Difference between revisions of "SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Wang Youjin"
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Map with Buildings, Roads, Natural Feature and Elevation in 1 view=== |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | [[File:Basemap allinone.PNG|800px|center]] | |
| − | [[File:Basemap allinone.PNG| | ||
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
</span></span></p> | </span></span></p> | ||
| − | |||
Data Source: | Data Source: | ||
| + | 1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [https://data.gov.sg/dataset/master-plan-2014-subzone-boundary-no-sea]. | ||
| + | 2. Roads(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 3. Buildings(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 4. Natural(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA | ||
| + | [https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search?m=-7.175!25.59375!1!1!0!0%2C2]. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 40: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | === | + | ===Map with 4 Views on Buildings, Roads, Natural Feature and Elevation in 1 Map=== |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | [[File:1.4.2.PNG| | + | | |
| + | [[File:1.4.2.PNG|800px|center]]<br> | ||
Description | Description | ||
| Line 44: | Line 55: | ||
style='color:windowtext'> | style='color:windowtext'> | ||
</span></span></p> | </span></span></p> | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> |
| + | |||
| + | Data Source: | ||
| + | 1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [https://data.gov.sg/dataset/master-plan-2014-subzone-boundary-no-sea]. | ||
| + | 2. Roads(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 3. Buildings(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 4. Natural(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA | ||
| + | [https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search?m=-7.175!25.59375!1!1!0!0%2C2]. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
===Write-up=== | ===Write-up=== | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | | | ||
| − | === | + | ====Roads(only service & tracks) ==== |
In view of the Accessibility Factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be close to local roads to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage, we are using roads layer as one of the base map. The data has been cleaned up as required to show only categorized service roads using thicker strokes and tracks using thinner strokes. There are 199 service roads and only 2 tracks. From observation,the service roads spread across of the target area and are more concentrated in the north east didtrict. | In view of the Accessibility Factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be close to local roads to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage, we are using roads layer as one of the base map. The data has been cleaned up as required to show only categorized service roads using thicker strokes and tracks using thinner strokes. There are 199 service roads and only 2 tracks. From observation,the service roads spread across of the target area and are more concentrated in the north east didtrict. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | === | + | ====Buildings ==== |
In view of the Health Risk factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be away from population to prevent the diseases from spreading to the public. By using categorize visualization of the building types, we can see there are 7 types including clinic, construction site, garage, place of worship, public space, residential area, and train station. However, 95%(505) of the building data are not known of its type which make it hard to present a clear understanding of the building type by categorizing it. | In view of the Health Risk factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be away from population to prevent the diseases from spreading to the public. By using categorize visualization of the building types, we can see there are 7 types including clinic, construction site, garage, place of worship, public space, residential area, and train station. However, 95%(505) of the building data are not known of its type which make it hard to present a clear understanding of the building type by categorizing it. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | === | + | ====Natural Features==== |
In view of the Natural Conservation factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should be also be away from natural features, such as forests, parks and water bodies. From the OSM data, we can see there are 1 forest, 4 parks and 3 water bodies in the target area. Since these features are special regions and are reserved - we will use special color scheme to identify them 1)forest is in grey green, 2)parks is in light green 3)water bodies is in light blue. | In view of the Natural Conservation factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should be also be away from natural features, such as forests, parks and water bodies. From the OSM data, we can see there are 1 forest, 4 parks and 3 water bodies in the target area. Since these features are special regions and are reserved - we will use special color scheme to identify them 1)forest is in grey green, 2)parks is in light green 3)water bodies is in light blue. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | === | + | ====Digital Elevation==== |
In view of the Economic factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should avoid steep slopes to reduce the development costs for cut-and-fill construction techniques. The lowest elevation is 8 meters above sea level, depicted in grey/white.The highest elevation with 145 meters above sea level, depicted in dark black. | In view of the Economic factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should avoid steep slopes to reduce the development costs for cut-and-fill construction techniques. The lowest elevation is 8 meters above sea level, depicted in grey/white.The highest elevation with 145 meters above sea level, depicted in dark black. | ||
| Line 71: | Line 94: | ||
| − | == Part 2: Factor Layers:Proximity and Slope | + | == Part 2: Factor Layers:Proximity and Slope Analysis Views == |
| Line 79: | Line 102: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | + | === Map with 4 Decision Factors Views=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | [[File:Yiujin2.4.PNG|800px]] | |
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | ||
lang=EN-GB style='font-size:8.0pt;font-family:"Times New Roman",serif; | lang=EN-GB style='font-size:8.0pt;font-family:"Times New Roman",serif; | ||
| Line 132: | Line 120: | ||
style='color:windowtext'> | style='color:windowtext'> | ||
</span></span></p> | </span></span></p> | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | Data Source: | ||
| + | 1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [https://data.gov.sg/dataset/master-plan-2014-subzone-boundary-no-sea]. | ||
| + | 2. Roads(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 3. Buildings(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 4. Natural(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA | ||
| + | [https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search?m=-7.175!25.59375!1!1!0!0%2C2]. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
===WRITE UP=== | ===WRITE UP=== | ||
| − | === | + | |- |
| − | Darker values means the roads network are closer to the feature in the targeted are, which means it's more suitable of developing a | + | | |
| − | + | ==== Proximity to Roads==== | |
| − | + | Darker values means the roads network are closer to the feature in the targeted are, which means it's more suitable of developing a buildin. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ====Proximity to Buildings==== |
| − | + | Land lots with lighter values have higher suitability to be chosen to build the quarantine center because these locations are further away from the population. | |
| + | ====Proximity to Nature==== | ||
| + | Land lots that are further away from natural features have lighter values in the map, and they have higher suitability to be chosen to build the quarantine center. | ||
| − | + | ====Slope Analysis ==== | |
| + | Slopes are calculated using proximity to elevation. Land lots with darker values have flatter surfaces, and thus they have higher suitability to build the quarantine center. As seen from the map, most of the land lots in Gombak are flat and suitable for use although there are some uneven elevation in the region. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 192: | Line 158: | ||
== Part 3: Factor Layers with Criterion Scores == | == Part 3: Factor Layers with Criterion Scores == | ||
| − | With the proximity analysis done on the 4 selected features of interest, next we need to quantify the suitability. | + | With the proximity analysis done on the 4 selected features of interest, next we need to quantify the suitability by giving them a score that we can comprehend. Hence, applying the standardisation technique from Statistics, we can use the Max- Min method to standardise the above analysis results: |
Standardised Results = [Proximity to Features - Min(Proximity to Features)] / [Max(Proximity to Features) - Min(Proximity to Features)] | Standardised Results = [Proximity to Features - Min(Proximity to Features)] / [Max(Proximity to Features) - Min(Proximity to Features)] | ||
| − | + | This calculation can be achieved by using Raster Calculator in the processing tool. The x value will be the attribute available in the selection, then we will manually extract the max/min obtained from the proximity step. | |
| − | + | The results will range from 0-1 and we categorize them into 10 classes to give us a clearer understanding of the score distribution performance. | |
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| + | === Map with 4 Criterion Score Views of the 4 Decision Factor=== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | [[File:3.4.youjin.PNG|800px]] | |
| − | + | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
lang=EN-GB style='font-size:8.0pt;font-family:"Times New Roman",serif; | lang=EN-GB style='font-size:8.0pt;font-family:"Times New Roman",serif; | ||
mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";font-variant:small-caps;color:white'><span | mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";font-variant:small-caps;color:white'><span | ||
| − | style='color:windowtext'> | + | style='color:windowtext'>Proximity to Building</span></span></p> |
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | ||
lang=EN-GB style='font-size:8.0pt;font-family:"Times New Roman",serif; | lang=EN-GB style='font-size:8.0pt;font-family:"Times New Roman",serif; | ||
| Line 221: | Line 184: | ||
style='color:windowtext'> | style='color:windowtext'> | ||
</span></span></p> | </span></span></p> | ||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | Data Source: | |
| − | + | 1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [https://data.gov.sg/dataset/master-plan-2014-subzone-boundary-no-sea]. | |
| + | 2. Roads(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 3. Buildings(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 4. Natural(SHP) from osm | ||
| + | [https://download.bbbike.org/osm/bbbike/Singapore/]. | ||
| + | 5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA | ||
| + | [https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search?m=-7.175!25.59375!1!1!0!0%2C2]. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| − | || | + | ===WRITE UP=== |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | ==== Accessibility Factor==== | ||
| − | The selected site should be close to existing local roads, | + | The selected site should be close to existing local roads hence the standardizaiton score indicates the land lots that are further away from the local roads in lower score toward 0 represented by lighter green colors, while the ones nearer to local roads get a higher score toward 1, represented in darker green color. |
| − | + | ====Health Risk Factor==== | |
| − | + | For the quarantine center to achieve its objective, we need to ensure it is built further away from the concentrated population. Hence for land lot near to the building has a lower score, represented in lighter grey color; while the ones that are further away have a higher score, represented in darker grey color scheme. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Economic Factor==== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Slope Analysis are calculated using proximity to elevation to understand the surface height changes. Land lots with flatter surfaces are considered to be more suitable as it's less costly to conduct construciton work, hence we assign those flatter area with higher score, represented in green&blue color blocks. The steeper land lot is represented in orange/red color block as less suitable lots with lower scores. As seen from the map, most area are flat. | ||
| − | + | ====Natural Conservation Factor ==== | |
| − | + | We want to ensure the construction is further away from the natural features for the purpose of natural conservation course. Land lots that are further away from natural features have higher score, represented by darker blue color. The land lots that are nearer to the natural feature are represented in lighter blue - lower score is assigned. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | == Part 4: Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) input matrix== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | With the standardised criterion score on 4 decision factors, we can now us Analytical Hierarchical Process input matrix to assign them with different importance level. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| + | === AHP Results Report=== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Ahp1youjin.PNG|600px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
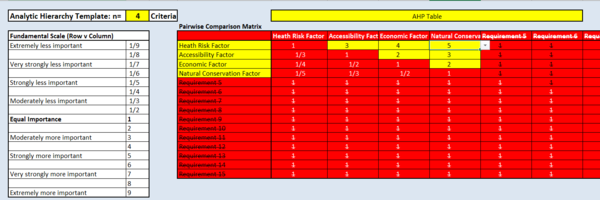
| + | we first, according to the score standards for APH , assign different importance score to the 4 decision factors in the yellow cells in the matrix table. The template auto calculated using the scores in pairwise comparison matrix. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Ahp2youjin.PNG|600px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
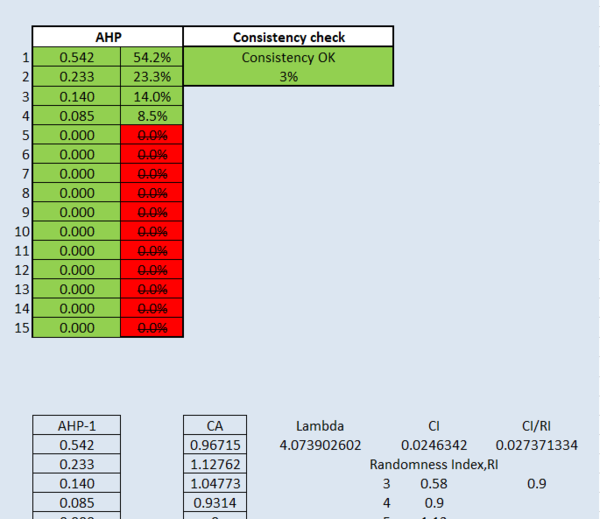
| + | Then, the scores are normalised by dividing the scores for each cell with the sum of its entire column. Finally, the average of the rows of the normalised matrix is taken, and that is the AHP score. we give health risk factor a high importance level, followed by accessibility, economic factor and lastly, natural conservatio factor. Their important score are 0.542, 0.233, 0.14 and 0.085 respectively. | ||
| − | + | The consistency is at 3%, which is a good indicator of the score assigned. Additionally, the CI we have is 0.024. This indicates that the inconsistency generated by the pairwise comparison matrix is very low and is acceptable & meaningful. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Data Source: | |
| + | AHP Template provided by SCB Associates | ||
| + | [https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=17&ved=2ahUKEwi198HV87_lAhXhjuYKHWn1AnEQFjAQegQICRAC&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.scbuk.com%2FAHP%2520Template%2520SCBUK.xls&usg=AOvVaw002J8QfYIxOE_I9PYqrH8_]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 313: | Line 255: | ||
== Part 5: Suitability land lot == | == Part 5: Suitability land lot == | ||
| − | + | Finally, we are able to calculate the final score with the weight & standardized decision factors score to plot out the suitability map that are of the ideal score range. | |
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | === AHP Results Report=== | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Youjin score Ahp.PNG|600px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | We apply the formula Decision factor * weight from AHP Analysis in the raster calculator in QGIS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:AhpBASESCOREYOUJIN.PNG|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, when we look at the categorized map of the APH score map, we realized the number is not of normal distribution. Hence, we apply standardization technique once again to normalize the data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Ahpscore2youjin.PNG|600px||center]] | ||
| + | [[File:YOUJINSuitabilityAHP.PNG|600px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is the improved version AHP score map we got after standardize the numbers. Next, we reduce the classes in order to generalize it for the suitability analysis. Keeping in mind we need an area with at least 10,000 meter square size for construction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Ahpstandaidzedyoujin.PNG|600px|center]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next, we further generalize them into 2 basket. 1 is not suitable for land use as their AHP standardized score is lower than 60, the other group is suitable with score range from 60 -100. The reason why we use 60 as the cutting score is due to the area size consideration. If we set the suitability score bar too high, we end up with suitable land lot that are too small. Hence, after trial and error by testing different score range, we decide to use 60 as the cutting point. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:YiujinSuitabilityrange.png|600px|center]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
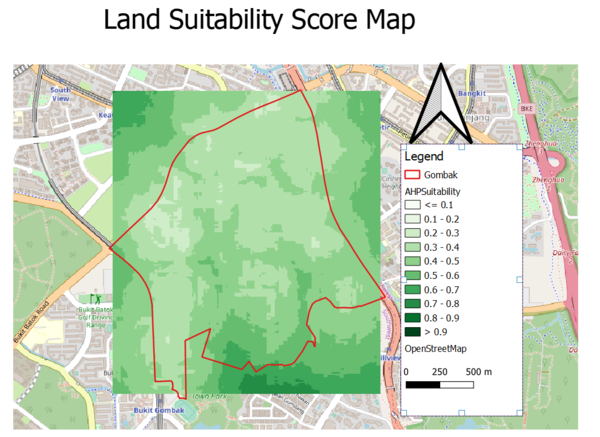
| + | As seen from the map above, the southern part of study area ranked higher in terms of the standardized score, and is suitable to build the national quarantine centre. We identify the area with the most regular shape & high score in the box as the potential target. | ||
| + | |||
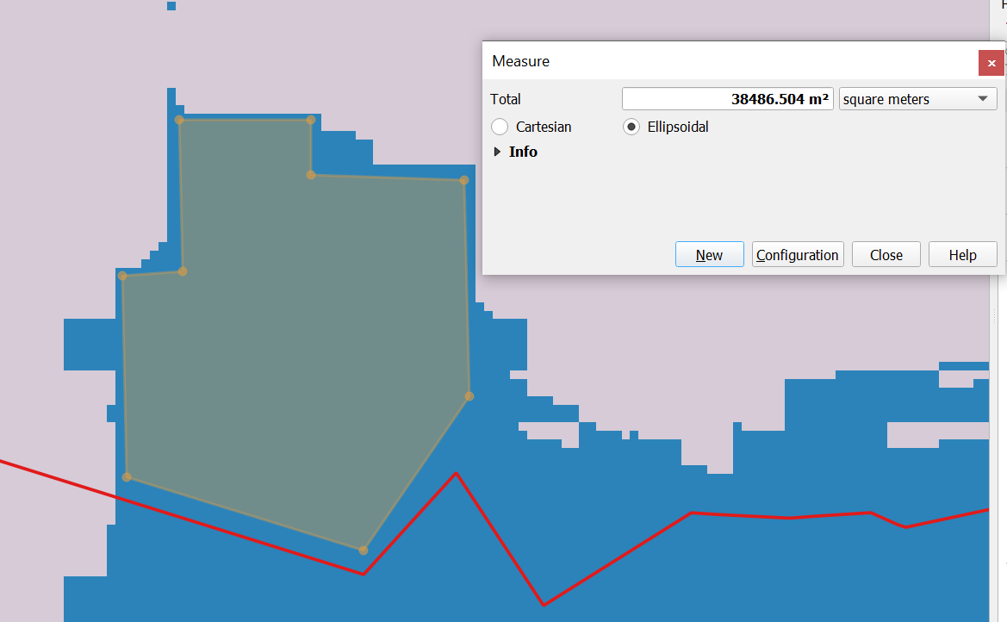
| − | + | [[File:YjAreasize check.png|center]]<br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The suitable land lots we identified have a total area of more than 38,000 meters square, which is larger than the stipulated contiguous area of 10,000 meters square. | |
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | As some land lots are not connected to other land lots, some narrow parts of the identified target area might not be suitable in the actual construction work - hence, the suitable land plot is more concentrated in the center of the identified target area. | |
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:05, 10 November 2019
Contents
Part 1: Base Map Views
In order to identify a location suitable for building a National Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre given in the task question, we have to first look at the important aspects for consideration in targeted Gombak planning subzone by building the base map views 1) Gombak Road 2) Gombak Building 3) Gombak Natural Features 4) Digital Elevation together with targeted study area - Bukit Gombak:
Map with Buildings, Roads, Natural Feature and Elevation in 1 view |
|
Gombak Target Road
Data Source:
1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [1].
2. Roads(SHP) from osm
[2].
3. Buildings(SHP) from osm
[3].
4. Natural(SHP) from osm
[4].
5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA
[5].
|
Map with 4 Views on Buildings, Roads, Natural Feature and Elevation in 1 Map |
|
Description Digital Elevation Layer
Data Source: 1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [6]. 2. Roads(SHP) from osm [7]. 3. Buildings(SHP) from osm [8]. 4. Natural(SHP) from osm [9]. 5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA [10]. |
Write-up |
Roads(only service & tracks)In view of the Accessibility Factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be close to local roads to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage, we are using roads layer as one of the base map. The data has been cleaned up as required to show only categorized service roads using thicker strokes and tracks using thinner strokes. There are 199 service roads and only 2 tracks. From observation,the service roads spread across of the target area and are more concentrated in the north east didtrict.
BuildingsIn view of the Health Risk factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be away from population to prevent the diseases from spreading to the public. By using categorize visualization of the building types, we can see there are 7 types including clinic, construction site, garage, place of worship, public space, residential area, and train station. However, 95%(505) of the building data are not known of its type which make it hard to present a clear understanding of the building type by categorizing it.
Natural FeaturesIn view of the Natural Conservation factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should be also be away from natural features, such as forests, parks and water bodies. From the OSM data, we can see there are 1 forest, 4 parks and 3 water bodies in the target area. Since these features are special regions and are reserved - we will use special color scheme to identify them 1)forest is in grey green, 2)parks is in light green 3)water bodies is in light blue.
Digital ElevationIn view of the Economic factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should avoid steep slopes to reduce the development costs for cut-and-fill construction techniques. The lowest elevation is 8 meters above sea level, depicted in grey/white.The highest elevation with 145 meters above sea level, depicted in dark black. |
Part 2: Factor Layers:Proximity and Slope Analysis Views
Next, we did a proximity analysis to show the closeness of all features in target area to the identified features of interest. As shown in the screenshot below, the darker parts the maps below depict higher closeness to the features of interest.
Four views showing the proximity map to 1)target roads layer, 2) buildings layer,3) target natural features layer and 4) slope layer that are created in Part 1.
Map with 4 Decision Factors Views |
|
Proximity to Building
Data Source: 1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [11]. 2. Roads(SHP) from osm [12]. 3. Buildings(SHP) from osm [13]. 4. Natural(SHP) from osm [14]. 5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA [15].
|
WRITE UP |
Proximity to RoadsDarker values means the roads network are closer to the feature in the targeted are, which means it's more suitable of developing a buildin. Proximity to BuildingsLand lots with lighter values have higher suitability to be chosen to build the quarantine center because these locations are further away from the population. Proximity to NatureLand lots that are further away from natural features have lighter values in the map, and they have higher suitability to be chosen to build the quarantine center. Slope AnalysisSlopes are calculated using proximity to elevation. Land lots with darker values have flatter surfaces, and thus they have higher suitability to build the quarantine center. As seen from the map, most of the land lots in Gombak are flat and suitable for use although there are some uneven elevation in the region.
|
Part 3: Factor Layers with Criterion Scores
With the proximity analysis done on the 4 selected features of interest, next we need to quantify the suitability by giving them a score that we can comprehend. Hence, applying the standardisation technique from Statistics, we can use the Max- Min method to standardise the above analysis results:
Standardised Results = [Proximity to Features - Min(Proximity to Features)] / [Max(Proximity to Features) - Min(Proximity to Features)]
This calculation can be achieved by using Raster Calculator in the processing tool. The x value will be the attribute available in the selection, then we will manually extract the max/min obtained from the proximity step.
The results will range from 0-1 and we categorize them into 10 classes to give us a clearer understanding of the score distribution performance.
Map with 4 Criterion Score Views of the 4 Decision Factor |
|
Proximity to Building
Data Source: 1. Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA [16]. 2. Roads(SHP) from osm [17]. 3. Buildings(SHP) from osm [18]. 4. Natural(SHP) from osm [19]. 5. Raster ASTER Elevation(TIFF) from NASA [20].
|
WRITE UP |
Accessibility FactorThe selected site should be close to existing local roads hence the standardizaiton score indicates the land lots that are further away from the local roads in lower score toward 0 represented by lighter green colors, while the ones nearer to local roads get a higher score toward 1, represented in darker green color. Health Risk FactorFor the quarantine center to achieve its objective, we need to ensure it is built further away from the concentrated population. Hence for land lot near to the building has a lower score, represented in lighter grey color; while the ones that are further away have a higher score, represented in darker grey color scheme. Economic FactorSlope Analysis are calculated using proximity to elevation to understand the surface height changes. Land lots with flatter surfaces are considered to be more suitable as it's less costly to conduct construciton work, hence we assign those flatter area with higher score, represented in green&blue color blocks. The steeper land lot is represented in orange/red color block as less suitable lots with lower scores. As seen from the map, most area are flat. Natural Conservation FactorWe want to ensure the construction is further away from the natural features for the purpose of natural conservation course. Land lots that are further away from natural features have higher score, represented by darker blue color. The land lots that are nearer to the natural feature are represented in lighter blue - lower score is assigned.
|
Part 4: Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) input matrix
With the standardised criterion score on 4 decision factors, we can now us Analytical Hierarchical Process input matrix to assign them with different importance level.
AHP Results Report |
|
we first, according to the score standards for APH , assign different importance score to the 4 decision factors in the yellow cells in the matrix table. The template auto calculated using the scores in pairwise comparison matrix.
Then, the scores are normalised by dividing the scores for each cell with the sum of its entire column. Finally, the average of the rows of the normalised matrix is taken, and that is the AHP score. we give health risk factor a high importance level, followed by accessibility, economic factor and lastly, natural conservatio factor. Their important score are 0.542, 0.233, 0.14 and 0.085 respectively. The consistency is at 3%, which is a good indicator of the score assigned. Additionally, the CI we have is 0.024. This indicates that the inconsistency generated by the pairwise comparison matrix is very low and is acceptable & meaningful. Data Source: AHP Template provided by SCB Associates [21].
|
Part 5: Suitability land lot
Finally, we are able to calculate the final score with the weight & standardized decision factors score to plot out the suitability map that are of the ideal score range.
| === AHP Results Report=== |
|
However, when we look at the categorized map of the APH score map, we realized the number is not of normal distribution. Hence, we apply standardization technique once again to normalize the data. This is the improved version AHP score map we got after standardize the numbers. Next, we reduce the classes in order to generalize it for the suitability analysis. Keeping in mind we need an area with at least 10,000 meter square size for construction. Next, we further generalize them into 2 basket. 1 is not suitable for land use as their AHP standardized score is lower than 60, the other group is suitable with score range from 60 -100. The reason why we use 60 as the cutting score is due to the area size consideration. If we set the suitability score bar too high, we end up with suitable land lot that are too small. Hence, after trial and error by testing different score range, we decide to use 60 as the cutting point.
The suitable land lots we identified have a total area of more than 38,000 meters square, which is larger than the stipulated contiguous area of 10,000 meters square. As some land lots are not connected to other land lots, some narrow parts of the identified target area might not be suitable in the actual construction work - hence, the suitable land plot is more concentrated in the center of the identified target area.
|