SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Fernanda Tan Qian Xuan
Contents
Land Suitability Analysis to build a national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre
To identify a suitable location for the construction of a national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre, there are several criteria to be satisfied. The four concerning factors are as such:
- Economic factor: The selected site cannot be on a steep slope to prevent additional construction costs.
- Accessibility factor: The selected site should be close to service roads and tracks.
- Health risk factor: The selected site should be away from the general populace.
- Natural conservation factor: The selected site should be away from forested land, park and water.
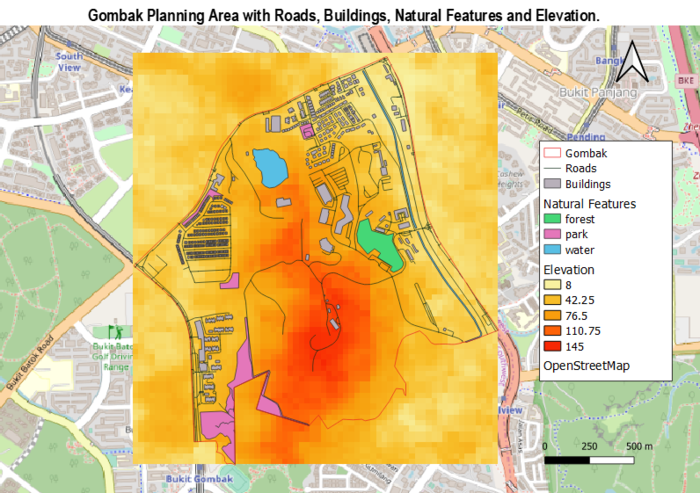
The following map shows the Gombak Planning Area and the factors to be taken into consideration:
Study Area: Gombak Planning Area
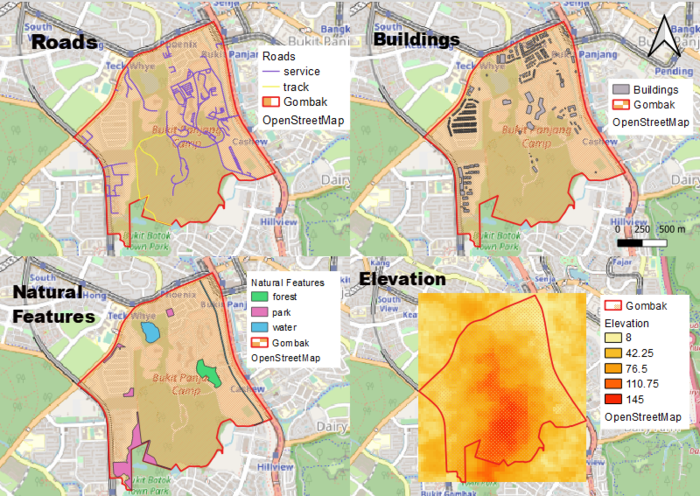
View 1 shows the Road Network in Bukit Gombak. For the purpose of the land suitability analysis, we will focus on tracks and service roads which are shown in yellow and purple respectively. View 2 shows the Buildings in Bukit Gombak. View 3 shows the Natural features, which consist of forest (green), parks (pink) and water features (blue). View 4 shows the elevation in Bukit Gombak, where darker areas are of higher grounds and lighter areas are low-lying areas.
Proximity Analysis
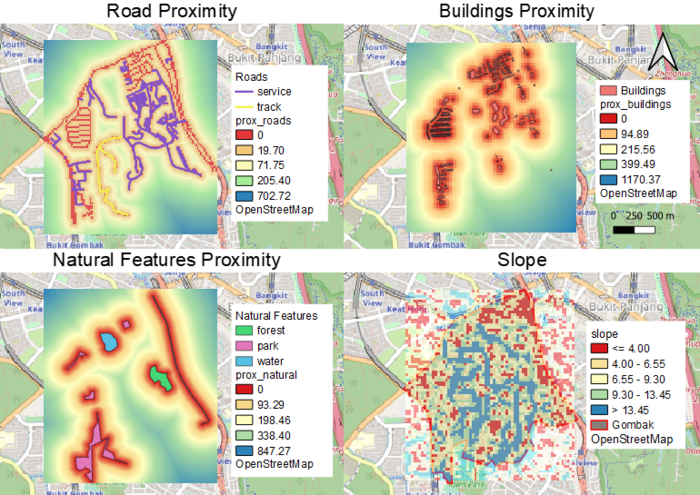
View 1: Road Proximity
Proximity analysis of the road network in Bukit Gombak, ranging from a distance of 0 to 702.72 meters. 0 meters, indicated in red, refers to the road itself. As the distance from the road increases, the color spectrum changes from orange to blue, with blue representing areas furthest from the road network and hence the least accessible.
View 2: Buildings Proximity
Proximity analysis of buildings in Bukit Gombak, ranging from a distance of 0 to 1170.37 meters. Areas indicated in red are in closest proximity to the buildings while areas indicated in blue are furthest from the buildings.
View 3: Natural Features Proximity
Proximity analysis of natural features including forest, parks and water features in Bukit Gombak, ranging from a distance of 0 to 847.27 meters. Areas indicated in red are nearest to the natural features while areas indicated in blue are the furthest away.
View 4: Slope
Slope map which indicates the level of elevation at different parts of Bukit Gombak. Areas indicated in red are low lying areas below 4.00 meters elevation while areas indicated in blue are of higher grounds of more than 13.45 meters.
Criterion scoring
To standardize the proximity analysis results, I used the following formula:
Standardised Results = [Proximity to Features - Min(Proximity to Features)] / [Max(Proximity to Features) - Min(Proximity to Features)]
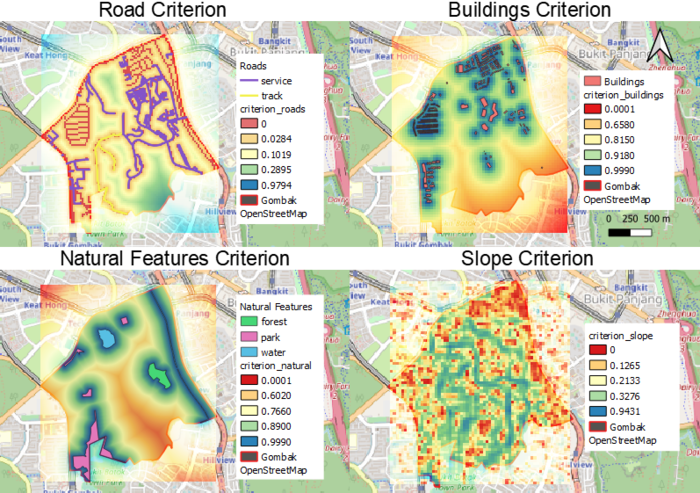
View 1: Road Criterion
The Road Criterion map shows the criterion scoring of the road network in Bukit Gombak. Red and orange areas are nearest to the roads hence the centre should be built around there to allow be better accessibility and transportation of materials.
View 2: Buildings Criterion
The Buildings Criterion map shows the criterion scoring of buildings in Bukit Gombak, which is calculated using '1 - Proximity Analysis Results of Buildings'. Since the centre should be built away from the population to prevent the spread of disease, areas in red which are the furthest from housing estates and office buildings will be suitable locations to place the centre.
View 3: Natural Features Criterion
The Natural Features Criterion map shows the criterion scoring of natural features (forest, parks, water features) in Bukit Gombak, which is calculated using '1 - Proximity Analysis Results of Natural Features'. Red areas are furthest away from these natural features, hence the centre should be built in one of these areas to prevent contamination.
View 4: Slope Criterion
The Slope Criterion map shows the criterion scoring of elevation levels in Bukit Gombak. Red areas are low-lying areas where there are less steep slopes, hence the centre should be built in these areas to reduce development cost.
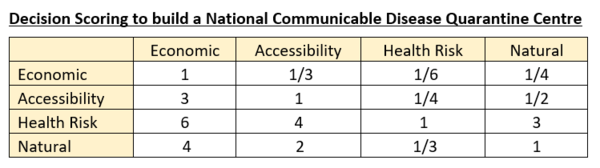
Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP)
The four decision factors were ranked in terms of importance, with the most important criteria being 'Health Risk', followed by 'Accessibility', then 'Economic' and the least important criteria being 'Natural Features'.