Difference between revisions of "SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Tan Wei Long Ryan"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
== Part Two: Proximity Map Layers == | == Part Two: Proximity Map Layers == | ||
[[File:AS2 Part2.png|1200px|thumb|center]] | [[File:AS2 Part2.png|1200px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
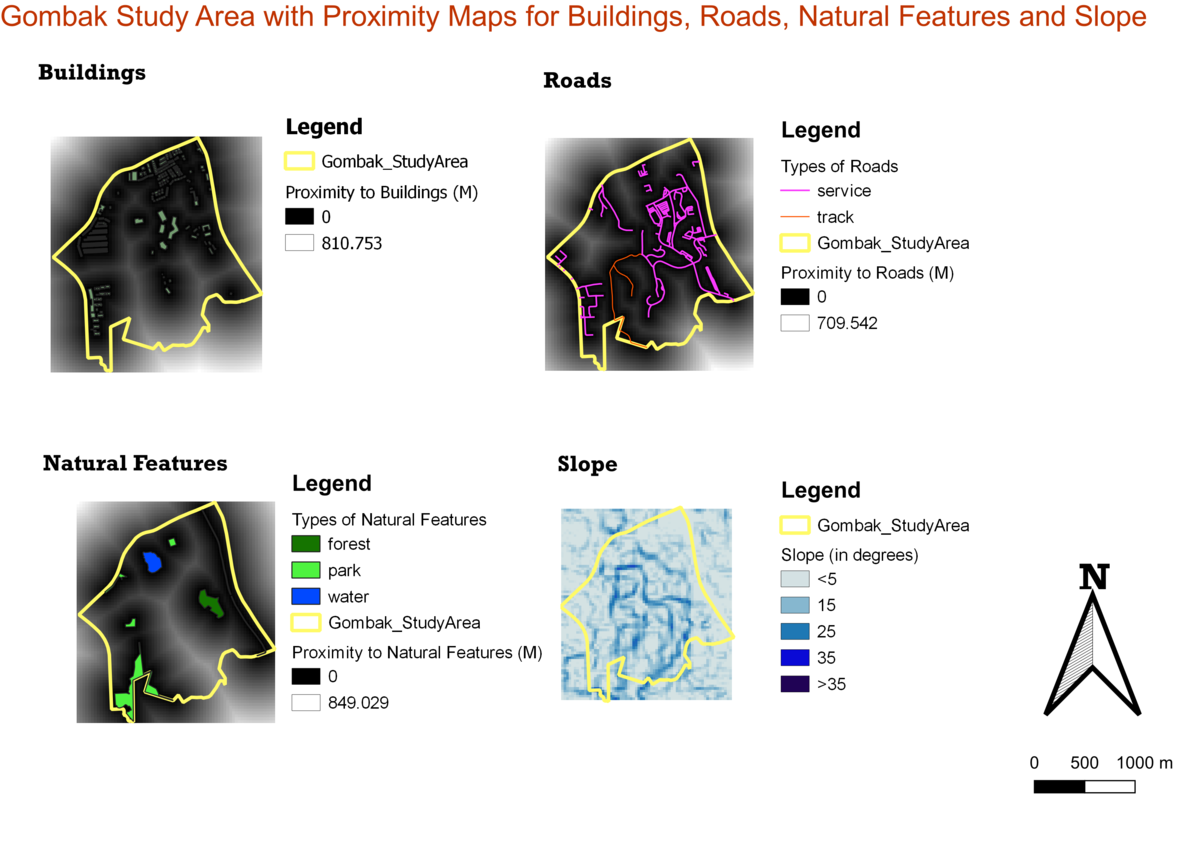
| + | '''Proximity Calculation''' : For the proximity maps of the buildings, roads and natural features, the features were rasterised such that the proximity of the features can be calculated using the proximity function in QGIS. The slope map was obtained by performing a slope analysis on the extracted GDEM layer of Gombak | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Buildings:''' The furthest distance from any point to a building within the Gombak study area is 826.62m whereas the closest distance to a building is 0m. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Roads:''' The furthest distance within the Gombak study area to a road is 722.496m and the closest distance is 0m. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Natural Conservation:''' The furthest distance within the Gombak study area to natural features is 863.669m and the closest distance is 0m. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Slope:''' The minimum and maximum of slope features within Gombak is 0 and 36.4308 degrees respectively. | ||
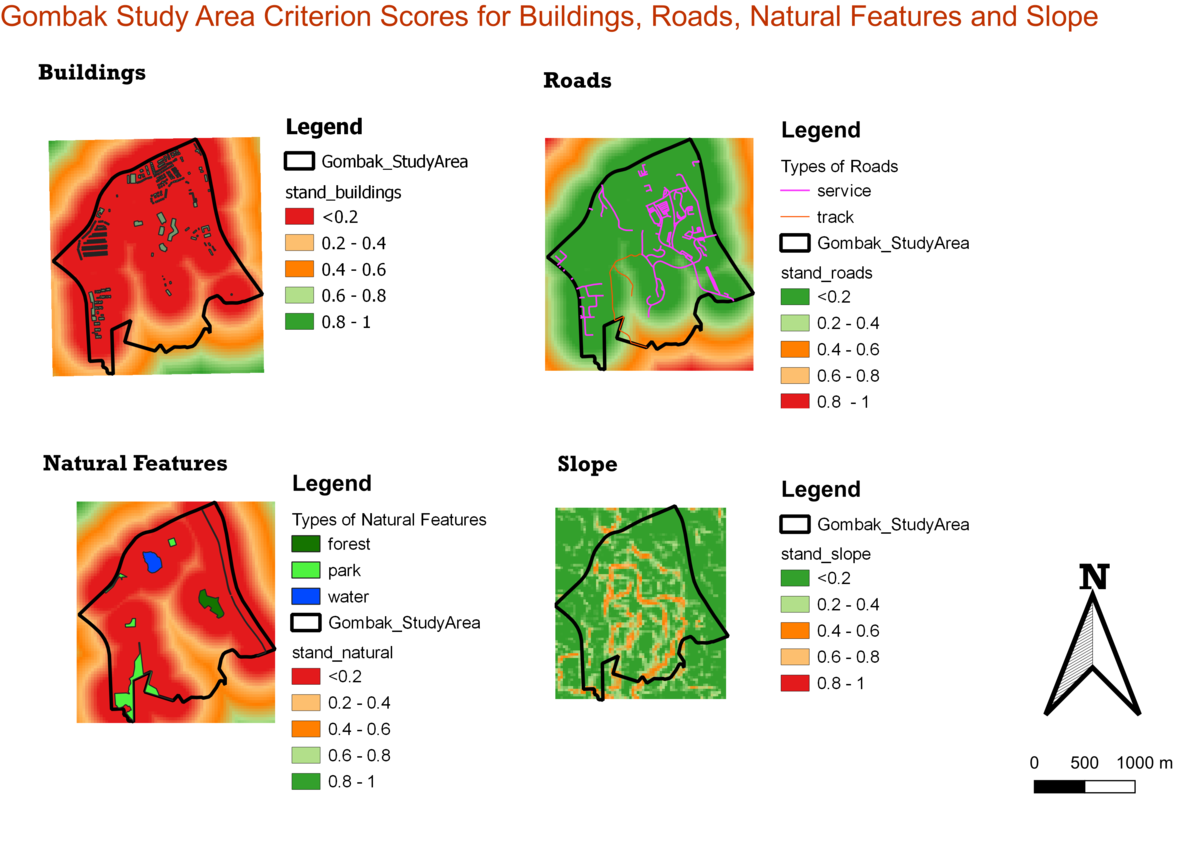
== Part Three: Criterion Score of Factor Layers == | == Part Three: Criterion Score of Factor Layers == | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 10 November 2019
Contents
- 1 Project Objective
- 2 Part One : Map View with Study Area and Target Roads, Buildings, Natural Features, Digital Elevations Layer
- 3 Part Two: Proximity Map Layers
- 4 Part Three: Criterion Score of Factor Layers
- 5 Part Four: Analytical Hierarchical Process Input Matrix & Result Report
- 6 Part Five: Suitability Land Lot
- 7 References and data sources
Project Objective
In this exercise, you are tasked to identify a location suitable for building a national Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre. The selected site must be located at Gombak planning subzone, with a contiguous area of at least 10,000m2 and it must meet the following decision factors:
Economic factor: The selected site should avoid steep slope. This is because construction at steep slope tends to involve a lot of cut-and-fill and will lend to relatively higher development cost.
Accessibility factor: The selected site should be close to existing local roads, namely: service roads and tracks. This is to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage.
Health risk factor: The selected site should be away from population i.e. housing areas and offices in order to avoid disease spreading to the nearby population.
Natural conservation factor: The selected site should be away from forested land, park and water.
Part One : Map View with Study Area and Target Roads, Buildings, Natural Features, Digital Elevations Layer
In line with our project objectives, we first created a map view with the buildings, roads, natural features and elevation of our target area (Gombak planning subzone) to understand the various features there are in Gombak that will help us investigate which is the most suitable location to construct the disease centre.
Buildings: The data of all the buildings were extracted from BBBike@Singapore, from its OSM data sets, from which, the buildings in Gombak were sieved out. The buildings range from residences to commercial areas, of which all of them will contain population. As such, we have to find an area that is far away from these buildings as there is a risk that the disease from the centre might spread to the people in these areas if it is constructed in too close proximity which will be a catastrophe. We can see that towards the south of Gombak, there are lesser buildings.
Roads: The data of all the roads were extracted from BBBike@Singapore, from its OSM data sets from which, the roads (namely service roads and tracks that will aid in transportation during construction) in Gombak were sieved out. These roads were extracted by 'select features using an expression' to extract the service roads and tracks from the 'type' column. The site for the disease centre will ideally be near to these roads as it will save on transportation costs.
Natural Conservation: The data of all buildings were extracted from BBBike@Singapore, from its OSM data sets from which, the natural features in Gombak were sieved out. In Gombak, there are mainly 3 features, forests, parks and water bodies. The selected site should avoid being near forested land and parks as these areas are usually protected land. Additionally, the site should be away from water bodies as there may be a chance that the diseases can be spread into the water source, which will have dire consequences. These features seem to be far from the south-eastern part of Gombak
Elevation: The elevation data was extracted from NASA's EarthData Search Site, from its Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) data set. The higher the value, the higher the elevation of the location , measured in meters. This higher value would mean higher costs of construction of this disease centre as construction at steep slopes tends to involve a lot of cut-and-fill and will lend to relatively higher development cost.
Part Two: Proximity Map Layers
Proximity Calculation : For the proximity maps of the buildings, roads and natural features, the features were rasterised such that the proximity of the features can be calculated using the proximity function in QGIS. The slope map was obtained by performing a slope analysis on the extracted GDEM layer of Gombak
Buildings: The furthest distance from any point to a building within the Gombak study area is 826.62m whereas the closest distance to a building is 0m.
Roads: The furthest distance within the Gombak study area to a road is 722.496m and the closest distance is 0m.
Natural Conservation: The furthest distance within the Gombak study area to natural features is 863.669m and the closest distance is 0m.
Slope: The minimum and maximum of slope features within Gombak is 0 and 36.4308 degrees respectively.