Difference between revisions of "Group06 proposal"
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" | {| class="wikitable" width="100%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #899db3;color:#fbfcfd;width: 30%;" | | + | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #899db3;color:#fbfcfd;width: 30%;" |Dataset/Source |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #899db3;color:#fbfcfd;width: | + | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #899db3;color:#fbfcfd;width: 35%;" |Variables & Description |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #899db3;color:#fbfcfd;width: | + | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #899db3;color:#fbfcfd;width: 35%;" |Rationale of Usage |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| − | < | + | <b>Dataset:</b> GCI_Dataset_2007-2017 <br><br> |
| − | + | <b>Source: </b>[http://reports.weforum.org/global-competitiveness-index-2017-2018/downloads/|Source: World Economic Forum] | |
| − | |||
</center> | </center> | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 76: | Line 75: | ||
<li> <b> Number of Sessions Per User</li> | <li> <b> Number of Sessions Per User</li> | ||
<li> <b> Page Views</li> | <li> <b> Page Views</li> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | abc | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 20:14, 12 April 2020
|
Growth Signal |
|
|
|
|
Contents
Problem & Motivation
Problem
In Singapore, education is one of the sectors that is heavily invested by the state besides defence and health. As years progress, more data are accumulated and made available to the public by various government institutions such as Singapore Department of Statistics and data.gov. Despite the abundance of data, it is often not easy for someone fresh out of post-secondary education to plan for further studies in an efficient and thorough manner due to decentralisation and lack of visualisation (data are in raw/unstructured/tabular form).
Motivation
Enrolling in higher education such as polytechnics, especially universities is becoming a commonplace in Singapore. Not only does it prepare the next generation for the future (individual level), the country as a whole can significantly benefit as a result of a highly-educated population. This interactive visualisation will serve as a platform for post-secondary individuals to analyse the changing landscape and trends of higher education where they can uncover interesting insights and make well-informed decisions to ensure a sustainable future.
Objectives
Target Group: Post-Secondary individuals
Many of the available data such as Graduate Employment Survey, Enrolment of students in institutions of higher education and government expenditure are located either on various institutions’ website, government generated reports or on data sites. The general reader is unable to get the full information on higher learning institutions in Singapore.
As such, our Dashboard will fulfil the following objectives:
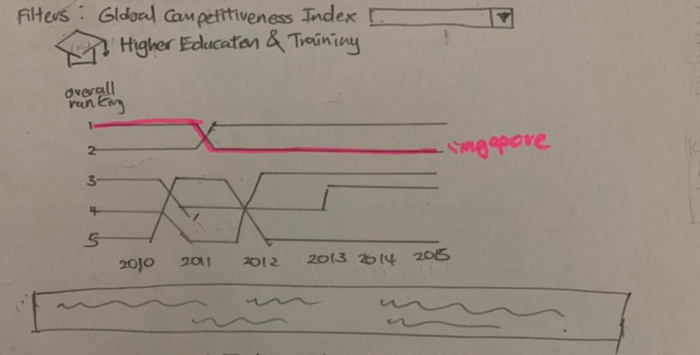
- Visualise Singapore’s ranking in various metrics of GCI’s 5th pillar (higher Education and Training) over time
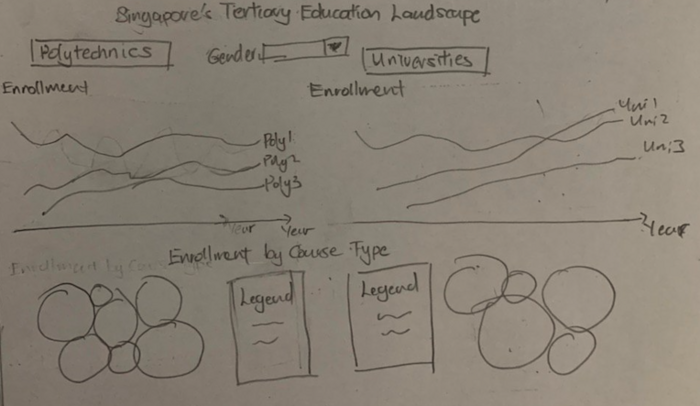
- Identify enrolment demographic across different institutions and courses and how they changed over time.
- Comparison of Governments’ efforts in developing Polytechnics and Universities with different sectors and other levels of education
- Identify the courses which churns out the most successful graduates by employment rates and starting income.
Dataset
| Dataset/Source | Variables & Description | Rationale of Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
Dataset: GCI_Dataset_2007-2017 |
|
abc |
Background Survey
| Research | Learning points | Improvement |
|---|---|---|
|
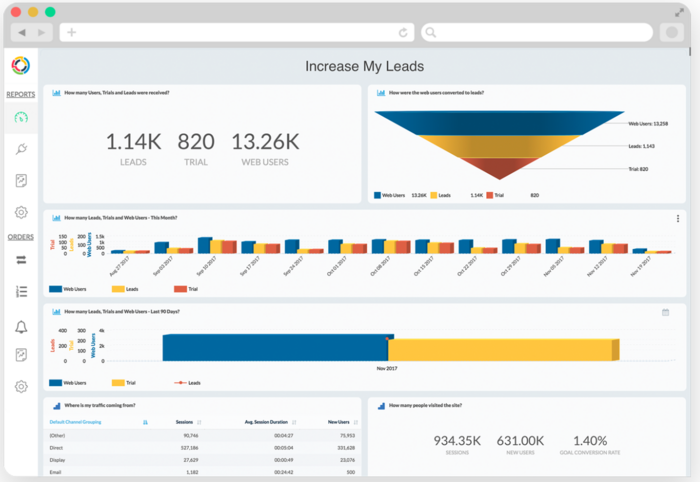
Example of sales funnel (top right) on the to show conversion of Users to Leads and Trial. Can be broken down into timeline as well. The sales funnel would give an accurate idea of how many percentage of users are really interested in the advertisement or those that actually manage to secure leads. However, diagrams in 3D can be misleading due to overlaps and is not very neat. How many leads in the last 90 days or this month can be combined. |
Can add Interaction for across a time period. Funnel can be broken down into more categories such as number of potential leads, marketing leads, sales leads, deals etc. Can give top 5 sources of traffic | |
|
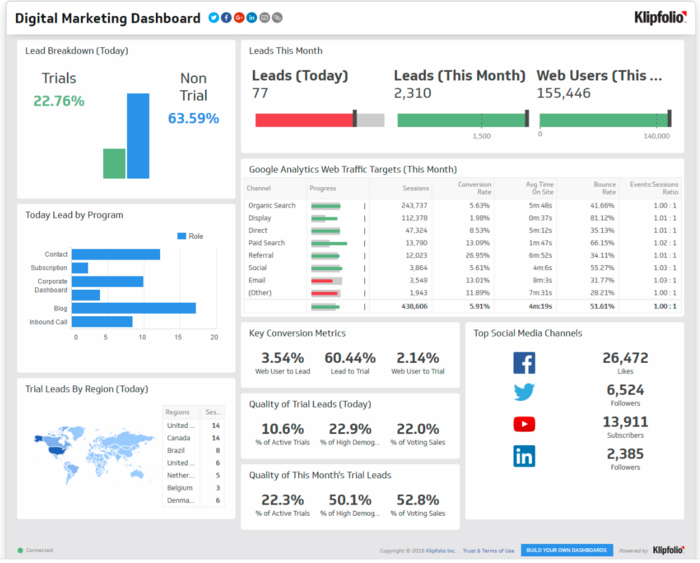
Another dashboard example provided by kilpfolio. Useful example to show metrics such as quality of leads and conversion metrics, leads by region and top few social media channels. It can be animated or add a scale to show changes across timing However, leads by region is too small. Google web analytics Web traffic targets is not labeled and just shows the bar. Can change to label with highlight of red and green (based on whether the progress is negative or positive) |
Perhaps can show the top 5 areas instead and table can be replaced by a bar graph. Key conversion metrics and quality of leads can be replaced with line graph to show changes over time. |
References
- 6 Steps to Creating a Better Marketing Dashboard
- Klipfolio - Digital Marketing Dashboard
- 100 Tasks
- Web Analytics 2.0 by Avinash Kaushik
Technical Challenges
| Challenge | Description | Mitigation Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Unfamiliarity with Tools | Most of the team members are not too familiar with R and R Shiny. |
|
| Lack of policy knowledge | There may be gaps in knowledge of policy jargons. |
|
| Data Quality & Integrity | Difficult to consolidate data as they are from different government agencies. Some of the data are in an unstructured format. |
|
Storyboard
| Dashboards | Description |
|---|---|
Dashboard 1: Higher Education Ranking |
|
Dashboard 2: Enrollment |
|
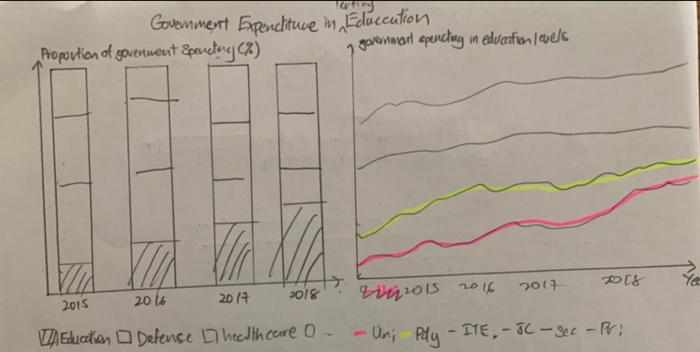
Dashboard 3: Government Expenditure |
|
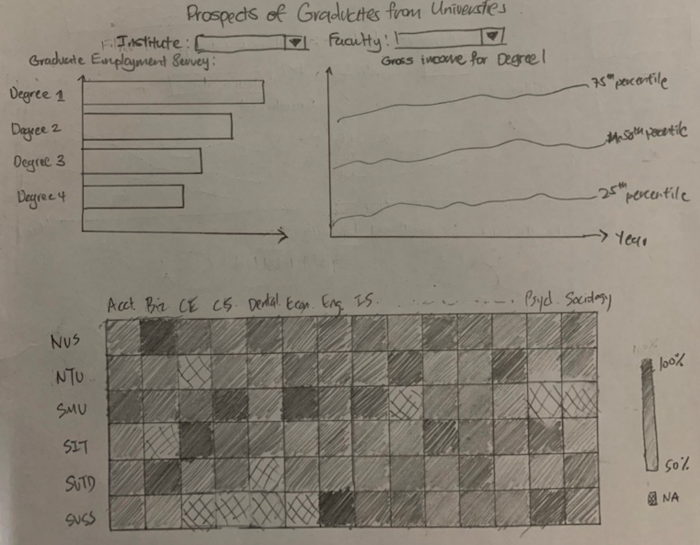
Dashboard 4: Graduate's Prospects |
|
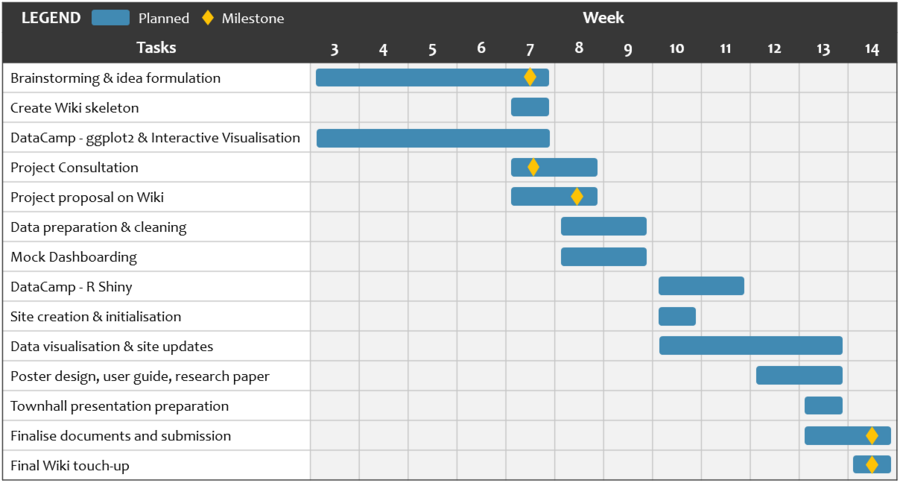
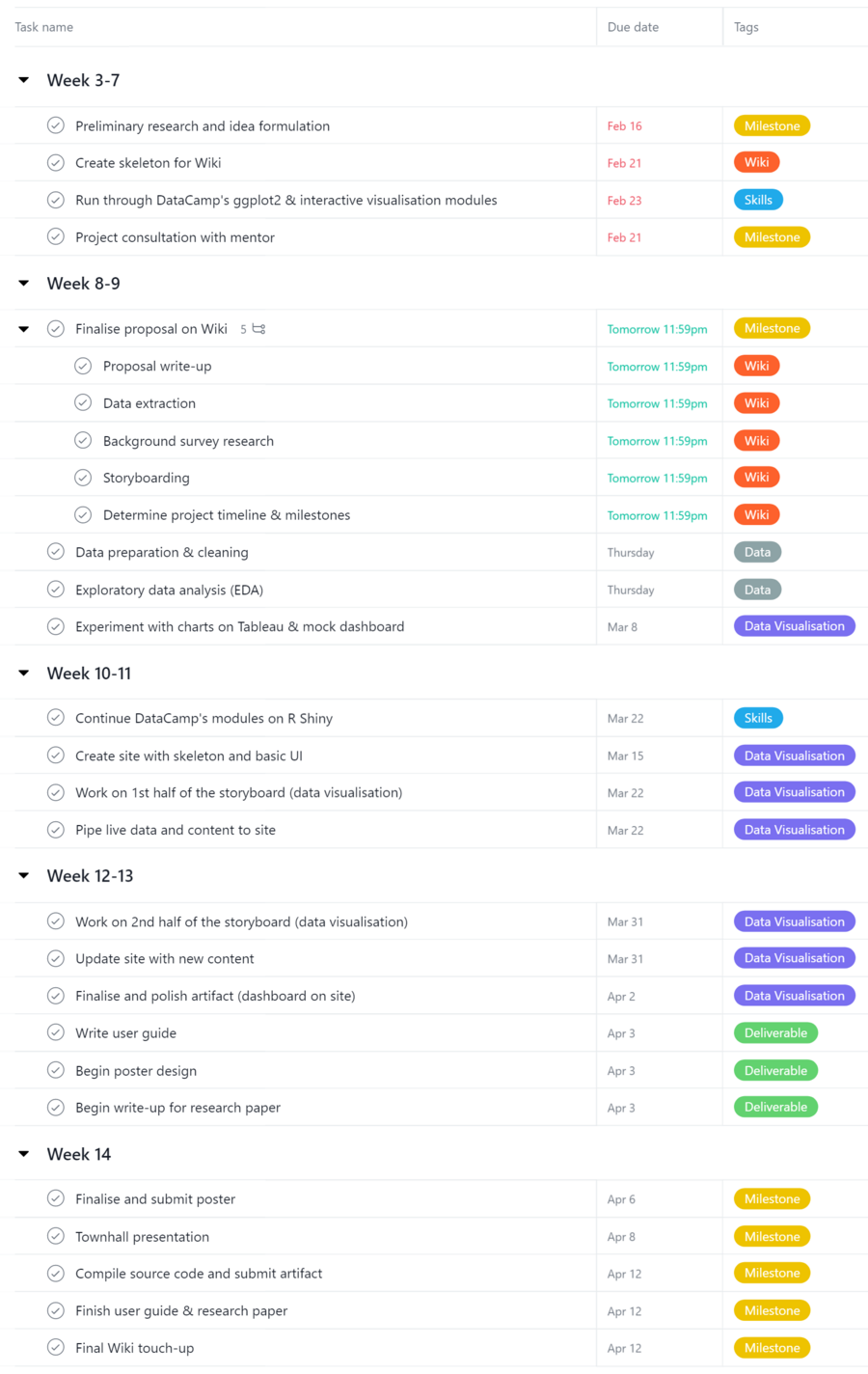
Project Timeline & Milestones
Comments
| Name | Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| (Name) | (Date) | (Comment) |
| (Name) | (Date) | (Comment) |
| (Name) | (Date) | (Comment) |