Difference between revisions of "IS428 AY2019-20T2 Assign CERULEAN KOH SHILIANG"
(Created page with "==HomePage== Given data from the 2018 SMU Library Survey, covering 4 demographics of Undergraduates, Postgraduates, Faculty and Staff, I aim to explore interesting trends, pa...") |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|- | |- | ||
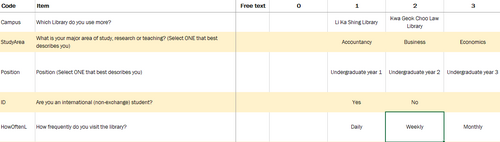
| 2 || Data Preparation || We look at the legend and take note of which names correspond to which numbers. | | 2 || Data Preparation || We look at the legend and take note of which names correspond to which numbers. | ||
| − | [[File:SS2.png|500px|thumb]] | + | [[File:SS2.png|500px|thumb|center]] |
|- | |- | ||
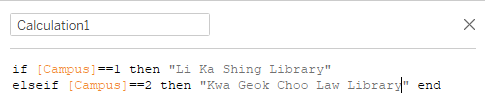
| 3 || Data Preparation || We use calculated fields to assign the right names to the numerically represented attributes. | | 3 || Data Preparation || We use calculated fields to assign the right names to the numerically represented attributes. | ||
| − | [[File:SS3.png|500px|thumb]] | + | [[File:SS3.png|500px|thumb|center]] |
|- | |- | ||
| 4 || Data Preparation || We rename these calculated fields appropriately, leaving the I01-I26, P01-26 and NA01-26 the same. We hide comment1 as the data for suggestions is in another file, as well as the original columns the calculated fields are derived from. | | 4 || Data Preparation || We rename these calculated fields appropriately, leaving the I01-I26, P01-26 and NA01-26 the same. We hide comment1 as the data for suggestions is in another file, as well as the original columns the calculated fields are derived from. | ||
| + | [[File:SS4.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 5 || EDA || For undergraduate students, we first use simple views to explore Library Preference, Study Area, Year Breakdown, International or not, Frequency of visiting the library and campus, and likeliness to recommend library services. We remove null values by filtering them out. | | 5 || EDA || For undergraduate students, we first use simple views to explore Library Preference, Study Area, Year Breakdown, International or not, Frequency of visiting the library and campus, and likeliness to recommend library services. We remove null values by filtering them out. | ||
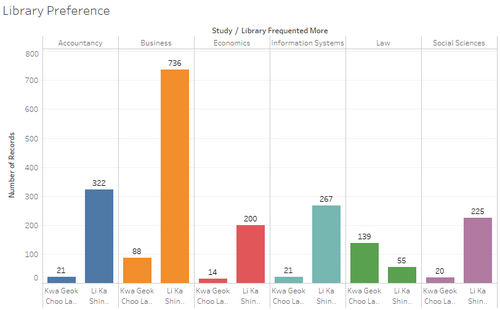
For our first visualization, we see how students from different schools use the Library. First, we filter the position so we are only looking at year 1 to 4 undergraduates. Then, we drag the calculated field Study over to the Columns. We then filter out others in the Study field. We rename the visualization library preference. | For our first visualization, we see how students from different schools use the Library. First, we filter the position so we are only looking at year 1 to 4 undergraduates. Then, we drag the calculated field Study over to the Columns. We then filter out others in the Study field. We rename the visualization library preference. | ||
| + | [[File:SS5.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 6 || EDA || For our second visualization, we explore whether there is the potential that exchange students are not aware of either library. To accomplish this, we plot a similar bar chart as before, except now instead of study area, we check whether they are exchange students. | | 6 || EDA || For our second visualization, we explore whether there is the potential that exchange students are not aware of either library. To accomplish this, we plot a similar bar chart as before, except now instead of study area, we check whether they are exchange students. | ||
| + | [[File:SS6.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 7 || EDA || For our third and fourth visualization, we compare the frequency of visiting the library versus visiting the campus. | | 7 || EDA || For our third and fourth visualization, we compare the frequency of visiting the library versus visiting the campus. | ||
We create two visualizations for this, changing them to tree maps then adding percentage of total number of records as labels, so that we can see clearly the proportions of the frequency of those who go to the library versus those who go to campus. | We create two visualizations for this, changing them to tree maps then adding percentage of total number of records as labels, so that we can see clearly the proportions of the frequency of those who go to the library versus those who go to campus. | ||
| − | + | [[File:SS7.png|500px|thumb|center]] | |
|- | |- | ||
| 8 || EDA || Now, we look at the likeliness for undergraduates to recommend library services. This can easily be seen in a bar graph. We convert likeliness to recommend into a dimension, then plot it against the Library they seem to frequent more. We also remove null values from the likeliness to recommend. We then show this as a percentage so we can compare the libraries. | | 8 || EDA || Now, we look at the likeliness for undergraduates to recommend library services. This can easily be seen in a bar graph. We convert likeliness to recommend into a dimension, then plot it against the Library they seem to frequent more. We also remove null values from the likeliness to recommend. We then show this as a percentage so we can compare the libraries. | ||
We create 2 visualizations here, one filtered for the Law Library and the other for Li Ka Shing. Here we use a gradient of colours to show the ordinal nature of the numerical values. | We create 2 visualizations here, one filtered for the Law Library and the other for Li Ka Shing. Here we use a gradient of colours to show the ordinal nature of the numerical values. | ||
| − | + | [[File:SS8.png|500px|thumb|center]] | |
|- | |- | ||
| 9 || EDA || Now, we will calculate overall net promoter score for the two libraries, which we will attain by first grouping 6 and below as detractors, 7,8 as passives and 9,10 as promoters. We can show this in a pie chart. By taking detractor percentage from promoter percentage, we can get the net promoter score. For undergraduates, we will not display this but simply display it in a table. | | 9 || EDA || Now, we will calculate overall net promoter score for the two libraries, which we will attain by first grouping 6 and below as detractors, 7,8 as passives and 9,10 as promoters. We can show this in a pie chart. By taking detractor percentage from promoter percentage, we can get the net promoter score. For undergraduates, we will not display this but simply display it in a table. | ||
| + | [[File:SS9.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:SS9b.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 10 || EDA || Now, we start to look more into the importance and performance of the 26 listed factors. We pivot I1 to I26, add Pivot Field Names and Pivot Field Values into the Columns, and add SUM of Number of Rows into the Rows, ensuring that the calculation is across the pane. | | 10 || EDA || Now, we start to look more into the importance and performance of the 26 listed factors. We pivot I1 to I26, add Pivot Field Names and Pivot Field Values into the Columns, and add SUM of Number of Rows into the Rows, ensuring that the calculation is across the pane. | ||
| + | [[File:SS10.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 11 || EDA || Now, let us run the same process on P1 to P27 to see the performance across the 27 measures. At this point, we need to change all SUM(number of rows) in previous visualizations into CNTD(ResponseID) due to the pivoting so we don’t show duplicates. | | 11 || EDA || Now, let us run the same process on P1 to P27 to see the performance across the 27 measures. At this point, we need to change all SUM(number of rows) in previous visualizations into CNTD(ResponseID) due to the pivoting so we don’t show duplicates. | ||
| Line 46: | Line 52: | ||
We open a new worksheet and load the comments data source. We filter by position to be undergraduate and remove null form area of study. We colour code by the schools so we can see which school the comment came from. | We open a new worksheet and load the comments data source. We filter by position to be undergraduate and remove null form area of study. We colour code by the schools so we can see which school the comment came from. | ||
| − | + | [[File:SS12.png|500px|thumb|center]] | |
|- | |- | ||
| 13 || EDA || Now, we move on to Postgraduate Students. For the following three subsets of the demographic, we will show similar data, but use slightly different visualizations, hopefully to get new insights. | | 13 || EDA || Now, we move on to Postgraduate Students. For the following three subsets of the demographic, we will show similar data, but use slightly different visualizations, hopefully to get new insights. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 59: | ||
For our first visualization, we now filter by Masters and Doctoral students. Here, we use a circle view to compare the frequency of how often masters and doctoral students come to campus and visit the library. | For our first visualization, we now filter by Masters and Doctoral students. Here, we use a circle view to compare the frequency of how often masters and doctoral students come to campus and visit the library. | ||
| − | + | [[File:SS13.png|500px|thumb|center]] | |
|- | |- | ||
| 14 || EDA || Now, we will look at the breakdown of study position, area of study, and likeliness to recommend library services. | | 14 || EDA || Now, we will look at the breakdown of study position, area of study, and likeliness to recommend library services. | ||
| + | [[File:SS14.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:SS14b.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 15 || EDA || Next, we look at preference between the two libraries. We look at the library that is preferred and show the likelihood of recommendation. | | 15 || EDA || Next, we look at preference between the two libraries. We look at the library that is preferred and show the likelihood of recommendation. | ||
| + | [[File:SS15b.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 16 || EDA || Next, we show the individual importance and performance for each of the questions. | | 16 || EDA || Next, we show the individual importance and performance for each of the questions. | ||
We use stack bars to show the importance, and filter by page for performance to compare individual questions to the importance. | We use stack bars to show the importance, and filter by page for performance to compare individual questions to the importance. | ||
| − | + | [[File:SS16.png|500px|thumb|center]] | |
| + | [[File:SS16b.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 17 || EDA || We do a simple pie chart to see how the performance was overall. | | 17 || EDA || We do a simple pie chart to see how the performance was overall. | ||
| + | [[File:SS17.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 18 || EDA || Next, we visualize the NPS in two forms, bar chart and pie chart. We use the calculated NPS field found earlier. | | 18 || EDA || Next, we visualize the NPS in two forms, bar chart and pie chart. We use the calculated NPS field found earlier. | ||
We show mark labels for the pie chart | We show mark labels for the pie chart | ||
| − | + | [[File:SS18.png|500px|thumb|center]] | |
|- | |- | ||
| 19 || EDA || We show the same suggestions as before, except we show it for postgraduates rather than undergraduates. | | 19 || EDA || We show the same suggestions as before, except we show it for postgraduates rather than undergraduates. | ||
| + | [[File:SS19.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 20 || EDA || Now, we will be looking at Faculty. | | 20 || EDA || Now, we will be looking at Faculty. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 92: | ||
For these visualizations and those in Staff the techniques we will use are similar to those used above, just that we take a different approach in how we view them (i.e attributes chosen and small details in visualization). | For these visualizations and those in Staff the techniques we will use are similar to those used above, just that we take a different approach in how we view them (i.e attributes chosen and small details in visualization). | ||
| + | [[File:SS20.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:SS21.png|500px|thumb|center]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 22:41, 15 March 2020
Contents
HomePage
Given data from the 2018 SMU Library Survey, covering 4 demographics of Undergraduates, Postgraduates, Faculty and Staff, I aim to explore interesting trends, patterns and insights that could potentially be of use to the surveyors.
Data Preparation
| Step | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Preparation | First, we load the excel file “Raw data 2018-03-07 SMU LCS data file – KLG” into Tableau. |
| 2 | Data Preparation | We look at the legend and take note of which names correspond to which numbers. |
| 3 | Data Preparation | We use calculated fields to assign the right names to the numerically represented attributes. |
| 4 | Data Preparation | We rename these calculated fields appropriately, leaving the I01-I26, P01-26 and NA01-26 the same. We hide comment1 as the data for suggestions is in another file, as well as the original columns the calculated fields are derived from. |
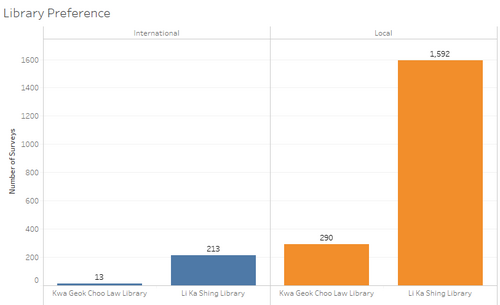
| 5 | EDA | For undergraduate students, we first use simple views to explore Library Preference, Study Area, Year Breakdown, International or not, Frequency of visiting the library and campus, and likeliness to recommend library services. We remove null values by filtering them out.
For our first visualization, we see how students from different schools use the Library. First, we filter the position so we are only looking at year 1 to 4 undergraduates. Then, we drag the calculated field Study over to the Columns. We then filter out others in the Study field. We rename the visualization library preference. |
| 6 | EDA | For our second visualization, we explore whether there is the potential that exchange students are not aware of either library. To accomplish this, we plot a similar bar chart as before, except now instead of study area, we check whether they are exchange students. |
| 7 | EDA | For our third and fourth visualization, we compare the frequency of visiting the library versus visiting the campus.
We create two visualizations for this, changing them to tree maps then adding percentage of total number of records as labels, so that we can see clearly the proportions of the frequency of those who go to the library versus those who go to campus. |
| 8 | EDA | Now, we look at the likeliness for undergraduates to recommend library services. This can easily be seen in a bar graph. We convert likeliness to recommend into a dimension, then plot it against the Library they seem to frequent more. We also remove null values from the likeliness to recommend. We then show this as a percentage so we can compare the libraries.
We create 2 visualizations here, one filtered for the Law Library and the other for Li Ka Shing. Here we use a gradient of colours to show the ordinal nature of the numerical values. |
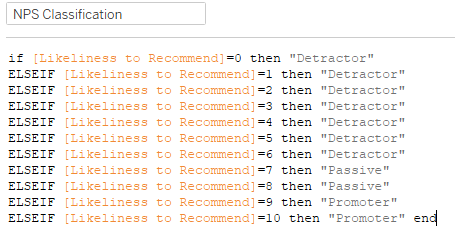
| 9 | EDA | Now, we will calculate overall net promoter score for the two libraries, which we will attain by first grouping 6 and below as detractors, 7,8 as passives and 9,10 as promoters. We can show this in a pie chart. By taking detractor percentage from promoter percentage, we can get the net promoter score. For undergraduates, we will not display this but simply display it in a table. |
| 10 | EDA | Now, we start to look more into the importance and performance of the 26 listed factors. We pivot I1 to I26, add Pivot Field Names and Pivot Field Values into the Columns, and add SUM of Number of Rows into the Rows, ensuring that the calculation is across the pane. |
| 11 | EDA | Now, let us run the same process on P1 to P27 to see the performance across the 27 measures. At this point, we need to change all SUM(number of rows) in previous visualizations into CNTD(ResponseID) due to the pivoting so we don’t show duplicates. |
| 12 | Data Preparation
and EDA |
As for the final visualization for Undergraduates, we look at the comments given.
We open a new worksheet and load the comments data source. We filter by position to be undergraduate and remove null form area of study. We colour code by the schools so we can see which school the comment came from. |
| 13 | EDA | Now, we move on to Postgraduate Students. For the following three subsets of the demographic, we will show similar data, but use slightly different visualizations, hopefully to get new insights.
We want to explore Library Preference, Study Area, Year Breakdown, International or not, Frequency of visiting the library and campus, and likeliness to recommend library services. We remove null values by filtering them out. For our first visualization, we now filter by Masters and Doctoral students. Here, we use a circle view to compare the frequency of how often masters and doctoral students come to campus and visit the library. |
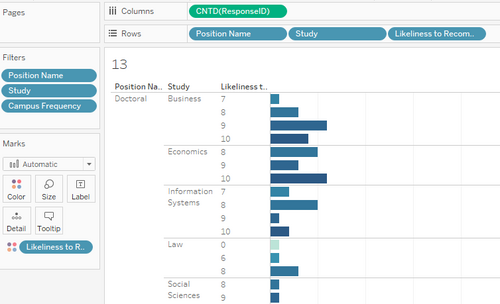
| 14 | EDA | Now, we will look at the breakdown of study position, area of study, and likeliness to recommend library services. |
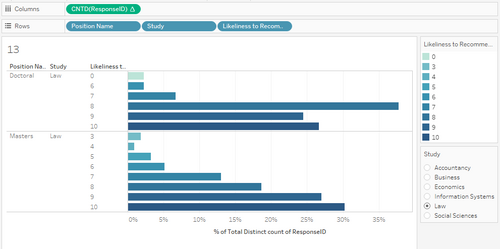
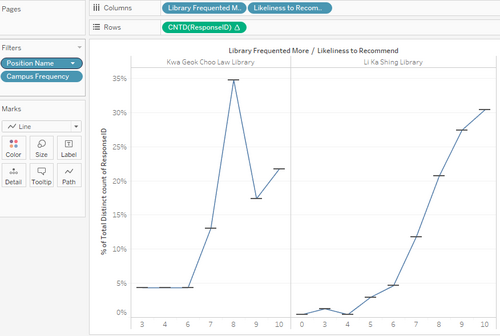
| 15 | EDA | Next, we look at preference between the two libraries. We look at the library that is preferred and show the likelihood of recommendation. |
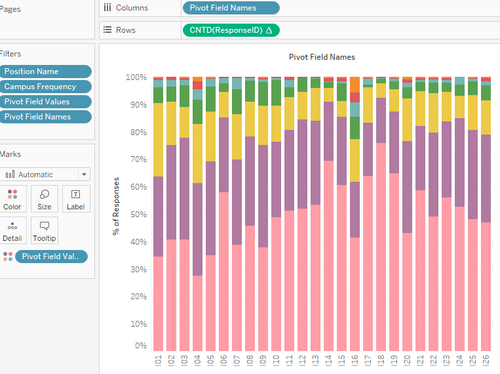
| 16 | EDA | Next, we show the individual importance and performance for each of the questions.
We use stack bars to show the importance, and filter by page for performance to compare individual questions to the importance. |
| 17 | EDA | We do a simple pie chart to see how the performance was overall. |
| 18 | EDA | Next, we visualize the NPS in two forms, bar chart and pie chart. We use the calculated NPS field found earlier.
We show mark labels for the pie chart |
| 19 | EDA | We show the same suggestions as before, except we show it for postgraduates rather than undergraduates. |
| 20 | EDA | Now, we will be looking at Faculty.
We want to explore Library Preference, Study Area, Year Breakdown, whether they are International or not, Frequency of visiting the library and campus, likeliness to recommend library services, their opinions on the survey questions and comments. As before, we remove null values by filtering them out. This time, we use histograms and box plots to visualize the faculty’s study area, library preference and frequency to recommend library services. For these visualizations and those in Staff the techniques we will use are similar to those used above, just that we take a different approach in how we view them (i.e attributes chosen and small details in visualization). |
Visualizations and Insights
Undergraduate
| Number | Visualization |
|---|---|
| 1 |
We can see that in all Schools except for Law, the Li Ka Shing Library is used far more, with the Law Library taking up approximately only 10% of the total for the other Schools. This may suggest that there is space in the law library that is not being used, and that should there be too many people in the Li Ka Shing, the school can push students to make use of the additional space in the Law Library. |
| 2 | We can see that it does not appear to be the case the international students are not aware of either library. The proportion of international and local students going to either library appears to be similar. |
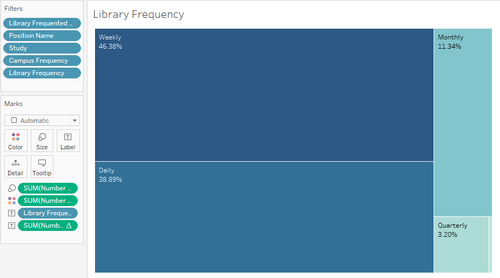
| 3 | We can see that most undergraduates come to school daily, while some go weekly. This is to be expected as many of them are taking modules spread out over several days. For those who go once a week, they may be schooling part time while they work, or putting all modules on a single day. This information is more useful once we contrast it to library frequency. |
| 4 | We can see that Library Frequency wise, most either visit Daily or Weekly. Interestingly, a substantial percentage of approximately 15% go monthly or quarterly. This may be due it being the exam period or finals period. As such, we could hypothesize that during such crunch times, we can expect around a 15% increase in library population for undergraduates. Of course, time-series data will have to be provided to see when this uptick happens, or if it is spread out. |
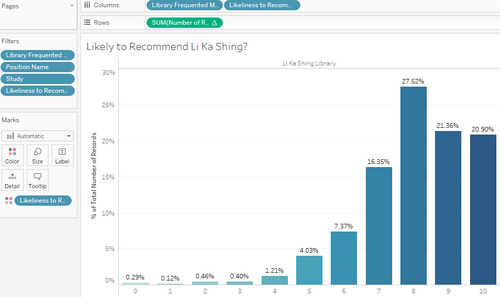
| 5 | We can see that majority of undergraduate students are likely to recommend Li Ka Shing. |
| 6 | We can see that this is the case as well for Kwa Geok Choo, with fewer outliers in the 0,1 and 2 categories. |
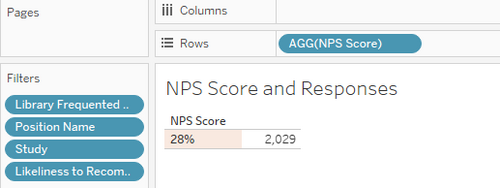
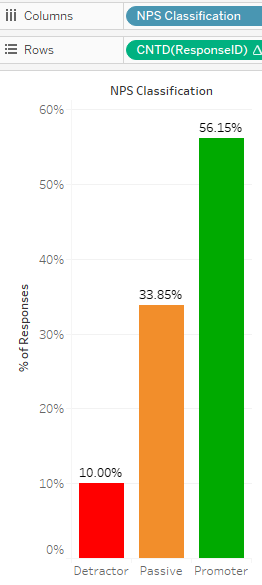
| 7 | We can tell that there is an NPS score of 28% over 2029 responses. Based on global NPS standards, this is a “good” score. |
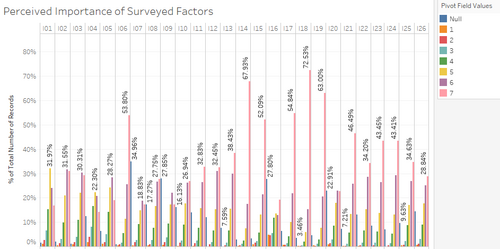
| 8 | Here we can see, three surveyed factors that seem the most important for undergraduates would be I14, I18, and I19. |
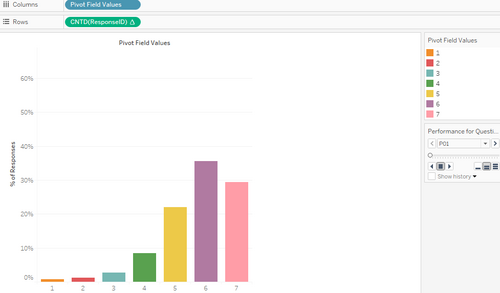
| 9 | Here we can see, the surveyed factor that appears to have performed the best for undergraduates would be P18, wireless access. This is something the library is doing well that is also perceived by undergraduates as important. Furthermore, of note is also that for P27, overall satisfaction with the library, a lot give a 6, indicating very good performance, yet not the best. It is important for us to uncover what potentially is causing the mode of the overall perception of the library to drop from a 7 to 6. |
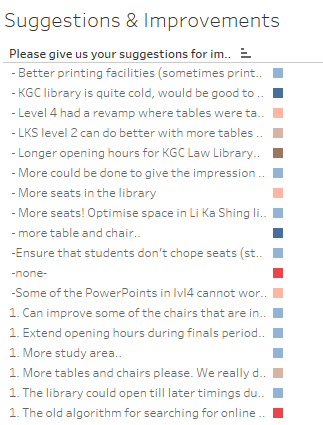
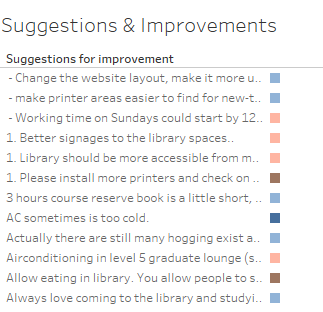
| 10 | This gives us a view of some examples of suggestions. For example, from here we can see that a law student wishes for longer opening hours in the Law Library. |
Postgraduate
| Number | Visualization |
|---|---|
| 1 |
We can see that in general, the frequency of coming to campus is similar between Doctoral and Masters students. |
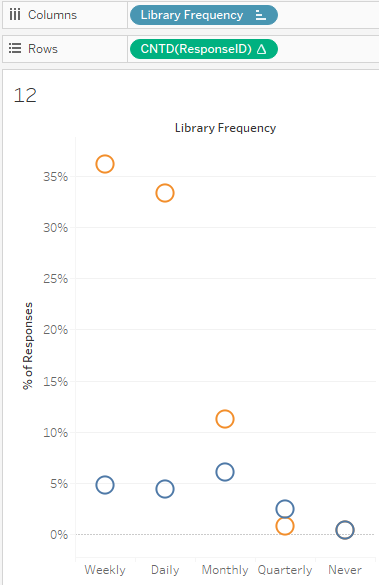
| 2 | We can see that there is some difference in the frequency in library visits. An interesting trend is that Doctoral students seem to go to the library Monthly or Quarterly, versus Masters students, who go more Weekly and Daily. This may be due to the different nature of their studies. |
| 3 | Here, we can see that in general, Masters Business students are less happy with the libraries than Doctoral students. |
| 4 | We can see that there is a peak for the Law library at a score of 8, while for Li Ka Shing, the peak is 10. |
| 5 | We can see that I18 has the highest proportion of full (7) scores. This is congruent with what we saw with the undergraduates. |
| 6 | Looking at P01, we can see that most are informed about services. However, a few responders appear not to be, which is crucial as they may not be able to fully take advantage of services the library offers. |
| 7 | Here we can see that majority of post graduate students score a 7 or 6 for performance. |
| 8 | We can see the distribution of promoters and detractors. It is clear that for postgraduates, we have much more promoters than detractors. |
| 9 | Here, we can see the breakdown by numbers. It is evident that the sample size for postgraduates is relatively smaller, but still substantial. |
| 10 | We can gain some insight by looking at this, for example, we can tell that postgraduates face similar issues with lack of seating, but we also can see some graduate specific complaints such as about the air-conditioning at the graduate lounge. |
Faculty
| Number | Visualization |
|---|---|
| 1 |
We can see that in all Schools except for Law, the Li Ka Shing Library is used far more, with the Law Library taking up approximately only 10% of the total for the other Schools. This may suggest that there is space in the law library that is not being used, and that should there be too many people in the Li Ka Shing, the school can push students to make use of the additional space in the Law Library. |
| 2 | We can see that it does not appear to be the case the international students are not aware of either library. The proportion of international and local students going to either library appears to be similar. |
| 3 | We can see that most undergraduates come to school daily, while some go weekly. This is to be expected as many of them are taking modules spread out over several days. For those who go once a week, they may be schooling part time while they work, or putting all modules on a single day. This information is more useful once we contrast it to library frequency. |
| 4 | We can see that Library Frequency wise, most either visit Daily or Weekly. Interestingly, a substantial percentage of approximately 15% go monthly or quarterly. This may be due it being the exam period or finals period. As such, we could hypothesize that during such crunch times, we can expect around a 15% increase in library population for undergraduates. Of course, time-series data will have to be provided to see when this uptick happens, or if it is spread out. |
| 5 | We can see that majority of undergraduate students are likely to recommend Li Ka Shing. |
| 6 | We can see that this is the case as well for Kwa Geok Choo, with fewer outliers in the 0,1 and 2 categories. |
| 7 | We can tell that there is an NPS score of 28% over 2029 responses. Based on global NPS standards, this is a “good” score. |
| 8 | Here we can see, three surveyed factors that seem the most important for undergraduates would be I14, I18, and I19. |
| 9 | Here we can see, the surveyed factor that appears to have performed the best for undergraduates would be P18, wireless access. This is something the library is doing well that is also perceived by undergraduates as important. Furthermore, of note is also that for P27, overall satisfaction with the library, a lot give a 6, indicating very good performance, yet not the best. It is important for us to uncover what potentially is causing the mode of the overall perception of the library to drop from a 7 to 6. |
| 10 | This gives us a view of some examples of suggestions. For example, from here we can see that a law student wishes for longer opening hours in the Law Library. |
Staff
| Number | Visualization |
|---|---|
| 1 |
We can see that in all Schools except for Law, the Li Ka Shing Library is used far more, with the Law Library taking up approximately only 10% of the total for the other Schools. This may suggest that there is space in the law library that is not being used, and that should there be too many people in the Li Ka Shing, the school can push students to make use of the additional space in the Law Library. |
| 2 | We can see that it does not appear to be the case the international students are not aware of either library. The proportion of international and local students going to either library appears to be similar. |
| 3 | We can see that most undergraduates come to school daily, while some go weekly. This is to be expected as many of them are taking modules spread out over several days. For those who go once a week, they may be schooling part time while they work, or putting all modules on a single day. This information is more useful once we contrast it to library frequency. |
| 4 | We can see that Library Frequency wise, most either visit Daily or Weekly. Interestingly, a substantial percentage of approximately 15% go monthly or quarterly. This may be due it being the exam period or finals period. As such, we could hypothesize that during such crunch times, we can expect around a 15% increase in library population for undergraduates. Of course, time-series data will have to be provided to see when this uptick happens, or if it is spread out. |
| 5 | We can see that majority of undergraduate students are likely to recommend Li Ka Shing. |
| 6 | We can see that this is the case as well for Kwa Geok Choo, with fewer outliers in the 0,1 and 2 categories. |
| 7 | We can tell that there is an NPS score of 28% over 2029 responses. Based on global NPS standards, this is a “good” score. |
| 8 | Here we can see, three surveyed factors that seem the most important for undergraduates would be I14, I18, and I19. |
| 9 | Here we can see, the surveyed factor that appears to have performed the best for undergraduates would be P18, wireless access. This is something the library is doing well that is also perceived by undergraduates as important. Furthermore, of note is also that for P27, overall satisfaction with the library, a lot give a 6, indicating very good performance, yet not the best. It is important for us to uncover what potentially is causing the mode of the overall perception of the library to drop from a 7 to 6. |
| 10 | This gives us a view of some examples of suggestions. For example, from here we can see that a law student wishes for longer opening hours in the Law Library. |
Project URL
https://public.tableau.com/profile/cerulean.koh.shiliang#!/vizhome/MidTerm_15842782941690/HomePage