SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Lee Wan Ning
Part 1: Input Layers
Deliverables
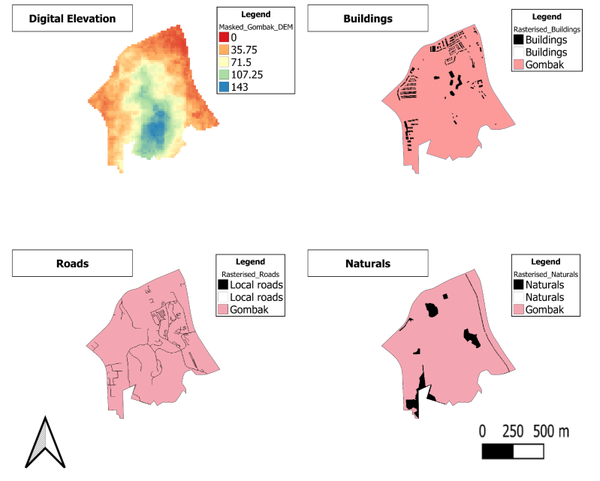
• A map layout with four views showing:
• the study area and the target roads,
• the study area and buildings,
• the study area and the target natural features,
• the study area and digital elevation, and
a short description of not more than 100 words for each view.
The digital elevation layer is in raster format, whereas the other layers are in vector format.
After importing all the data layers, i have subsequently used the "Clip" function under vector->geoprocessing tools to extract only the area of study, Gombak planning subzone for the vector layers. For the raster layer, i used "Clip Raster By Extent" under raster->extraction.
For the purpose of the analysis later on, i have rasterised all the vector layers.
Furthermore, i have categorised the digital elevation layer according to range of the elevation values(in metres) in the Gombak planning subzone.
For example, yellow shaded areaa on the digital elevation layer would mean that the land there is 71.5m above sea level.
Part 2: Analysed Layers
Deliverables
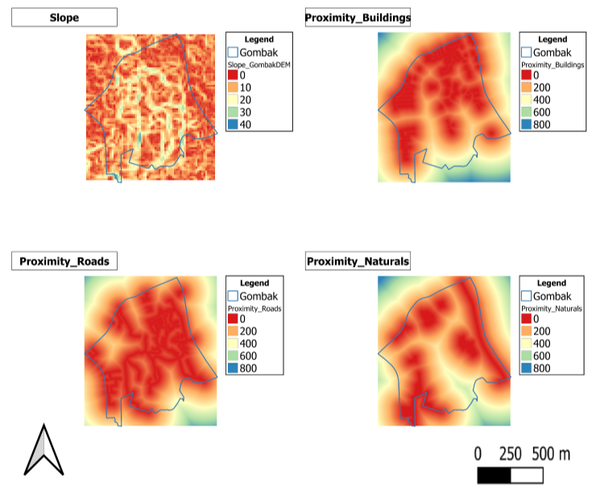
• A map layout with four views showing:
• the study area and proximity to target roads layer,
• the study area and proximity to buildings layer,
• the study area and proximity to target natural features layer,
• the study area and slope layer, and
• a short description of not more than 150 words for each view.
I have performed slope analysis on the digital elevation layer and proximity analysis on the rasterised buildings, roads and naturals layers.
I have also classified the resulting proximity layers according to the range of raster distances(in m) using a common scale.
Using "proximity_buildings" layer as an example, the higher the value in the legend, the greater the raster distance away from the sshaded area is from buildings.
The "slope" layer is classified according to the range of the slope(in degrees).Using "slope" layer as an example, the higher the value in the legend, the higher the value in the legend, the steeper the the land is around the shaded area