SMT201 AY2019-20G2 EX2 Neo Yin Li Amelia
Contents
Part 1: Map Layout with four views
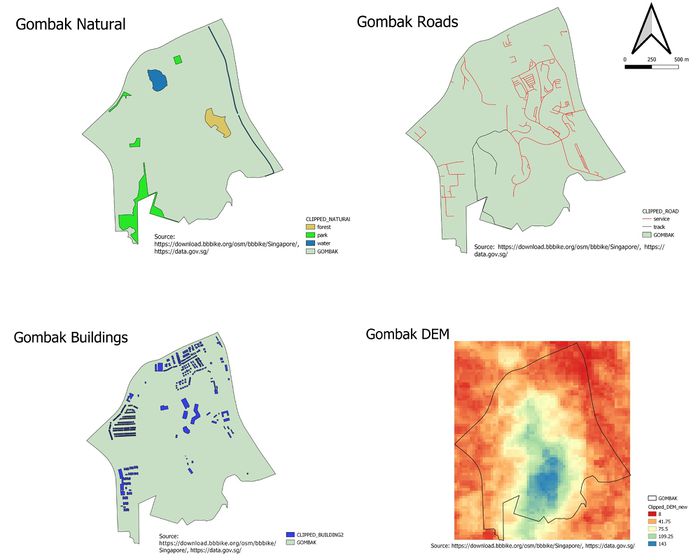
Economic factor
The selected site should avoid steep slopes to reduce the development costs for cut-and-fill construction techniques. The lowest point in Gombak is 8 meters above sea level, depicted in red. The Southern region of Gombak has the highest elevation with 143 meters above sea level, depicted in blue. Most of the nature features, roads and buildings are located on lower level land.
Accessibility factor
The target road consists of service road and track, in which the service road is represented by red lines and track is represented by black line. We can see that there is more service road than track road in Gombak region. The selected site should be close to these roads to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage. The service roads spread across most of the Gombak planning subzone, and are mostly concentrated in the North-East region, whereas the 2 tracks are located at the South and central region of Gombak
Health risk factor
In Gombak, there are clinic, construction site, garage, place of worship, public, residential and train station infrastructures. However, many buildings are not categorised into any of these types. Hence, categorisation of the buildings based on types do not occur as the buildings that do not have any “type” will not show up on the map if the “unknown” category is removed from the categorisation. Also, there is no point doing so. All buildings help to identify the health risk factor, in which the selected site should be away from the buildings to prevent the diseases from spreading to the general population.
Natural conservation factor
In Gombak, there is a large area of park and small section of forest and water body. The selected site should be also be away from these natural features. The large area of park is near the left region of Gombak. The northern region contains the water body and the western region contain the forest. The forest is depicted with beige colour on the map, while the parks and the water bodies are depicted using neon green and blue respectively.
Part 2: Map Layout with four views (Proximity)
Economic factor
The slope layer shows a range of values from 0 to 36 degrees, where black represent 0 and white represent the highest value of 36 degrees. From the map, most of the central region is relatively steep due to the higher amount of white areas.
Accessibility factor
The proximity layer for road shows a range of values from 0 to 722 metres, where black represent 0 and white represent the highest value of 722 metres. From the map, most of the central region is relatively near the roads, specifically service road and track, which is to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage.
Health risk factor
The proximity layer for building shows a range of values from 0 to 827 metres, where black represent 0 and white represent the highest value of 827 metres. From the map, most of the northern and western region is relatively near the buildings i.e. housing areas and offices which means these regions are near the general population.
Natural conservation factor
The proximity layer for natural shows a range of values from 0 to 864 metres, where black represent 0 and white represent the highest value of 864 metres. From the map, most of the south-western, north-western and east regions are relatively near the nature features, specifically forested land, park and water.
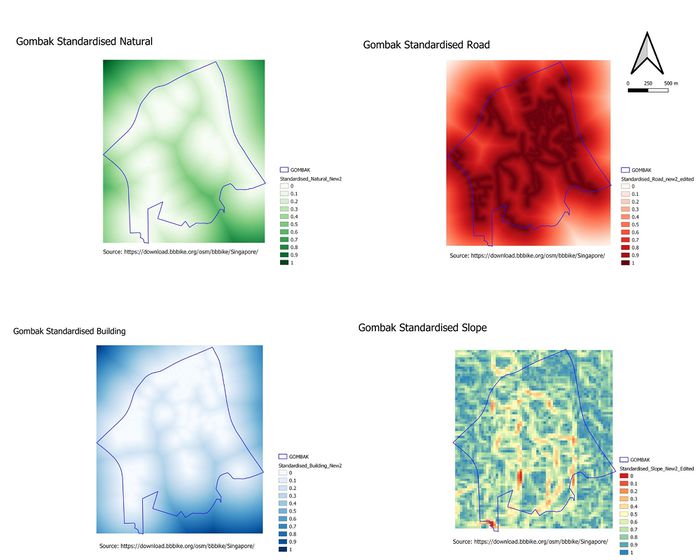
Part 3: May Layout with four views (Criterion Scores)
For all factors, the values are standardised using min-max method such that the min of the standardised value is 0 and max is 1. They are categorised into 11 classes: 0, 0.1, 0.2, … , 1.0. The views look similar to the proximity views. However, there is a slight difference such that higher values for 'buildings' and 'natural' layers were better, whereas lower values for 'roads' and 'slope' layers were better. Thus, for 'roads' and 'slope' layers, further modification was done to the values by taking “1 – standardised_road_new2 / standardised_slope_new2”, to rectify this problem, such that the values will be properly standardised.
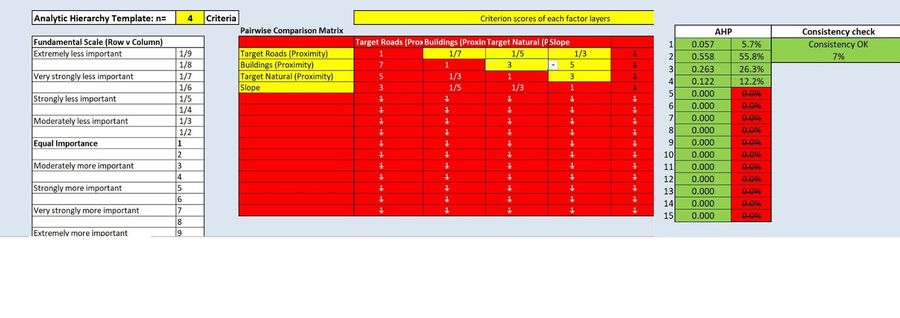
Part 4: Analytical Hierarchical Process
Accessibility factor has the lowest weightage of 0.057 as it is the least important factor due to its short-term importance for construction period. Health risk factor has the highest weightage of 0.558 as it is the most important factor due to the purpose of the quarantine centre which is to prevent spread of diseases to population. Thus, distance from buildings is important for this purpose. Natural conservation factor is the second most important factor with weightage of 0.263 as animals may be infected by disease and spread to the public if these nature features are too near to the centre. Lastly, economic factor has a weightage of 0.122. It is more important than accessibility as the centre will be on the ground for long-term and will affect construction cost too with less importance than the other two factors. The consistency level is 7% which makes the model suitable.
Part 5: Map Layout (Suitability)
Economic factor:
Accessibility factor:
Health risk factor:
Natural conservation factor: