SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX1 Lee Jayin
Part One: Thematic Mapping
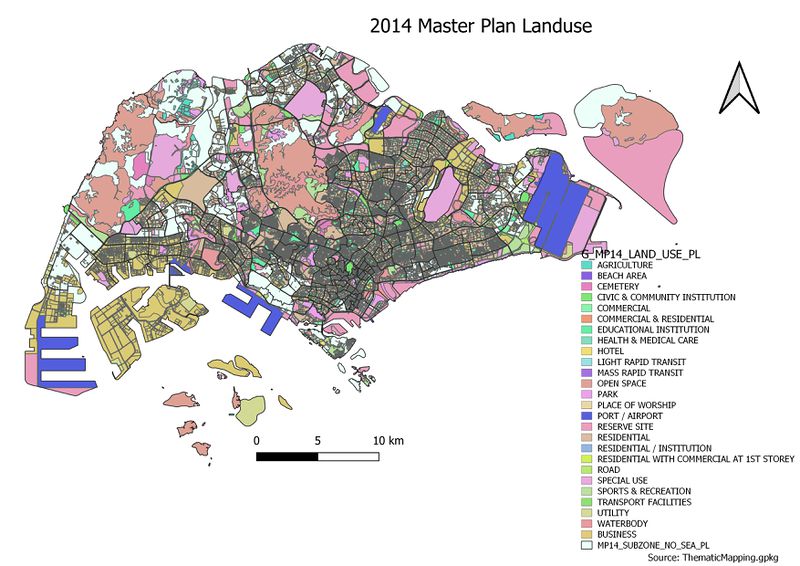
2014 Master Plan Landuse
Upon classifying the data using categorized symbology method (as the data was discrete), there were 20 over categories. Classes should be optimally kept under 6, thus I chose to group them into 5 categories under residential, utilities, recreational, business areas and others. The categories are grouped this way as these are the main categories needed in a city. Different colours are used to differentiate the different categories clearly.
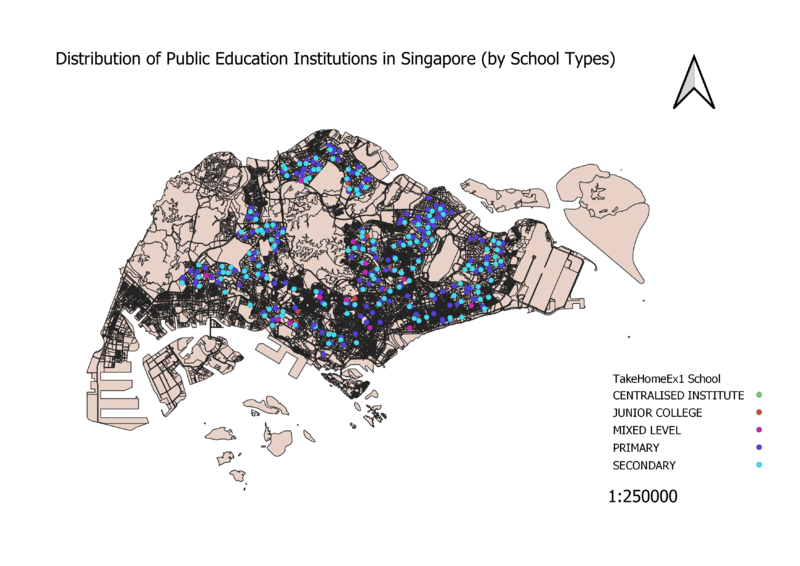
Level of Schools
As data of educational institutes in Singapore are discrete, the categorized symbology method was used. When classified, this allows for 5 clear-cut categories of educational institutes to be seen. Different colours were used to differentiate the different categories more clearly. Also, as only ZIP codes were provided in the dataset, python had to be used to geocode the institutes data onto the GIS.
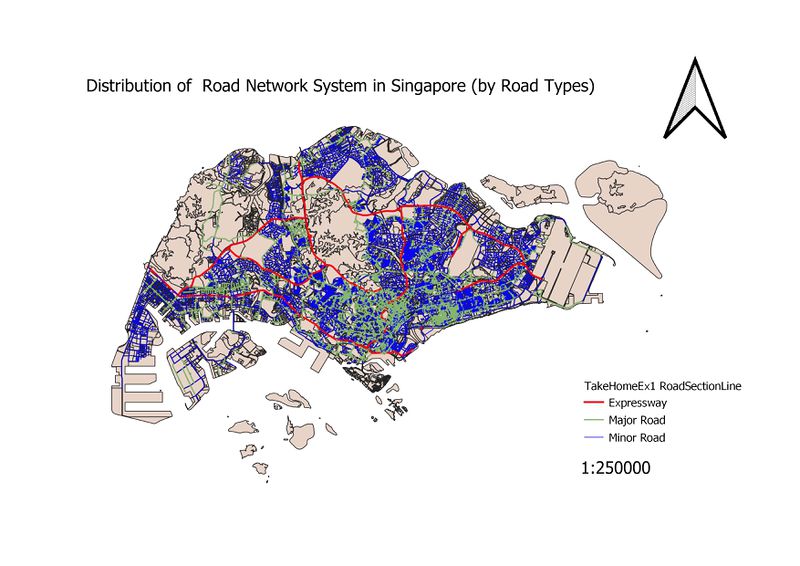
Road Network System
When classified, 3 road categories were produced – the expressway, major roads and minor roads. Different colours and widths were used for each category. Red for expressway as red is a sign of urgency, and the width is 3x the size of minor roads. This is to clearly indicate the more “crucial” roads. Major roads are set to be 2x the size of minor roads.
Part Two: Choropleth Mapping
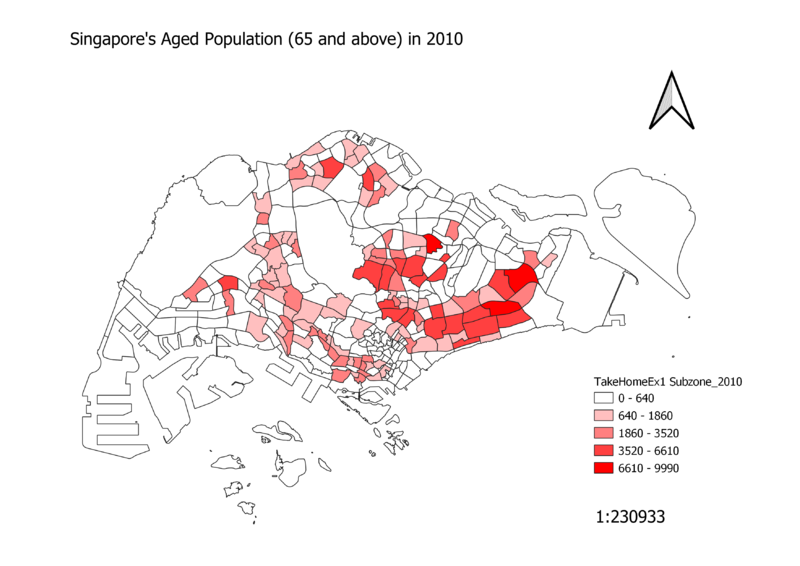
Singapore's Aged Population (65 and above) in 2010
Singapore's Aged Population (65 and above) in 2018
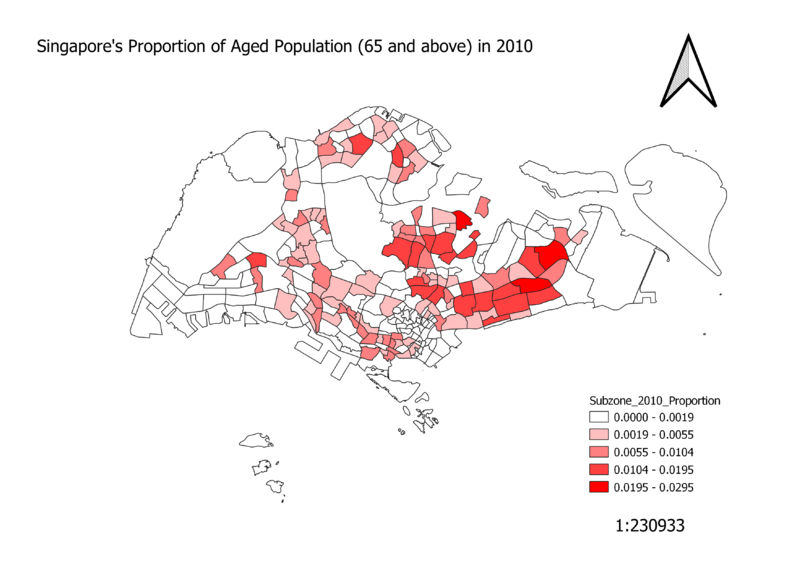
Singapore's Proportion of Aged Population (65 and above) in 2010
Singapore's Proportion of Aged Population (65 and above) in 2018