SMT201 AY2019-20G1 EX2 Seah Si Qi Christel
[[1]]
Contents
Q1. Map View with Study Area and Target Roads, Buildings, Natural Features, Digital Elevations Layer
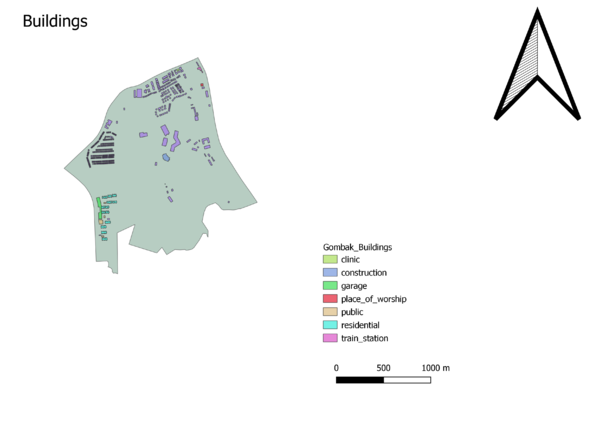
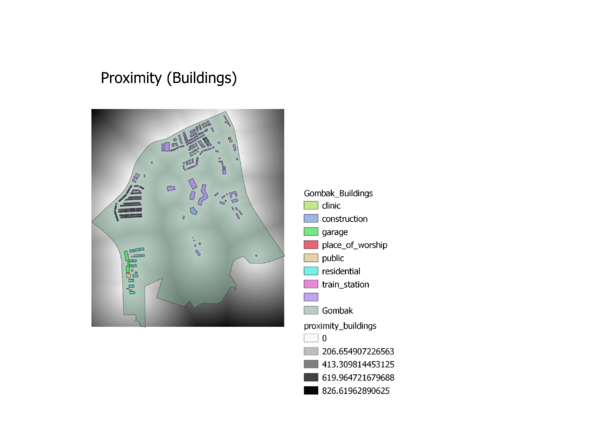
Buildings: If the National Communicable Disease Centre were to be located in Gombak area, it should not be located near the general populace to prevent the risk of diseases being transmitted. Disease Centres which serves as quarantine sites, as far as possible should be located away from the general populace
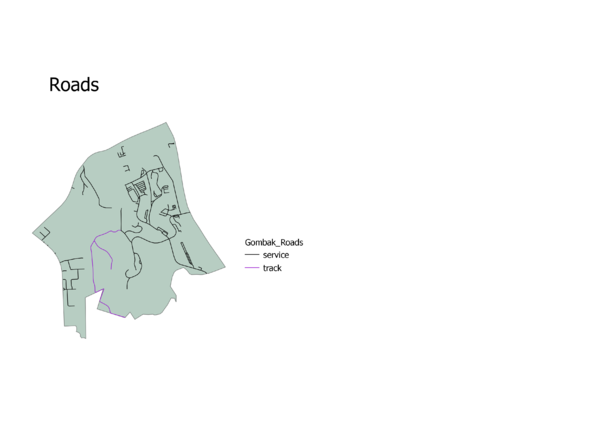
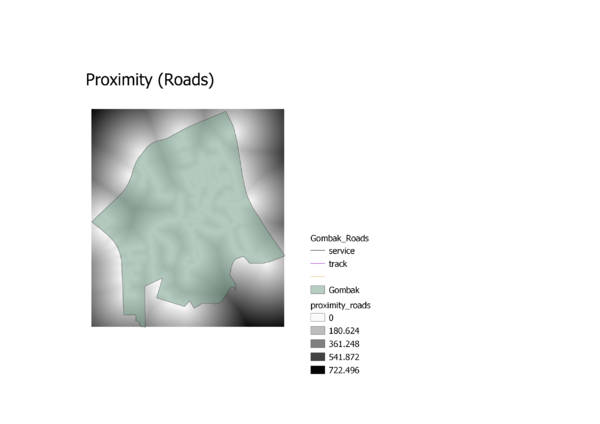
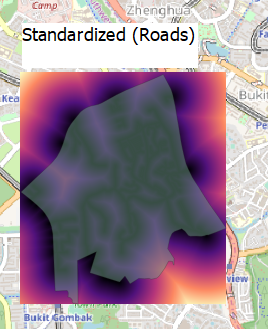
Target Roads:To build the National Communicable Disease Centre, it should be located on the Eastern side of Gombak planning area where there is a higher density of service and track roads. The benefit of being located to road networks is that it allows for the easier transportation of building materials during the construction stage, making the construction process more efficient and effectively savings costs
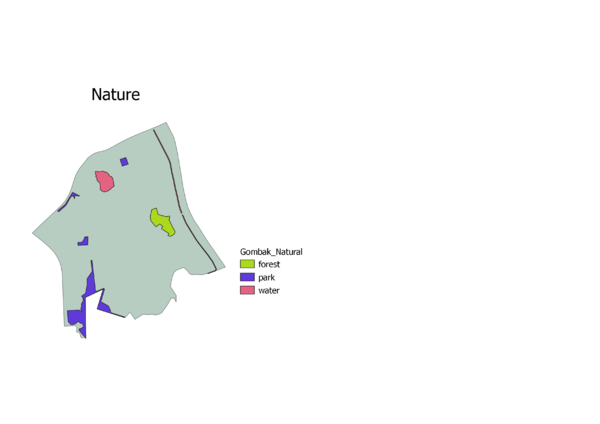
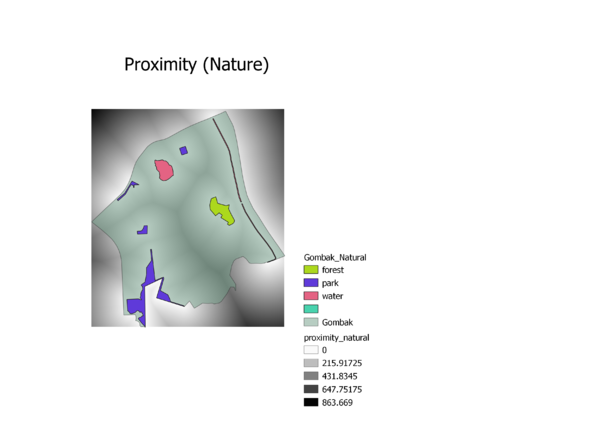
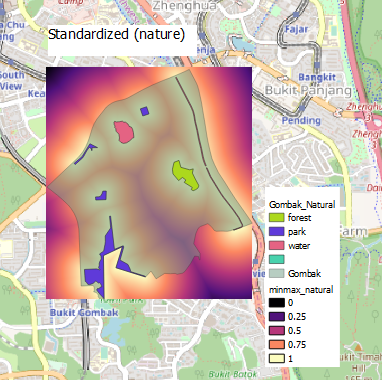
Natural Conservation: The National Communicable Disease Centre should be located away from natural conservation sites to reduce the likelihood of diseases entering the water bodies of Singapore. Furthermore, these nature spots are where many Singaporeans engage in recreational activities, increasing the risk of diseases being transmitted.
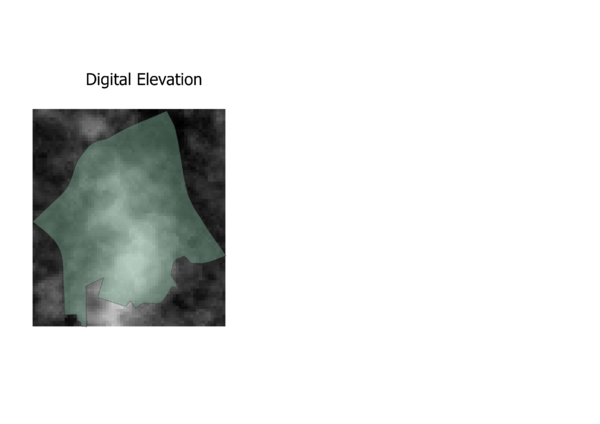
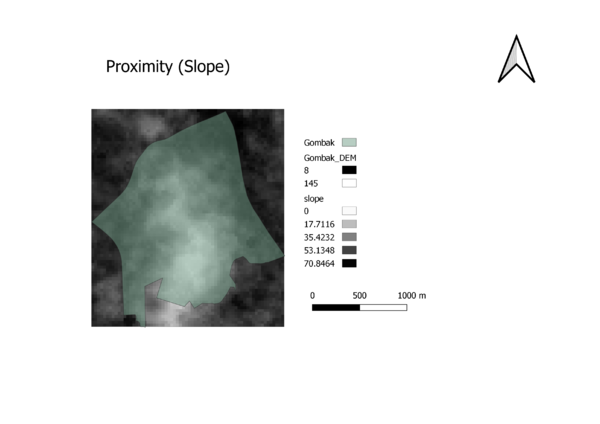
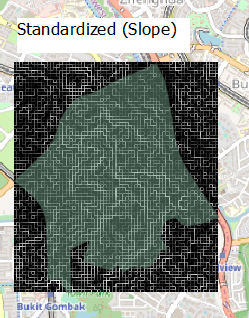
Digital Elevation: Steepness of slope is determined by the closeness of the contour lines. The South Central area is where the contour lines are most dense. The National Communicable Disease Centre should not be constructed on such a terrain as construction costs too would be steeper because of the additional considerations to work around construction on a slope.
Q2. Study Areas and its Features Proximity
Target Roads Proximity: The furthest distance within the Gombak study area to a road is 722.496m and the closest distance is 0m.
Buildings Proximity: The furthest distance from any point to a building within the Gombak study area is 826.619628m whereas the closest distance to a building is 0m.
Natural Conservation Proximity: The furthest distance within the Gombak study area to natural features is 863.6694946m and the closest distance is 0m.
Slope Layer Proximity: The minimum and maximum of slope features within Gombak is 0 and 36.4307708 degrees respectively.
Data Preparation : A raster analysis is used to calculate the proximity of the features. During the process of importing the layer in GIS, we need to do a raster analysis.
Q3. Criterion Scores Standardization
Making sense of the data obtained: It is better to have a higher score obtained. To better compare the scores between different factors of different scales (meters vs degree). I made use of the Min-Max Method to standardize the results. The formula for standardization is (X-Min)/Range
Criterion Score for Target Roads: (X – 0) / (722.49566650391 – 0) To determine accessibility, the area closer to the local roads should have a higher score attached to it
Criterion Score for Buildings: (X – 0) / (826.619628 – 0) To determine health risk, the higher the value, the more suitable it would be to build the National Communicable Diseases Centre as it means that the location is further away from the building.
Criterion Score for Natural Conservation: (X – 0) / (863.6694946 – 0) To determine natural conservation, a higher score means that the area is further away from natural spaces, reducing the risk of communicable diseases entering the nearby water bodies
Criterion Score for Slope Layer: (X – 0) / (36.4307708 – 0) Taking into consideration the economic aspect, a lower score would mean that the area is more suitable to build the centre as the slope is less steep, reducing construction costs due to the need for the cut and fill process on a steep slope
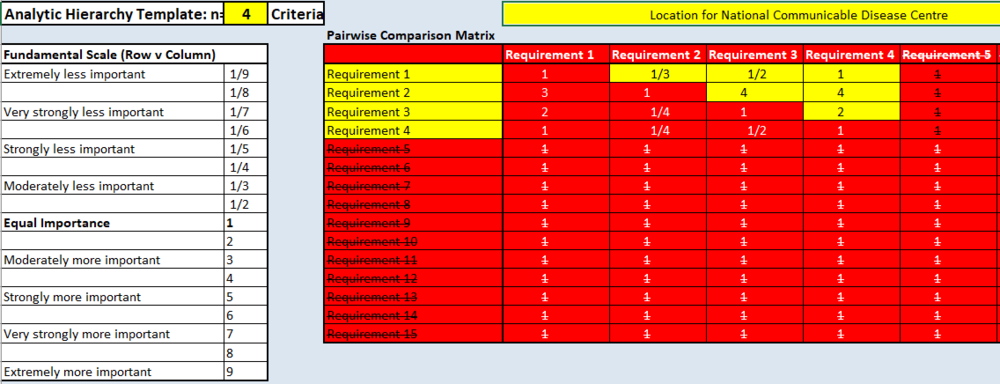
Q4. Analytical Hierarchal Process
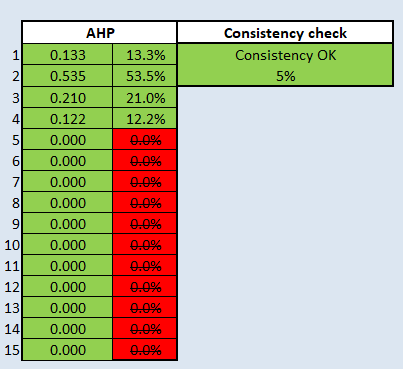
Making sense of the above results (relative importance of criteria) Requirement 1: Accessibility Requirement 2: Health Risk Requirement 3: Natural Conservation Requirement 4: Economic
From the above results, health risks is deemed as the most critical factor as it has the highest AHP Score of 0.535. In such a small and densely populated country like Singapore the extent and consequences of a spread of infectious disease would be disastrous on a national level. In order to ensure stability and the safety of Singaporeans, health risk is the most important consideration in determining the suitable location for the communicable disease centre.
On the other hand, the economic factor is the least weighted factor in determining a suitable location for the communicable disease centre. Not saying that this factor is not important, but rather is given less importance as compared to the rest of the other factors. Consistency check is below 10%
Q5. Map layout with Suitability Land Lots
The raster calculator was used to add up all the factors, taking into consideration each AHP weight. After which the demarcated land area in the map is then identified as the most suitable plot of land to build the new quarantine centre.