SMT201 AY2019-20G1 Ex2 Lim Shen Jie
Contents
Part 1: Standard view of study areas
Description
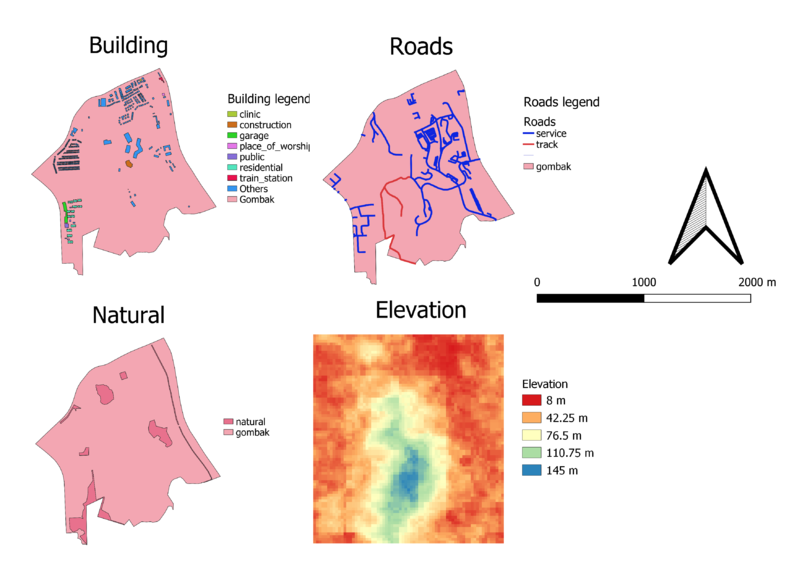
The cartographic technique used to categorize the schools by their main_level was hue. That is because the main_level attribute is a nominal data. Point symbols are the best for schools because it would be able to pinpoint their exact location.
Part 2: Raster view of the study areas
Description
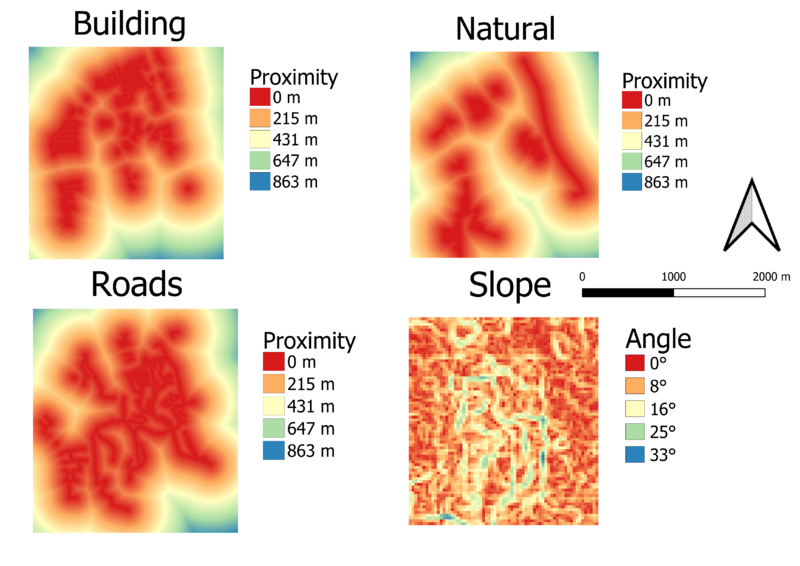
As the roads were not categorized by their road type, a calculated field was needed to generate the road type for the roads based on the name of the road. The cartographic technique used to categorize the roads by the RD_DESC was hue. That is because the RD_DESC data is nominal. To represent the roads on the map, lines are the best way to pinpoint the exact location of the roads.
Part 3: Raster view showing the criterion scores of the study areas
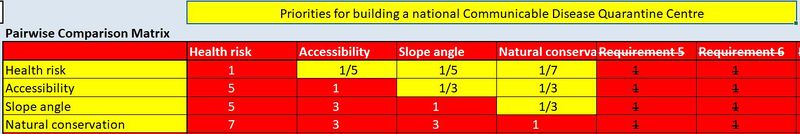
Part 4: AHP tables
Description
The number of people that were older than 65 years increased from 2010 to 2018
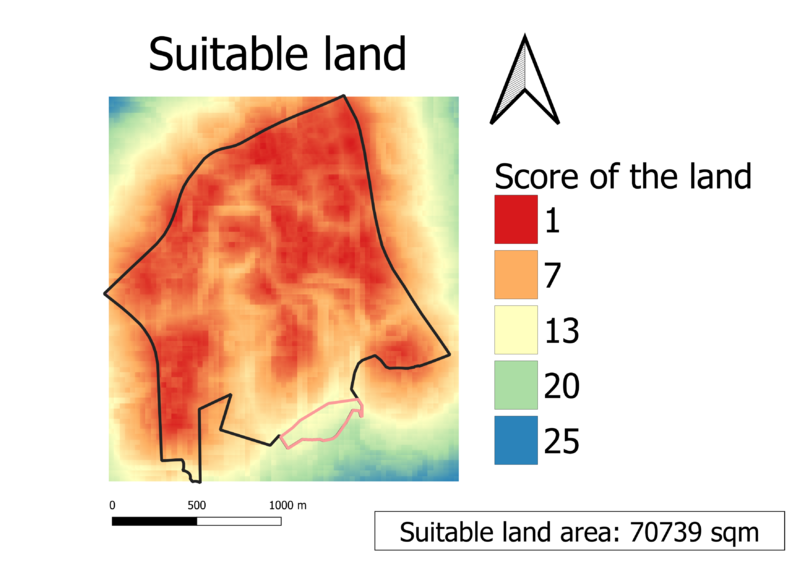
Part 5: Suitable land
Discussion
Sources
1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone (No Sea) 2. BBBike@Singapore 3. ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) dataset