SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Goh Jia Xin Genice
Contents
- 1 Overview of Task
- 2 Maps depicting the roads, buildings, natural areas and digital elevation in Gombak
- 3 Maps depicting the proximity to roads, buildings, natural areas and digital elevation in Gombak
- 4 Maps depicting criterion scores of proximity maps and slope in Gombak
- 5 Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) input matrix and result report
- 6 Land Suitability Map
Overview of Task
We are intending to identify a suitable location site to build a national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre within Gombak planning subzone. The location site should have a contiguous area of at least 10,000m2 and it must meet the following decisional factors:
- Accessibility Factor- Selected site should be close to local roads such as service roads and tracks
- Health-risk Factor- Selected site should be away from the population
- Natural Conservation Factor- Selected site should be away from natural areas
- Economic Factor- Selected site should avoid steep slope
More findings will be shared below.
Maps depicting the roads, buildings, natural areas and digital elevation in Gombak
The following maps show the roads (accessibility factor), buildings (health-risk factor), natural areas (natural conservation factor) and digital elevation (economic factor) in Gombak.
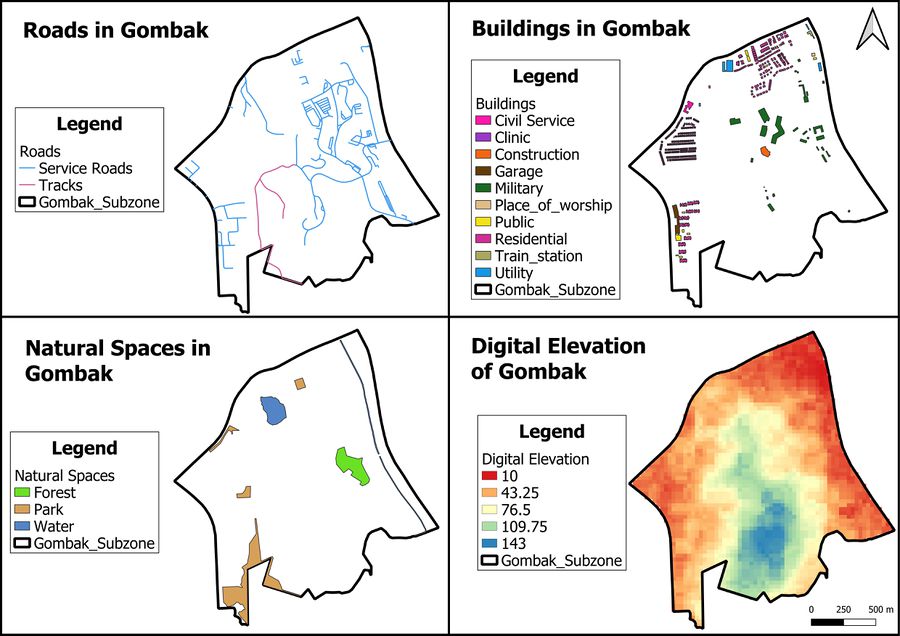
Accessibility Factor (Roads)
The selected site should be close to existing local roads such as service roads and tracks, so as to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage. The service roads and tracks are labelled blue and pink on the map respectively. We can see that service roads are more extensive than tracks in Gombak planning subzone, because the northeastern part of Gombak has many service roads while there is only one stretch of tracks in the central part of Gombak.
Health-risk Factor (Buildings)
The selected site should be away from the population, such as residential areas and offices. This is to prevent the spreading of diseases to the nearby population. The majority of buildings in Gombak are residential buildings. The residential areas are mainly concentrated in the northern, western and southwestern parts of Gombak, while military landuse is concentrated in central Gombak.
Natural Conservation Factor (Natural Areas)
The selected site should be away from forested lands, parks and water. This serves to reduce the harm caused towards the wildlife and natural environment as a result of the construction of the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre. The forest, park and waterbody are labelled in green, brown and blue on the map respectively. They are generally spread out in Gombak, covering the eastern, northwestern and southern parts of the planning subzone.
Economic Factor (Slope)
The selected site should avoid steep slopes because the construction at steep slopes tends involve a lot of cut-and-fill and will lead to higher development costs. The smallest digital elevation value is 10m and is labelled in red, while the largest digital elevation value is 143m and is labelled in blue on the map.
Maps depicting the proximity to roads, buildings, natural areas and digital elevation in Gombak
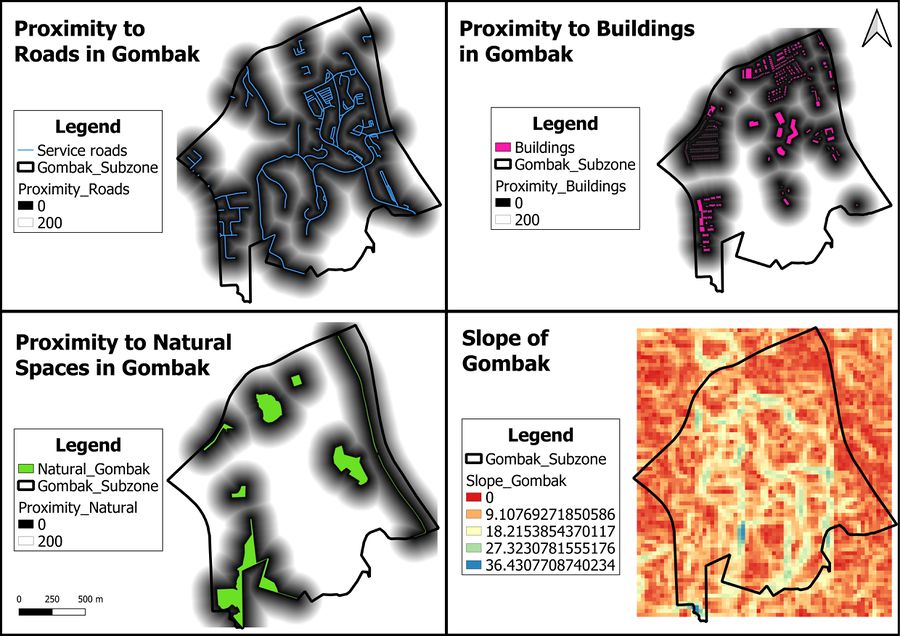
The proximity maps to roads, buildings and natural spaces in Gombak are standardised to show only the proximity range of 0 to 200m. This is to ensure that the three proximity maps can be uniformly compared against each other to gain insights on suitable location sites to build the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre.
Proximity to Roads
The darker spots on the map represent areas which are suitable for the building of the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre in terms of accessibility. The distance from a 5m by 5m land area to the nearest road is 0m while the furthest distance is 722.496m.
Proximity to Buildings
The lighter spots on the map represent areas which are suitable location sites for the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre in terms of health-risk. The distance from a 5m by 5m land area to the nearest building is 0m while the furthest distance is 826.62m.
Proximity to Natural Spaces
The lighter spots on the map represent areas which are suitable location sites for the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre in terms of natural conservation. The distance from a 5m by 5m land area to the nearest natural space is 0m while the furthest distance is 863.669m.
Slope in Gombak
The red areas on the map represent areas which are suitable location sites for the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre in terms of economic reasons. The smallest degree of slope in Gombak is 0 degrees, while the largest degree of slope is 36.431 degrees.
Maps depicting criterion scores of proximity maps and slope in Gombak
To create the criterion score maps, we have to inverse the raster pixel values for the proximity maps to buildings and natural spaces. This is because for maps depicting the slope in Gombak and proximity to roads, location sites are seen to be suitable if they have little slope and are close to roads. On the other hand, for maps depicting the proximity to buildings and natural spaces, location sites are seen to be suitable if they are further away from buildings and natural spaces.
| Factors | Criterion Scores |
|---|---|
Accessibility |
Proximity to Roads
|
Health-risk |
1 - Proximity to Buildings
|
Natural Conservation |
1 - Proximity to Natural Areas
|
Economic |
Slope in Gombak
|
Moreover, we need to standardise the scales across the maps using the min-max formula. This is because the proximity maps to roads, buildings and natural spaces in Gombak have different minimum and maximum values. In addition, the units used in the map depicting the slope in Gombak is in degrees and is different from the other maps which uses metres.
To achieve the steps above, we can use the raster calculator in QGIS. The sample formula is as follows:
(Proximity Map to feature – Minimum Value of Proximity to feature) / (Maximum Value of Proximity to feature - Minimum Value of Proximity to feature)
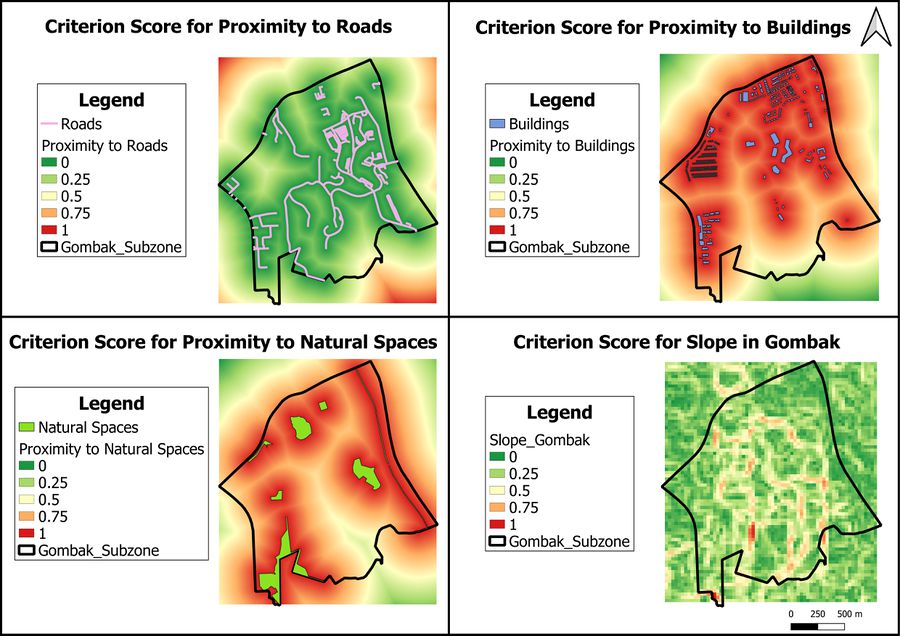
Criterion score for Proximity to Roads
The areas labelled in green are suitable for the building of the Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre because they are close to the roads in Gombak, while the areas in red are unsuitable.
Criterion score for Proximity to Buildings
The areas labelled in red are not favourable to build the Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre in Gombak since they are close to the residential buildings, while those in green are favourable.
Criterion score for Proximity to Natural Spaces
The areas labelled in red are not suitable to build the Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre since they are close to the natural spaces in Gombak, while the areas in green are suitable.
Criterion Score for Slope in Gombak
The areas labelled in green are suitable for the building of the Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre in Gombak because there is little slope, while the areas in red are unsuitable.
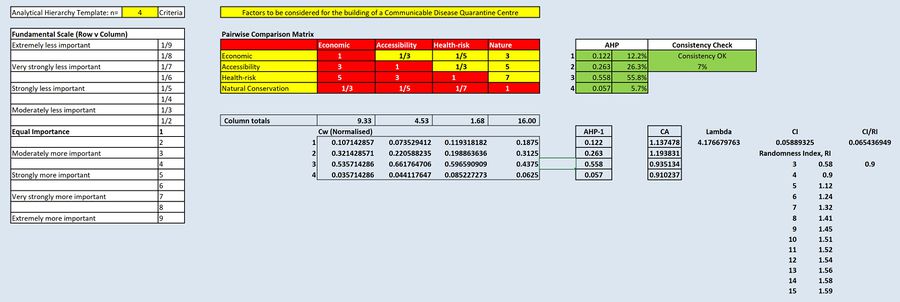
Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) input matrix and result report
The AHP input matrix and result report helps to determine the relative importance of each factor, which are namely health-risk, accessibility, natural conservation and economic. A higher AHP value will imply that the factor has a higher relative importance as compared to the others.
The table presents the rationale of the value of the input for the Pairwise Comparison Matrix, which represents the perceived importance of each factor in comparison to other factors.
| Priority | Factors |
|---|---|
1. |
Health-risk Factor Since the facility to be built is a Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre, it is of utmost importance that the diseases will not spread to the nearby population and cause an epidemic. |
2. |
Accessibility Factor It is also very crucial for the Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre to be accessible the roads, so as to allow easy transportation of patients in and out of the facility. |
3. |
Economic Factor Since the building for the Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre is a national project, it is necessary to ensure that the development cost will not exceed the allocated budget. |
4. |
Natural Conservation Factor Although natural conservation may be meaningful, it is not in our top priorities because the main concerns while choosing the location site should be based on concerns regarding the well-being of the population and economic costs. |
As a result of the AHP input matrix, we are able to obtain the AHP values of the factors as shown below. They act as weights for their respective criterion maps to create the final land suitability map.
| Factors | AHP Value |
|---|---|
Accessibility |
26.3%
|
Health-risk |
55.8%
|
Natural Conservation |
5.7%
|
Economic |
12.2%
|
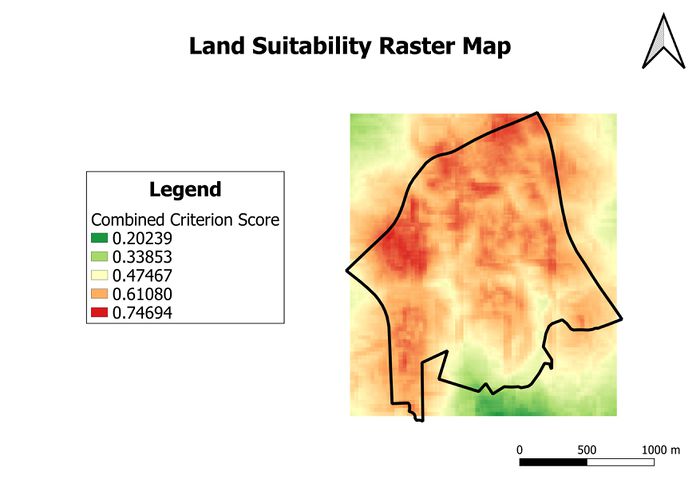
Land Suitability Map
After obtaining the AHP values from the previous section, we can combine the standardised criterion scores of the proximity to roads, buildings and natural areas, and the slope in Gombak into a single land suitability map. We do this using the raster calculator with the formula as shown below:
(“Proximity_Roads_Criterion@1” * 26.3%) +
(“Proximity_Buildings_Criterion@1” * 55.8%) +
(“Proximity_Natural_Criteria@1” * 5.7%) +
(“Slope_Gombak_Criteria@1” * 12.2%)
This produces a raster map will give us insights on the areas which are suitable for building the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre.
Similar to the criterion maps in the previous section, areas with a lower combined criterion score are more suitable for the building of the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre. This implies that areas coloured in green and yellow are suitable location sites.
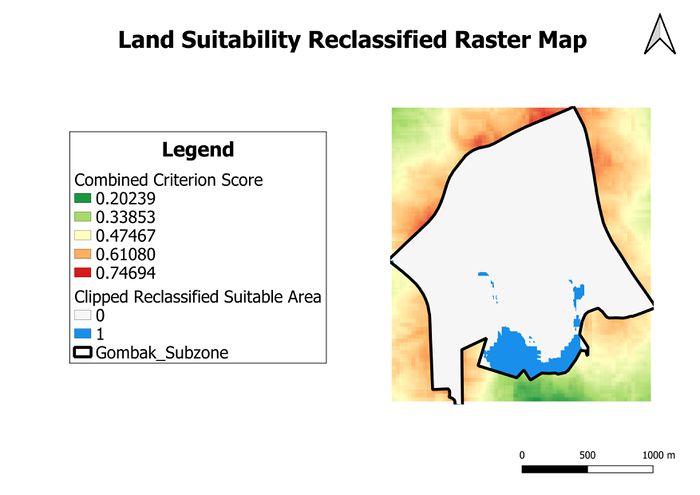
In order to obtain the suitable areas, we will have to reclassify the pixel values using the Reclassify by Table function in QGIS. In this case, I assigned areas with a combined criteria score ranging from 0 to 0.47467 (inclusive) to a value of 1 (suitable), while areas with a combined criterion score above 0.47467 are given a value of 0 (unsuitable).
The resulting reclassified raster map is also clipped to the map of Gombak planning subzone using the Clipped Raster by Masked Layer function. This is to provide easy visualisation of the suitable areas for building the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre in Gombak planning subzone.
This map shows us that the suitable location site is situated in the southern part of the Gombak planning subzone. To check if the suitable location site is more than 10,000 m2, we will have to transform the raster map into a vector map. We can do this by using the Polygonise (raster to vector) function in QGIS.
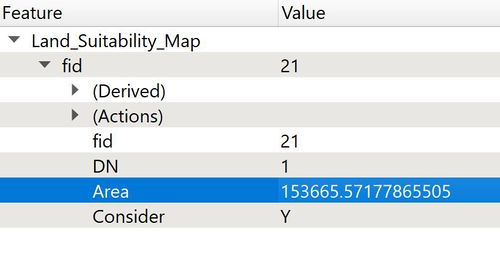
After obtaining the vector map, we will have to create a new field to calculate the area of the suitable location site. We are able to do this using the area$ function to calculate the derived area of the polygon.
This map depicts the land suitability vector map with buildings, roads, natural spaces and slope in Gombak included. Since the area of the polygon is 153665.57178 m2 and is larger than 10,000 m2, it is therefore suitable for the building of the national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre.