a tabular format with so many different colors. Other sites like the World Health Organisation provide separate data sets for AQI and GDP per Capita in table format, but this is not effective in showing the relationship or spotting trends in the data.
Data Description and What Data We're Using
The data we are using is scraped from http://aqicn.org using a Ruby script. There are 921 cities in total out of a target list of around 960 cities. There are 39 missing cities because there are no sensors for those cities – not all cities have fully functional sensors connected to the AQICN platform.
The target list is from a JSON file that looks something like this:
We will have to merge this dataset with geodata so we can visualize AQI on a map.
Background Survey & References
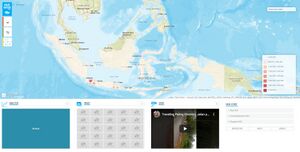
The data we've scraped comes from a website called AQICN. As you can see in the image, the website is rather busy and the visualisations can be quite clunky if you don't know what you're looking for.
Our project focuses on the correlations between economic development and political policy and the delta in the quantity of pollutants that results in, as well as any inverse relationships (i.e. does the quantity of pollutants affect economic development?). In that sense, compared to AQICN, we won't be showing as much data. Rather, we want to make it as concise as possible while showing the relationships we want to illustrate.
A notable example of another of the visualisations we're referencing to do is Hazegazer: Theirs is more focused on demographics and the Indonesian haze crisis, but we aim to have that level of clarity when showing hotspots of cities and the GDPs and how they correlate. However, there are many options that a new user might not comprehend. We hope to be more concise than this website in our application.
In a 2017 paper, Guillaume Vandenbroucke and Heting Zhu both argue that ‘We find that pollution in the United States, measured by particulate matter or CO2 emissions, rises with economic activity, but at a noticeably slower pace.' Given the GDP of a country/city and the pollutant data we have, we will test this trend across more than just the United States.
In a chapter by Ying Li and Ke Chen, they note that over 70 years of China’s history, ‘Control policies have been largely ineffective and air quality in the majority of the nation has not been significantly improved and even worsened in many urban areas’. For each policy and the timeframe that they are being implemented over, we’d like to see if this claim is true and show a correlation between the policy and pollutants.
References
https://research.stlouisfed.org/publications/economic-synopses/2017/06/23/measures-of-pollution
https://www.intechopen.com/books/energy-management-for-sustainable-development/a-review-of-air-pollution-control-policy-development-and-effectiveness-in-china
http://hazegazer.org/home
https://aqicn.org
Sketches
| Sketch | Description |
|---|---|
| We plan to track various policy implementations and their time frame, correlating to the Air Quality Index of that city. We want to track if the policies the city or state implements are truly effective in reducing or controlling air pollution. | |
| We want to track if there truly is a correlation between GDP and AQI. We aim to show the GDP per capita of various cities around the world as well as their air quality index on a map. In addition,
we will show the delta in GDP vs the delta in AQI. |
Key Technical Challenges & Approach
With the amount of data we have and the new platforms we have to learn, we anticipate a large challenge ahead in tackling this project.
| Potential Challenges | Solution |
|---|---|
| Not being familiar with R and R-Shiny.
We are all more used to programming in Python, React, Javascript, etc. |
Set up a group chat for the class to discuss about R and R-Shiny
Compile a list of useful resources we can all share with each other Pair program if we really have to Refer to R and R Shiny documentation Look at other people’s projects and how they did it (similar to how one learns from open source projects) |
| Dataset is not tagged and is not sorted by country; it is sorted only by city. | Find a convenient source of country vs city data and write a python script to organize and tag the data appropriately. |
| Correlation is not causation: We might find other factors that distort our findings. | Our dataset is large: we are able to scour through multiple cities to see if the trends we are predicting reflect in multiple cities. |
Storyboard
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
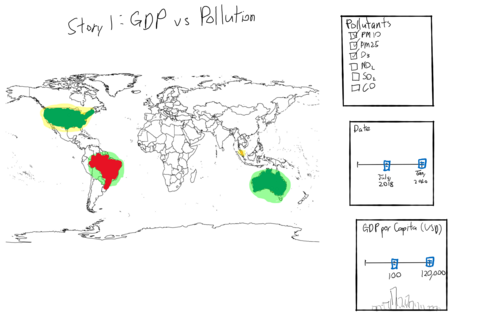
| We categorise various countries as high, medium and low GDP per capita. These countries are shaded in green, yellow and red respectively. In addition, we calculate an air quality index that includes PM25, PM10, O3, NO2, SO2 and CO. A worse air quality index will lead to a coloured layer overlaid on the country in a darker shade of red, and a better one will result in a darker shade of green. A range of time can be selected for which this data is calculated.
The aim of this visualisation is to determine a correlation between GDP and air pollution. Our hypothesis is that a higher GDP per capita leads to more air pollution as the country produces more value. | |
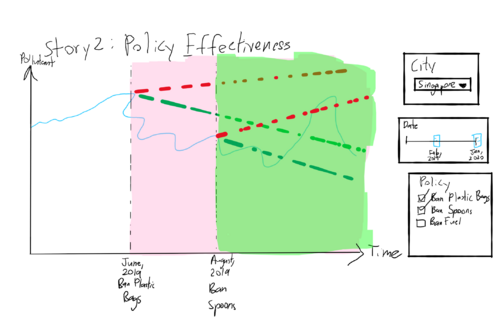
| Governments around the world implement policies that have a direct or indirect impact on the environment. We want to visualize the effectiveness of such policies in curbing the pollution levels in that country by doing a pre-post analysis.
This time series chart will show the pollutant levels in a city over time, as well as an indicator for when a policy was implemented. It will also show trendlines to visualize where the pollutant levels were heading at the time of implementation and how the trend changed after implementation of the policy. | |
| The third story focuses on comparing AQI against GDP within the country (within side by side boxplot) and then across countries (multiple side-by-side boxplots)
By using box plots, we can see the IQR, median and outliers. This will allow anyone to filter out which countries might be more interesting to explore. For instance, Beijing was supposedly very polluted in the developing 2000s because factories were built around it. It was hard for city dwellers to stay in Beijing without developing health isssues. However, in recent years, policies have been implemented to remove factories around Beijing and shift it elsewhere. The AQI should increase and exploring how this impacts GDP would be interesting too. |