SMT201 AY2019-20G2 Ex1 Soh Bai He
Contents
Part One: Thematic Mapping
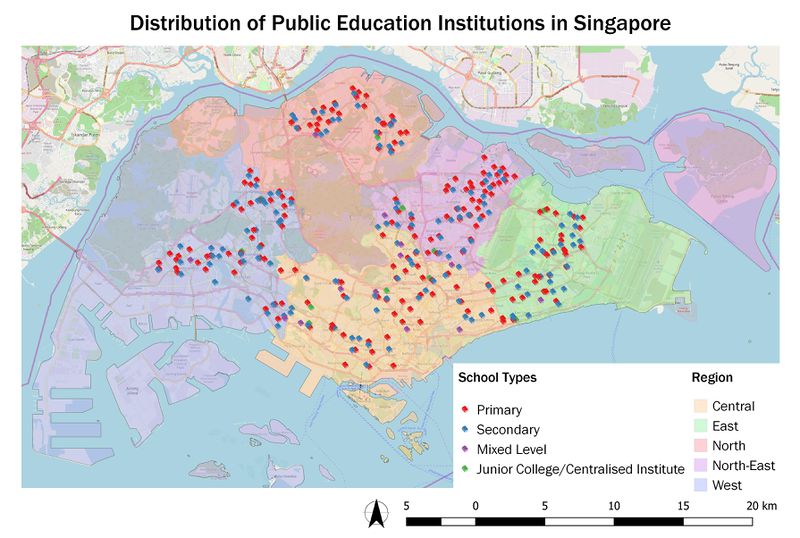
Public Education Institutions
Handling of Data: general-information-of-schools.csv is geocoded into school_information.shp
Choice of Classification:
1) Categorisation by school type. Junior College and Centralised Institute are grouped together as both offers pre-university courses and lead to the ‘A’ Level examinations.
2) Categorisation by region to facilitate easier visualisation of the distribution of schools by region.
Visual Variable: An SVG marker of a book is used as the symbol. Different colours are used for each school type/region for easier identification.
Feature count: Total (344), Primary (181), Secondary (138), Mixed Level (14), Junior College/Centralised Institute (11)
Observation: Of all school types, Junior College/Centralised Institute has the least number. However, the existing ones are well distributed across Singapore with every region covered.
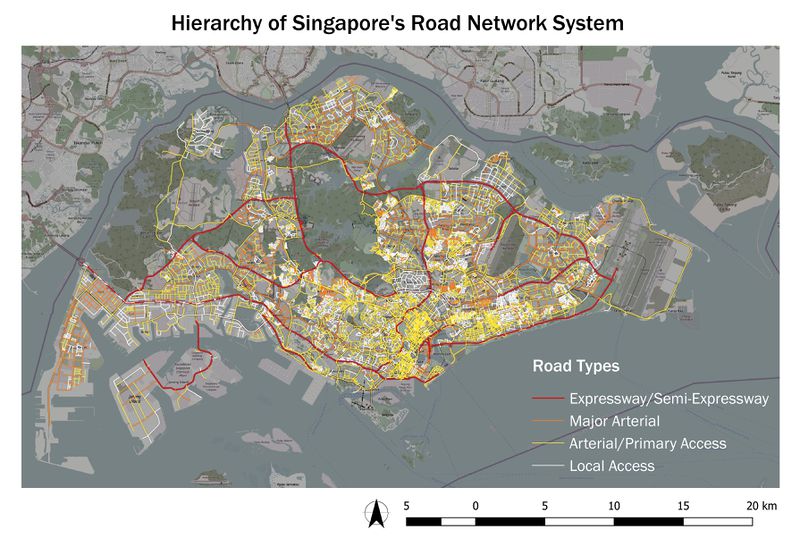
Road Network System
Handling of Data & Choice of Classification: RoadSectionLine.shp is exported into .csv format and new columns RD_CAT_NO, RD_MAIN_CAT are added on excel (road-section-category-sorted.csv). Roads are then categorised with reference to URA’s Handbook on Guidelines for Naming of Streets (p.13, Annex 1). Thereafter, I analysed the remaining roads (that do not include the street name descriptors in the table below) on the OpenStreetMap and grouped them into Arterial/Primary Access as they are minor roads that provide access to developments.
| Road Category | Street Name Descriptor |
|---|---|
| Expressway and Semi-Expressway (Cat 1) | Expressway, Highway, Parkway |
| Major Arterial (Cat 2) | Boulevard, Avenue, Way |
| Arterial & Primary Access (Cat 3 & 4) | Drive, Street, Road |
| Local Access Roads (Cat 5) | Walk, Lane, Link |
Visual Variable: Line symbols with different colours are used to represent each road type. A warm colour scheme (red > orange > yellow > white) is chosen to highlight the hierarchy of road types. Expressway is given the thickest width as they form the primary network in the road system.
2014 Master Plan Landuse
Choice of Classification: Categorisation by type of land use. To minimise the number of categories and colours that might overwhelm the user, several sub categories of the same type of development are grouped into a main category.
Visual Variable: Colour fill as the respective type of land use. I referenced URA’s Past Concept Plan colours for each development. Planning areas are labelled to aid in the visualisation of the distribution of land use in Singapore.
Observation: The West region is dominated by industrial developments along with the Western Water Catchment. There are fewer residential areas in the West, however, a new HDB town called Tengah will be built.