SMT201 AY2019-20G2 Ex2 Melanie Tan Ri Fang
Contents
Part One: Gombak in 4 Views
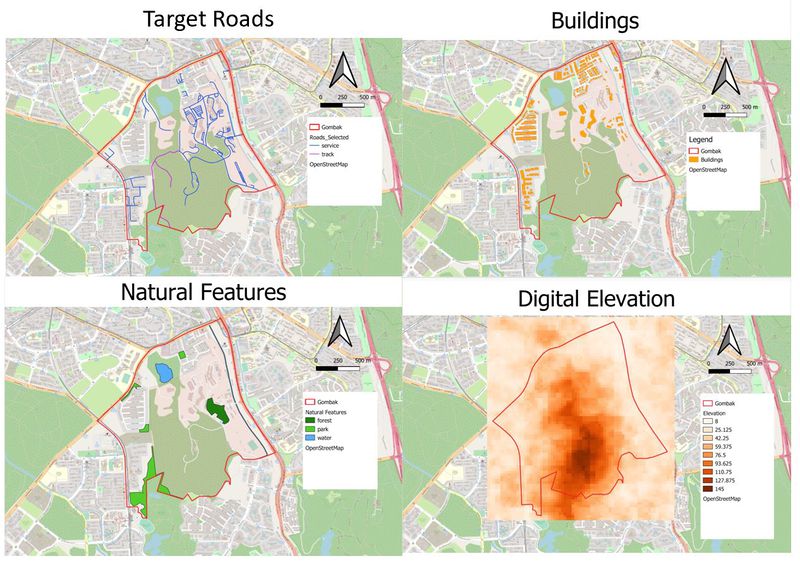
Gombak & Target Roads
Target roads have been filtered out with namely only - service roads and tracks. This is to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage, hence satisfying the accessibility factor when building the Quarantine Centre. Service roads are represented by the colour blue and Tracks are represented by the colour purple. There are a total of 199 service roads and 2 tracks in the study area of Gombak with majority of the service roads residing on the North-East side of Gombak and the 2 tracks mainly situated near to the Central part of Gombak.
Gombak & Buildings
Using selection by location feature, it can be seen that majority of the buildings are located on the North-West and North side of Gombak. This could be partially due to the fact that some of the lowest elevation of Gombak is situated near those areas. Thus, when building the contractors are able to save cost due to lesser cut-and-fill which might lead to higher development cost. As such, it can be seen that other features such as natural features and roads are located near these buildings in order to increase convenience and financial value. One thing to note while selecting an ideal location to build the Quarantine Centre would be to treat all buildings as population indicators and the selected site should be away from the buildings.
Gombak & Natural Features
Ideally, the Quarantine Centre should be away from forested land, park and water. As such, I have identified 1 forest , 4 parks and 3 water bodies labelled dark green as a representation of forests, light green as a representation of park and blue as a representation of water respectively. At one glance, the analyst is able to filter out areas near these facilities, hence helping them to narrow down the scope on deciding the ideal location to build the Quarantine Centre.
Gombak & Digital Elevation
The highest point of elevation for Gombak would be 145m above sea level and the lowest elevation would be 8m above sea level. The varying degree of elevation is represented over a spectrum of orange where the lower degrees of elevation is leaning more towards the lighter orange and the higher the elevation, the darker the orange. Therefore, as seen in the digital elevation analysis, the highest elevation of Gombak is situated right at the centre. On a side note, when using extracting clip raster by extent, we would have to adjust (increase) the numbers (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). This is because when calculating for the slope layer later on, QGIS will automatically cut off one pixel on each side of the grid which might possibly lead to the study area exceeding the Aster_GDEM, ultimately leading to inaccuracy in the figures following after as the Aster_GDEM did not cover all of the study area.
Part Two: Gombak in 4 Views (Proximity)
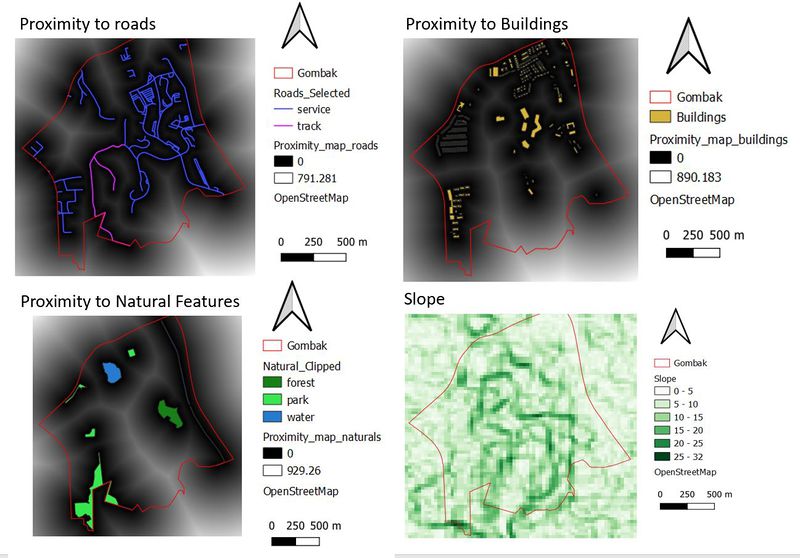
Gombak & Proximity Target Roads
The value of the distance from land lot to the nearest road is represented on a spectrum where the lowest distance is at 0m and the furthest distance is at 791.281m. The lighter the colour, the shorter the distance and as the colour changed to a darker purple, the distance increases. Thus, when looking to plan a Quarantine Centre, it would ideally be nearer to the road. Hence, when the analyst looks at the above analysis, the focal area / the ideal area would be the lighter colours. In fact, the lighter the better because it means that the roads are more accessible. Through the application of the min-max method, we can derive the criterion score, where the lower the score, the better it is.
Gombak & Proximity to Buildings
The value of the distance from land lot to the nearest building is represented on a spectrum where the lowest distance is at 0m and the furthest distance is at 890.183m. The lighter the colour, the shorter the distance and as the colour changes to a darker purple, it symbolises that the distance is increasing. However, the selected site should be away from the buildings.
Gombak & Proximity to Natural Features
The value of the distance from land lot to the nearest natural features is represented on a spectrum where the lowest distance is at 0m and the furthest distance is at 929.26m. The lighter the colour, the shorter the distance and as the colour changes to darker green, it symbolises that the distance is increasing. However, the selected site should be away from the natural features (forest, parks and water).
Gombak & Slope
The elevation of the slope is represented on a spectrum where the lowest elevation is at 0 degree and the highest elevation is at 32.6degrees and as the colour changes to darker green, it symbolises the increase in elevation of the slope. The higher the elevation, the darker the colour. Under the economic factor of avoiding slopes so as to reduce cut-and-fill which might lead to relatively higher development cost.
Map Layout With Criterion Scores
A map layout with four views showing the criterion scores of each factor layers and a short description of not more than 150 words for each view.
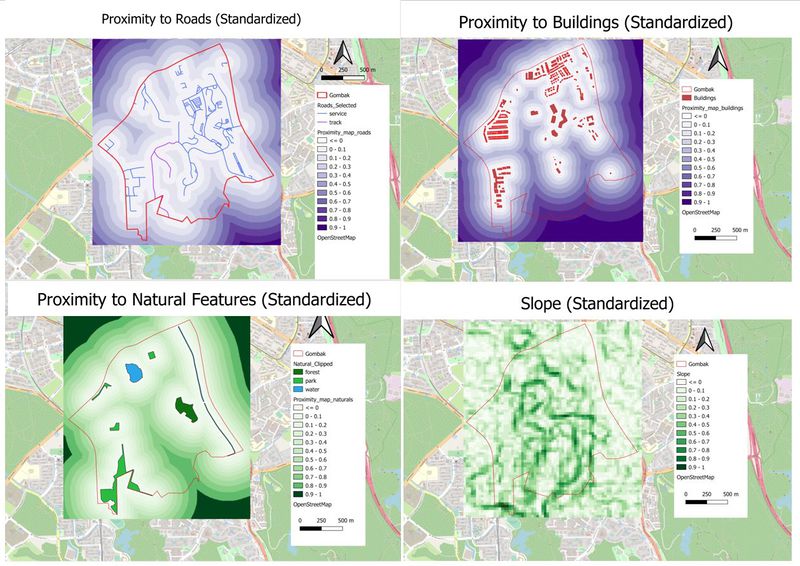
Proximity to Target Roads
Using the following factor, ( 1/proximity_map_roads) , I have inversed the colour representation of distance. Areas nearer to the features would be represented by whites and area further away would be represented by darker colours. The minimum number is now 0.0056 (4sf) and the maximum number is 0.2
Proximity to Buildings
In order to keep things constant where the whites represent closer distance and the darker colours represent further distance , I have decided to use standardization through the use of inverse. Using the following factor, ( 1/proximity_map_buildings) , I have inversed the colour representation of distance. Areas nearer to the features would be represented by whites and area further away would be represented by darker colours – in this case, green. The minimum number is now 0.0056 (4sf) and the maximum number is now 0.9999 (4sf). When planning for a Quarantine Centre, it is more ideal for the analyst to look at the darker colours as this would mean that there is a higher chance the selected site will not be near residential buildings as per the condition given by the Health Risk factor.
Proximity to Target Natural Features
In order to keep things constant where the whites represent closer distance and the darker colours represent further distance , I have decided to use standardization through the use of inverse. Using the following factor, ( 1/proximity_map_naturals) , I have inversed the colour representation of distance. Areas nearer to the features would be represented by whites and area further away would be represented by darker colours – in this case, green. The minimum number is now 0.2397 (4sf) and the maximum number is now 0.9837 (4sf).
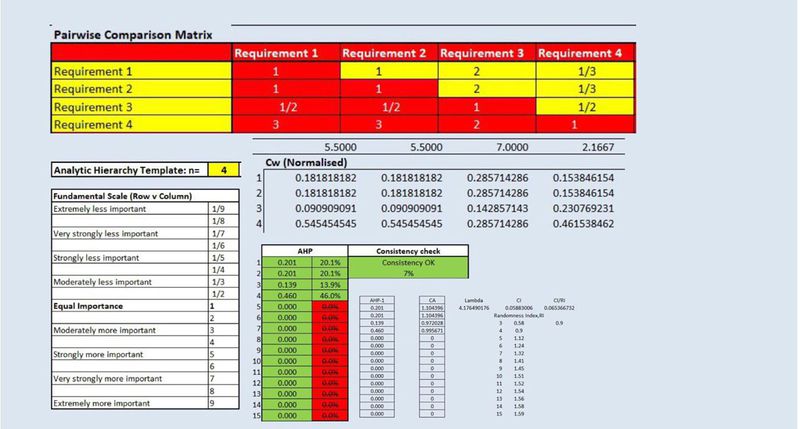
AHP Matrix And Result Report
In terms of the economic factor, I rated accessibility to be of equal importance as the selected site being a Quarantine Centre should also be accessible for employees to get to work and for transportation of medicinal drugs to the facility easier. Health risk factor is rated more important than the economic factor due to the nature of the selected site being a quarantine centre. It is very important for the facility to place health risk factor above anything else. Lastly, nature factor is ranked lower than the economic factor due to the fact that the facility it usually under lockdown hence nature does not really play a part. In terms of comparing it against the accessibility factor, I ranked health risk factor as of more importance than accessibility with the same reason mentioned above. As for nature, I also ranked it less important as compared to the accessibility factor due to the nature of the selected site as mentioned above. In terms of comparing it against the Health risk factor, economic and accessibility factor have been rated 1/3 due to the function of the AHP which will automatically calculate the inverse number of the original input. Hence, under that row, I only rated natural factor which was ranked lower importance due to the same reasons given above.
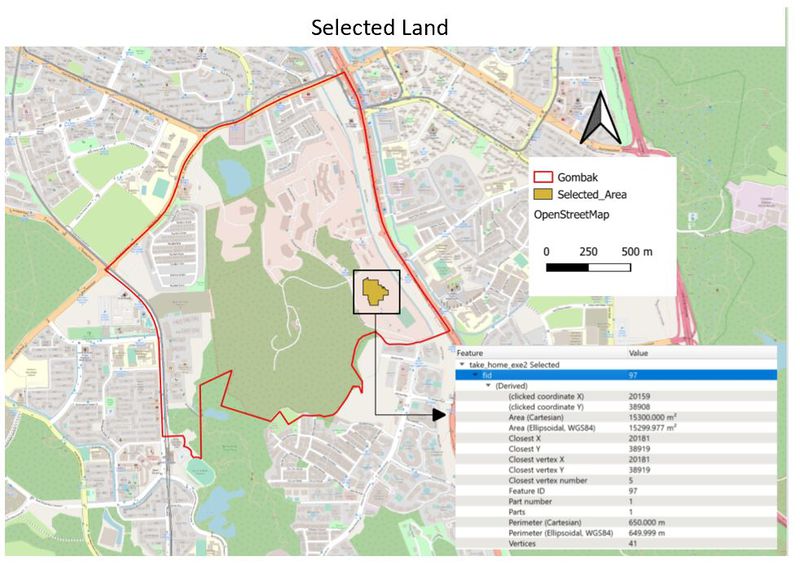
Map Layout With The Suitability Land Lot(s)
To test the suitability, I have chosen to utilize the AHP weightage for each factor. suitability = AHP percentage * min-max (repeating the steps for each factor) and add all of them up. In order to find the suitability, my cut-off point is set through the use of reclassification table. Having set the suitability percentage to be above 90% , this also implies that lots lower than 90% will not be considered. As such, I have also created a condition where values above90% will be assigned to value 1 and anything lower will be assigned to the value 0. This is done so as to help me group the relavant data in to 1 and 0, making the filtering of relavant data easier for me to see. I have shortlisted the top 3 ideal places and have scaled down to one as per shown in the picture above. This is because in terms of the area size, I chose the one nearest to it as well as making sure it fits all the 4 factors (economic, nature, accessibility and health). The chosen lot has an area of 15300m2, situated further away from the usually populated areas such as buildings located on the North of Gombak. The selected site is located on North-East of Gombak, where as previously mentioned, the bulk of the service roads are located on the North-East side making transportation of goods during construction easier. Also, analysing the elevation of the selected area, there is relatively lower elevation as compared to the centre of Gombak. In term of Health risk factor, it is situated far away from the buildings where majority are located in the North. Lastly, satisfying the natural feature factor as it is slightly further away from parks, forests and water. Hence, having seen that it has satisfied all of the above conditions, I have therefore chosen this site highlighted in mustard colour.