Difference between revisions of "SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX1 Chong Yun Yu"
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Part 2: Choropleth Mapping == | == Part 2: Choropleth Mapping == | ||
=== Aged Population (+65) in 2010 and 2018 === | === Aged Population (+65) in 2010 and 2018 === | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:Aged Population in 2010.png|495px|left|Aged Population in 2010]] | ||
| + | [[File:Aged Population in 2018.png|505px|right|Aged Population in 2018]] | ||
Data Source: | Data Source: | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
=== Proportion of Aged Population in 2010 and 2018 === | === Proportion of Aged Population in 2010 and 2018 === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Data Source: | ||
| + | Singapore Residents by Planning Area/Subzone, Age Group and Sex, June 2000 – 2018 (XLS).[https://www.singstat.gov.sg/find-data/search-by-theme/population/geographic-distribution/latest-data]. | ||
| + | Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP).[https://www.data.gov.sg/dataset/master-plan-2014-subzone-boundary-no-sea]. | ||
| + | Master Plan 2008 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP).[https://www.data.gov.sg/dataset/master-plan-2008-subzone-boundary-no-sea]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similar to the number of aged population, overall, the proportion of aged population in Singapore increased in 2018, as compared to 2010. The proportion of aged population is higher in the subzones in the South region, as compared to the North region. | ||
=== Percentage Change of Aged Population between 2010 and 2018 === | === Percentage Change of Aged Population between 2010 and 2018 === | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 15 September 2019
Part 1: Thematic Mapping
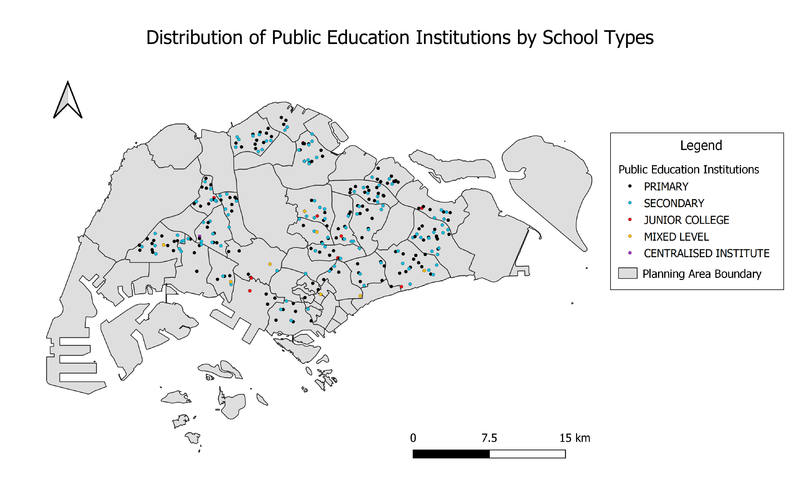
Distribution of Public Education Institution by School Types
Data Source: General information of schools.[1]. Master Plan 2014 Planning Area Boundary (No Sea) (SHP).[2].
To show the distribution of public education institution by school type, I used the variable “mainlevel_” to categorise the datasets. This classifies all school into the different school types, namely “Primary”, “Secondary”, “Junior College”, “Mixed Level” and “Centralised Institute”. I chose to use the same symbol, a coloured circle, for all classifications. I chose a different colour for each class, as shown in the legend. Rather than using different symbols for each category, I used this method as I think it is much easier to read and understand the distribution of the institutions using different colours than shapes.
Road Network System Hierarchy of Singapore
Data Source: Road Section Line.[3]. CoastalOutline from Prof Kan’s Hands-on_Ex01.
According to the URA Handbook on Guidelines for Naming of Streets [4], roads can be classified into 5 categories. I added a new column “RD_TYPE” in the file downloaded from LTA Datamall and classified all roads into the different categories, using the URA guidelines. The 5 categories, from the highest hierarchy to the lowest hierarchy, are “Expressway”, “Major Arterial Road”, “Minor Arterial Road”, “Primary Access Road” and “Local Access Road”. I used a different colour to represent each classification, where all classification has the same line width, as shown in the legend, for better visualisation.
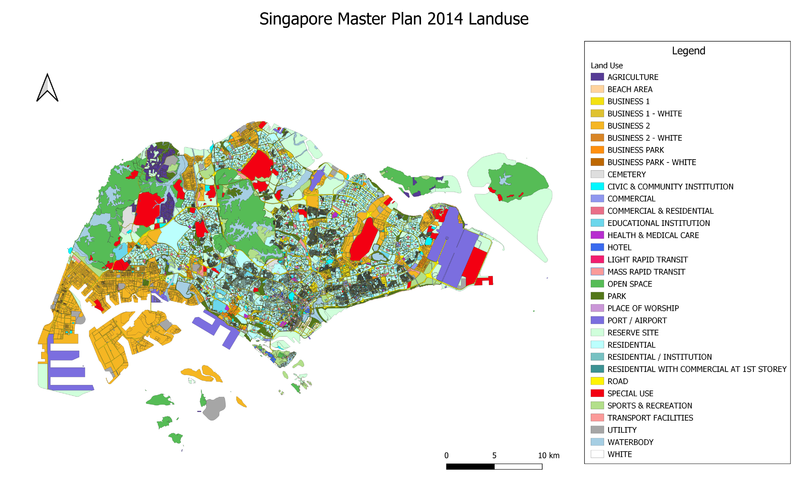
2014 Master Plan Landuse Singapore
Data Source: Master Plan 2014 Land Use (SHP).[5].
To show the landuse in Singapore, I used “LU_DESC”, which contains the description of land usage for each parcel of land, to classify the data. As there are 32 different categories of landuse, it is quite difficult to identify each category easily with the random colours generated by QGIS. I attempted to make the visualisation better by changing the colours to make them make more sense. For example, I used different hues of green for open spaces and parks, bright red for special use and light grey for cemetery.
Part 2: Choropleth Mapping
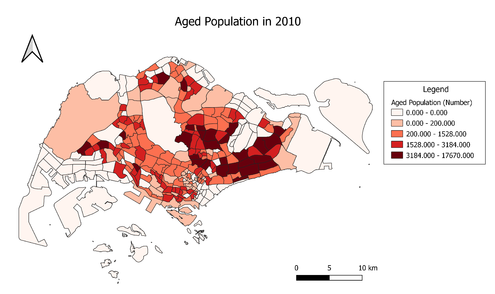
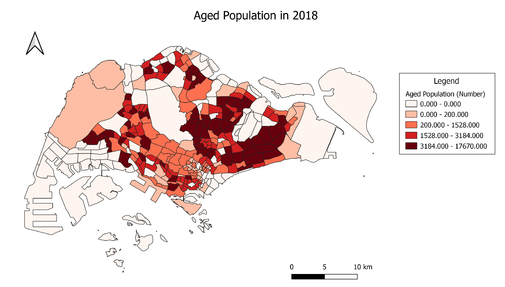
Aged Population (+65) in 2010 and 2018
Data Source: Singapore Residents by Planning Area/Subzone, Age Group and Sex, June 2000 – 2018 (XLS).[6]. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP).[7]. Master Plan 2008 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP).[8].
The number of aged population increased overall in 2018, as compared to 2010. Many subzones in the East and Central regions in Singapore have more than 3184 aged persons. The number of subzones with more than 3184 aged persons more than doubled in 2018 (65 subzones) as compared to 2010 (29 subzones).
Proportion of Aged Population in 2010 and 2018
Data Source: Singapore Residents by Planning Area/Subzone, Age Group and Sex, June 2000 – 2018 (XLS).[9]. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP).[10]. Master Plan 2008 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP).[11].
Similar to the number of aged population, overall, the proportion of aged population in Singapore increased in 2018, as compared to 2010. The proportion of aged population is higher in the subzones in the South region, as compared to the North region.
Percentage Change of Aged Population between 2010 and 2018
Discussion
test test