SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Lee Jung Jae
Contents
- 1 Part 1: A map layout with four views showing Gombak (Roads, Natural Features, Buildings and Elevation)
- 2 Part 2: Gombak and Proximity to Roads, Buildings, Natural Features and Slope
- 3 Part 3: Criterion Scores of Each Factor Layers
- 4 Part 4: Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) Input Matrix & Result Report
- 5 Part 5: The Suitability Land Lot(s)
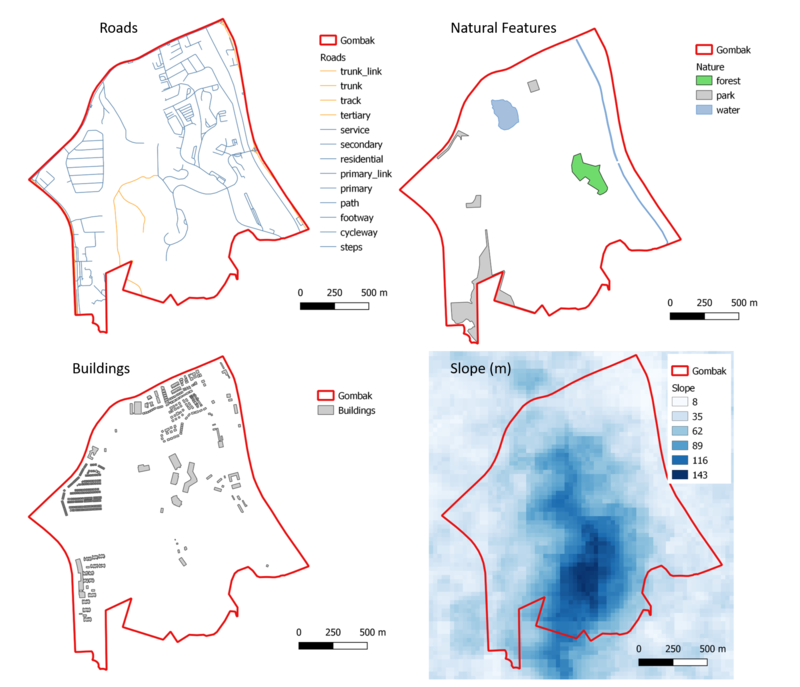
Part 1: A map layout with four views showing Gombak (Roads, Natural Features, Buildings and Elevation)
Roads
Buildings
Natural Features
Elevation model
Part 2: Gombak and Proximity to Roads, Buildings, Natural Features and Slope
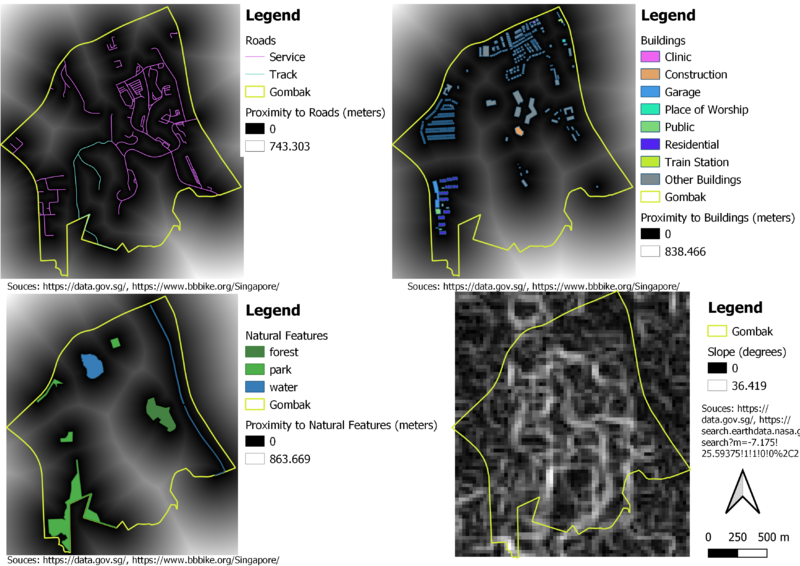
Gombak and Proximity to Roads
Black being the nearest to the existing roads and white being the furthest away from roads. The tone range between black and white provides a good and clear visualization of proximity to roads. This helps to determine where CDQC should be site at Gombak based on the proximity to roads.
Gombak and Proximity to Buildings
The shading of the proximity to buildings is by the gradient between black and white. Black being the nearest to the buildings and white being the furthest away from buildings. The gradient of black and white provides a good and clear visualization of proximity to the buildings. This helps to determine where should CDQC be located at as it should be away from population.
Gombak and Proximity to Natural Features
The proximity to natural features such as forest, park and water is represented by the gradient between black and white. The closer it is to black, the nearer it is to natural features. The closer it is to white, the further it is away from the natural features. This map layout helps to determine where should CDQC be situated at based on the proximity of the natural features.
Gombak and Proximity to Slope
The degree of slope is represented by the gradient between black and white. The closer it is to black, the degree is closer to 0 degrees. This means that there is no slope or less steep slope. The closer it is to white, the degree is closer to 36.419 degrees. This means that there is a steeper slope. CDQC should be located at a less steep slope. With this layout, it helps to determine where is a suitable place to build CDQC.
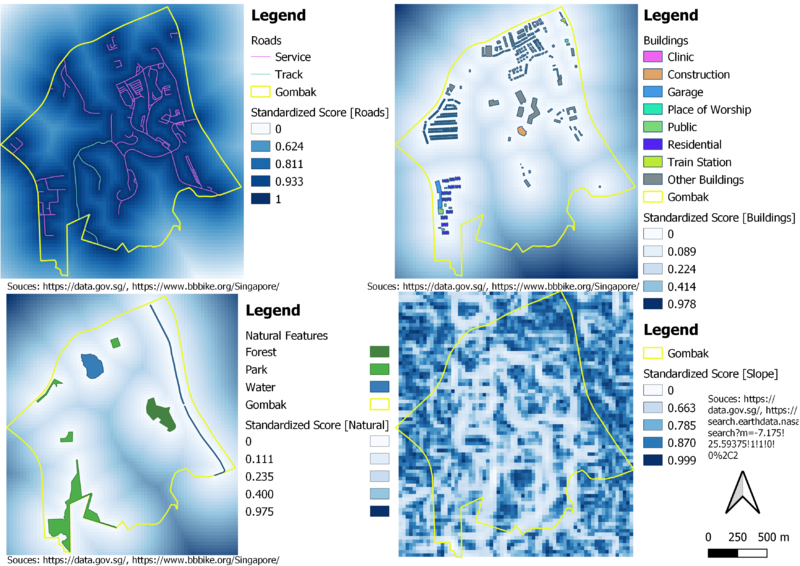
Part 3: Criterion Scores of Each Factor Layers
Among all the criteria standardisation techniques, Min-Max technique will be apply to standardize the four raster layers from Part 2 to derive their criterion score.
Let X be the value.
The formula of Min-Max technique is [(X - Min) / (Max - Min)].
Criterion Score for Roads
Formula (in meters): 1 - [(X - 0) / (743.303 - 0)]
The higher the standardized value the nearer it is to the existing service roads and tracks.
The reason why there is a 1 subtracting Min-Max formula is to inverse the standardized value. The existing Min-Max technique will give a standardized value where the higher the standardized value, the further it is to the existing service roads and tracks. However, the decision factor for accessibility is to have the selected site close to existing service roads and tracks.
Criterion Score for Buildings
Formula (in meters): (X - 0) / (838.466 - 0)
The higher the standardized value, the further it is away from the buildings.
Criterion Score for Natural Features
Formula (in meters): (X - 0) / (863.669 - 0)
The higher the standardized value, the further it is away from forested land, park and water.
Criterion Score for Slope
Formula (in degrees): 1 - [(X - 0) / (36.419 - 0)]
The higher the standardized value, the lower the degree of the slope.
The reason why there is a 1 subtracting Min-Max formula is to inverse the standardized value. The existing Min-Max technique will give a standardized value where the higher the standardized value, the higher the degree of the slope. However, the decision factor for economic is the selected site should avoid steep slope.
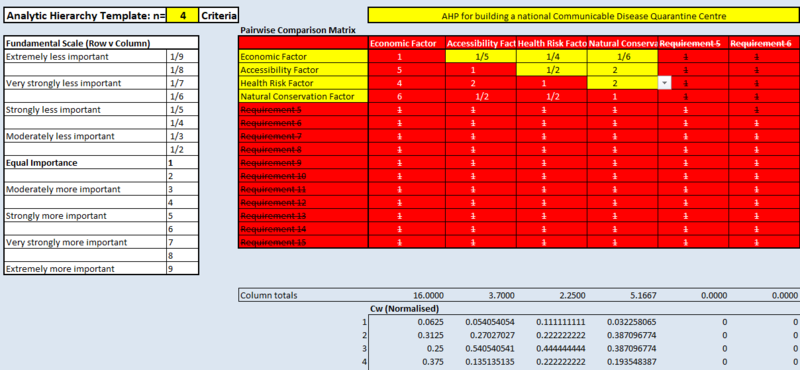
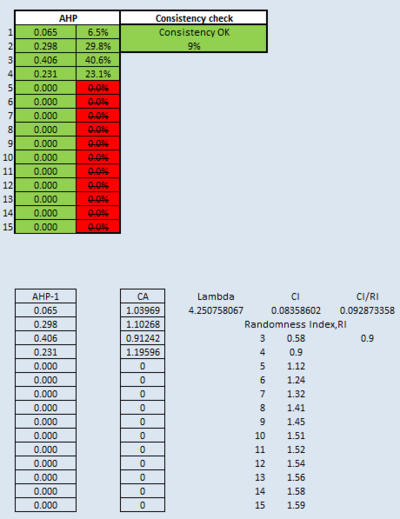
Part 4: Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) Input Matrix & Result Report
Based on the AHP input matrix and result report above, health risk factor, accessibility factor, natural conservation factor and economic factor have AHP of 40.6%, 29.8%, 23.1% and 6.5%. Health risk factor is the most important factor when considering the place to build CDQC. This is because CDQC is to isolate infected people away from healthy population. Accessibility factor is more important than the other two factors (natural conservation factor and economic factor) because in times of need, time is key to save a life. With CDQC being build close to existing roads and tracks, it can reduce cost to build additional roads. Natural conservation factor is more important than economic factor because infectious diseases may spread through air or water and may cause mutation to trees in the park and forest. Also, people may visit such places for tranquility. Last but not least, economic factor should be considered when building CDQC. If the area has steep slope, there is more cost involved to reduce the steepness before building CDQC.