SMT201 AY2018-19T1 EX2 Wang Zhuo Wei
Contents
Assignment Objective
This assignment aims to identify a location suitable for building a national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre. The selected site should be located in Gombak planning subzone with a area of at least 10,000 square meters. Additionally, the site selection must fulfill the following decision factors:
Factors to Consider
Economic factor: The selected site should avoid steep slope.
Accessibility factor: The selected site should be close to existing local roads, such as service roads and tracks
Health risk factor: The selected site should be away from current buildings
Natural conservation factor: The selected site should be away from forested land, park and water.
Data Collection
Data used for this assignment are gathered from the following sources:
1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [1]
2. Roads(SHP) from osm[2].
3. Buildings(SHP) from osm [3].
4. Natural(SHP) from osm [4].
5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA[5].
Decision Analysis
Decision Factor 1: Economic factor (Slope)
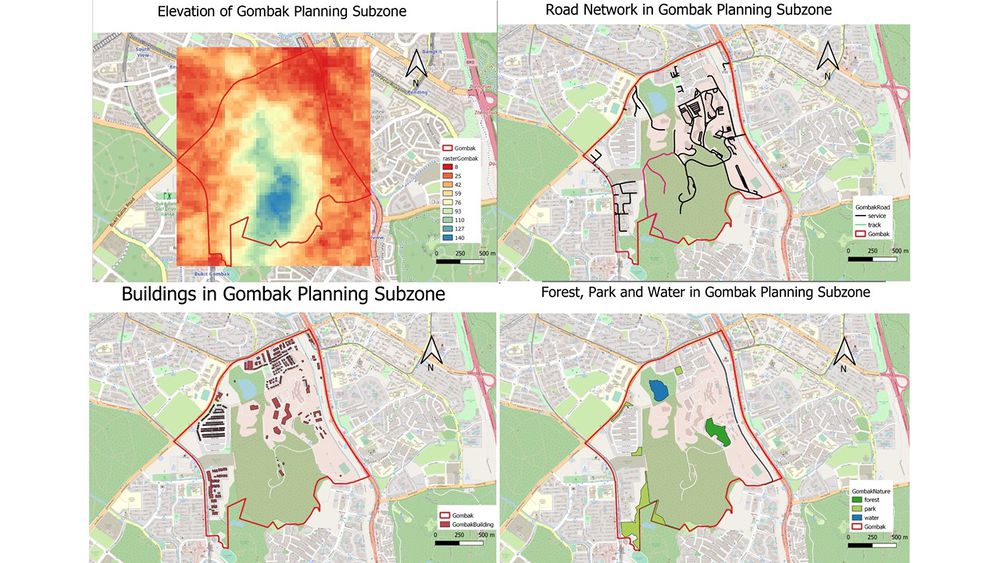
The Economic factor is that the slope should not be too steep so that it is easier to access. In general, the lowest point in Gombak is 8m above sea level, highlighted in red, and the highest point is 145m above sea level, highlighted in blue. From the elevation map, it is obvious that near the border of Gombak, the elevation value is lower. At the centre of Gombak area, the elevation value is higher.
Decision Factor 2: Accessibility factor (Road)
The selected site should be close to existing service roads and tracks, so that it allows easy access for vehicles. Most road networks are service roads, highlighted in black and there are only two tracks, highlighted in black. The road networks generally gather at the north east part of Gombak.
Decision Factor 3: Health risk factor (Building)
To avoid transmission of disease, the site selection should be far from buildings. In Gombak, most buildings are located near the northwest and southwest border in huge clusters. The building type ranges from residential to place of warship and clinic. The rest buildings are scatter around different parts of Gombak.
Decision Factor 4: Natural conservation factor(Natural Features)
At Gombak, there are 3 different types of natural features: forest, water and park. The site should be located far from these natural features to avoid contamination and protect the environment. There is 1 water body and 1 forest in the subzone with several parks.
Decision Factors Aggregation
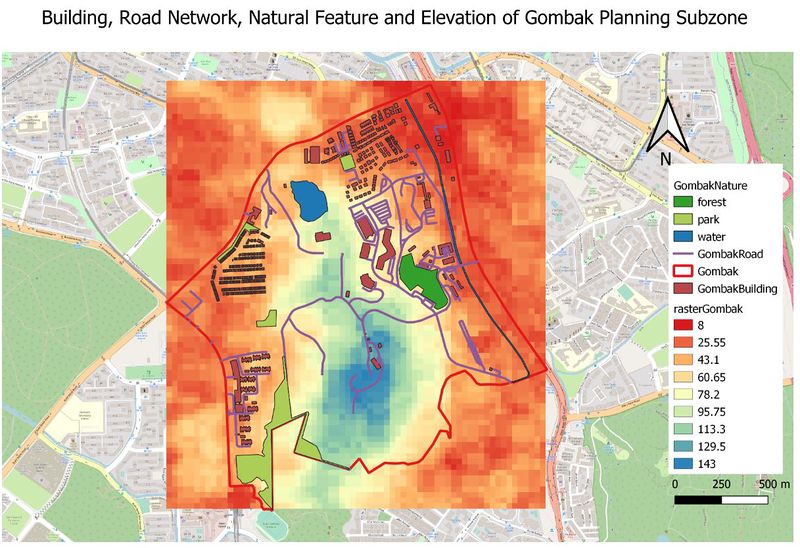
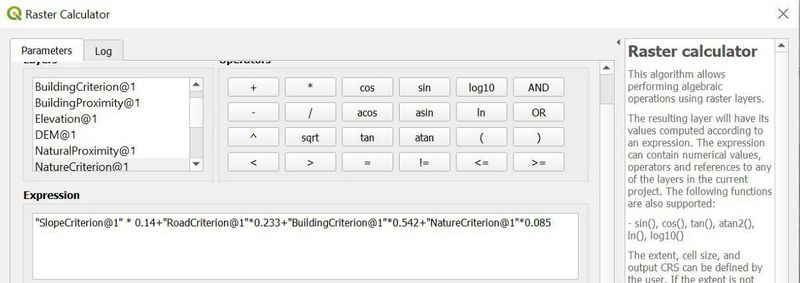
By combining the 4 decision factors into 1 map, we could see that there is space available near the south border of Gombak. This area could be the potential area for our site selection but given that it satisfies all the factors at the first place.
Proximity Analysis
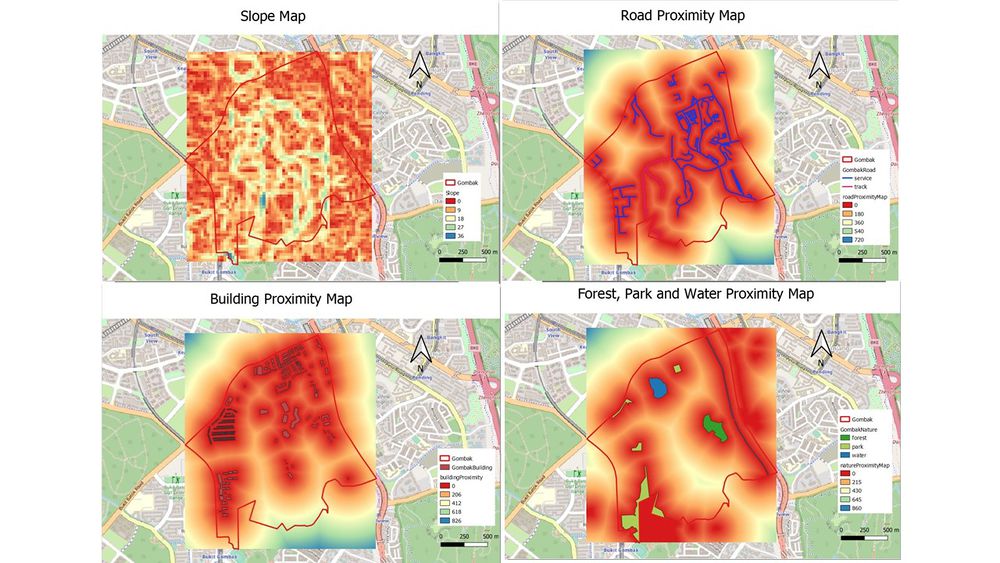
To located the area that is suitable for the site selection and take into consideration of the 4 factors, proximity maps are necessary to identify the distance to each decision factor. For elevation, it should be as low as possible to have better accessibility. Road proximity should be as low as possible to have better transportation. Building proximity should be as high as possible to avoid transmission. Lastly, natural features proximity should be as high as possible to avoid contamination.
Decision Factor 1: Slope
Slope of Gombak area has a range from 0 to around 36.4 degrees. According to the Slop Map, most areas in Gombak has a slope of less than 17 degrees. Potentially, most areas in Gombak have a less step slope, suitable for site selection.
Decision Factor 2: Road Proximity
Proximity to service road and track has a range from 0 to 722 meters. Based on the proximity maps, it is apparent that most of the areas are colored in orange or red as they are less than 180 meters to the road network.
Decision Factor 3: Building Proximity
Proximity to buildings has a range from 0m to 826m. However, most of the area in Gombak fall within the radius of 206m from buildings, making them not suitable for our site selection.
Decision Factor 4: Natural Features Proximity
From the map, we could see that the southeast area of Gombak does not have any natural features, whereas, at other areas, there are water body, forest and park. Because these natural features cover a vast land, it leaves less area for our site selection as most area are within 430m from the boundary of these natural features.
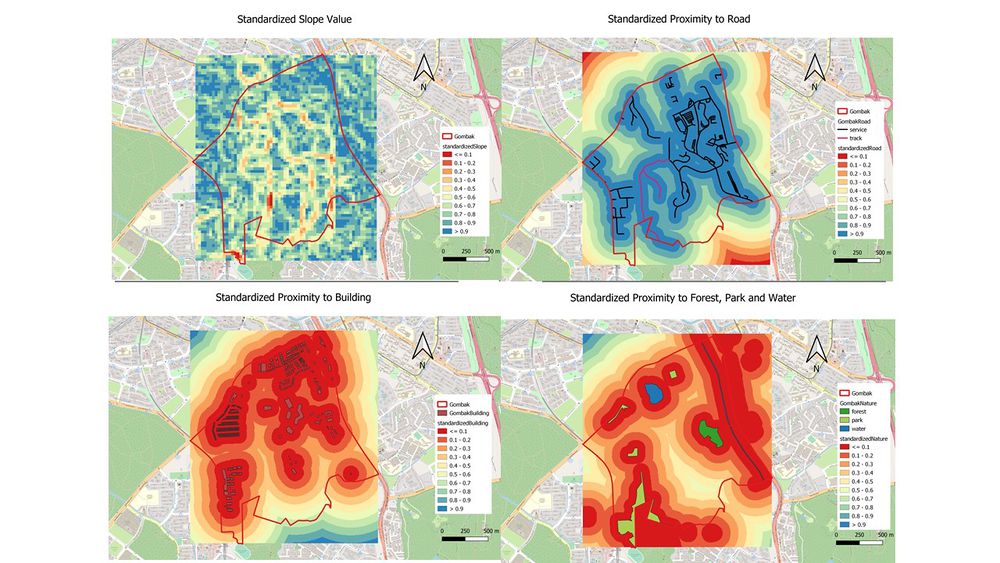
Proximity Standardization
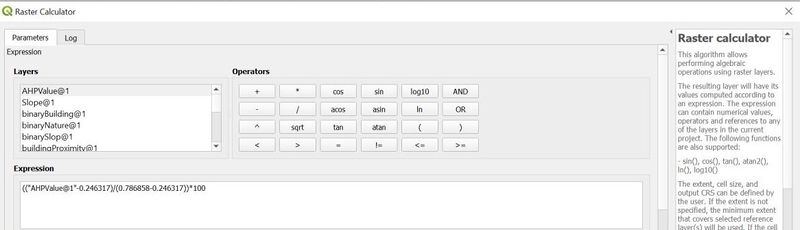
To calculate the criteria score, we need to obtain the standardized score using the formula:
Standardised Results = [Proximity to Features - Min(Proximity to Features)] / [Max(Proximity to Features) - Min(Proximity to Features)]
Since the minimun value is always 0 in this context, we could simply replace the minimum value with 0 and simply the formula for each decision factor. Meanwhile, because of the requirement difference, namely the distance requirements are different, the formula for each factor would also vary slightly.
Decision Factor 1: Economic factor (Slope)
Standardized result = 1-(slope/36.43) [36.43 is the highest slope]
From the map, we could see that most area has a high standard score more than or equal to 0.6. Because most area in Gombak is flat, so the standardized score will also be quite high in general.
Decision Factor 2: Accessibility factor (Road)
Standardized result = 1-(road proximity/722.49) [722.49 is the maximum distance from road network]
Similar to slope slope(the smaller the better), overall, accessibility score is high since the road network has a wide coverage in the planning subzone.
Decision Factor 3: Health risk factor (Building)
Standard result = building proximity/826.619 [826.619 is the maximum distance from building]
Since building occupies the majority of the land, the standard score does not have high value (>=0.7) in the planning subzone.
Decision Factor 4: Natural conservation factor(Natural Features)
Standard result = natural feature proximity/863 [863 is the maximum distance form natural features]
Same reason as building, the criteria score for natural features is generally low, having no values higher than 0.6.
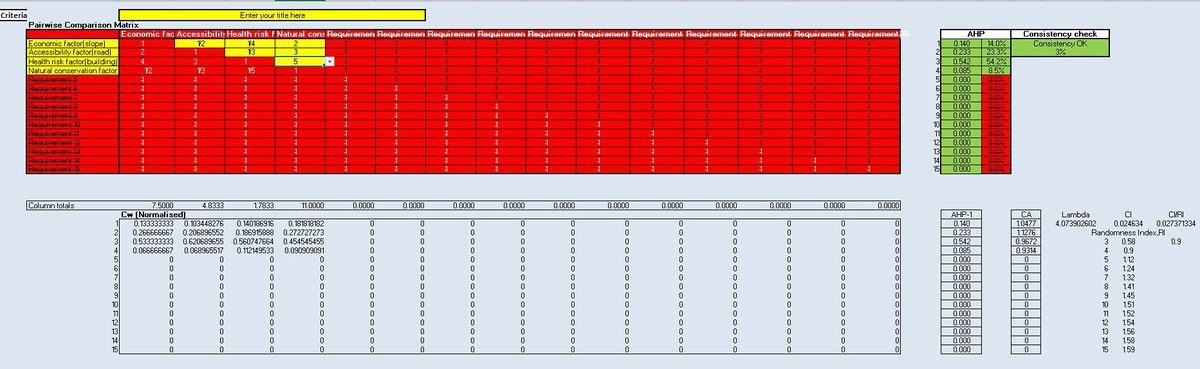
AHP
To build the AHP table, this is the importance comparison among the 4 factors: Health risk factor(building) > Accessibility factor(road) > Economic factor(slope) > Natural conservation factor. Based on this guideline, I built the AHP table as shown in the screenshot below. I give health risk factor the highest priority, so it has a 54.2% AHP value, more than 0.5. Following it, accessibility factor is the second most important factor with a AHP value of 23.3. Economic factor and Natural conservation factor are least import, having a AHP value of 14% and 8.5% respectively. The CI is 0.02, meaning that the result is highly consistent and suitable for further analysis.