Difference between revisions of "SMT201 AY2019-20G1 EX2 Riana"
Riana.2016 (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Objective == The motive of this project is to find a suitable location for building a National Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre. The selected site must be located in...") |
Riana.2016 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| − | + | == Overview of Gombak Subzone == | |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[File:Riana Gombak Overview.png | + | [[File:Riana Gombak Overview.png|Data Source: Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA. Roads, Buildings and Natural (SHP) from OpenStreetMap. ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) dataset (TIFF) jointly prepared by NASA and METI, Japan; raster dataset combined by Professor Kam Tin Seong.|800px|center]] |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | === Buildings (Health Risk Factor) === | |
| + | Buildings in Gombak subzone are mostly located around the boundary with some located in the central. It is densely populated in the northern part of Gombak subzone since there are quite a number of buildings situated. Therefore, southern part of Gombak subzone seems to be more appropriate to build the quarantine centre in order to satisfy the health risk factor. | ||
| − | === | + | === Natural Features (Natural Conservation Factor) === |
| − | + | Natural features in Gombak subzone seems to be spread across the whole area. In the east side there are forest and water bodies. North side have situated water body and 2 parks. Following by 2 parks located in western to south-west of Gombak Subzone. Looking at the spread, central and south-east of Gombak Subzone will be the appropriate place to build the quarantine centre. | |
| − | + | === Roads (Accessibility Factor) === | |
| + | Road’s spread in Gombak subzone are quite comprehensive of the area except on the southern part which are not covered by any part of roads. Eastern part of Gombak subzone is the most accessible as they has the most number of roads. Therefore, looking at the accessibility factor, building the quarantine centre in eastern part of Gombak subzone will be the most accessible. | ||
| − | == | + | === Elevation (Economic Factor) === |
| + | There are high elevation covered from central to southern of Gombak subzone. While around the boundary, there are less elevation especially on the northern part. Thus, looking at the economic factor, it is more appropriate to build the quarantine central at the northern part of Gombak subzone. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Proximity of the Four Factors == | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | <br>[[File: | + | [[File:Riana Proximity.png|800px|frameless|Data Source: Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (No Sea) (SHP) from URA. Roads, Buildings and Natural (SHP) from OpenStreetMap. ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) dataset (TIFF) jointly prepared by NASA and METI, Japan; raster dataset combined by Professor Kam Tin Seong.]] |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Building Proximity (Health Risk Factor)=== |
| − | + | The green color depicts suitable area while red color otherwise. The furthest distance from the buildings is 816.36 meters. The southern part and some part of the central are the suitable lot for building a quarantine centre. | |
| − | + | ===Natural Features Proximity (Natural Conservation Factor)=== | |
| − | + | The green color depicts suitable area while red color otherwise. The furthest distance from the natural conservation is 847.27 meters. The southern, central, and some part of west are the suitable lot for building a quarantine centre. | |
| − | === | + | ===Road Proximity (Accessibility Factor)=== |
| − | + | The green color depicts accessible area while red color otherwise. The furthest distance from the road is 717.03 meter. I have chosen below 200 meter as a cut off for accessible area since walk time for 200 meter should take around 5 minutes. Most area of Gombak are quite accessible by roads except the southern part as said above. Therefore, looking at the road proximity, all area is suitable to build the quarantine centre except southern area. | |
| − | + | ===Slope Proximity (Economy Factor)=== | |
| − | + | The green color depicts flatter area while red color otherwise. The steepest area has a degree of 36.43. Despite high coverage of elevated area, it seems that Gombak subzone as a rather flatten steep. It is suitable to build the quarantine centre on the green area of the map. | |
Revision as of 23:40, 9 November 2019
Objective
The motive of this project is to find a suitable location for building a National Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre. The selected site must be located in Gombak Planning Subzone. Criteria: 1. A contiguous area of 10,000 m2 2. Factors: a. Economic Factor: avoid steep slope b. Accessibility Factor: close to existing local roads, namely: service roads and tracks c. Health Risk Factor: The selected site should be away from population d. Natural Conservation Factor: The selected site should be away from forested land, park and water.
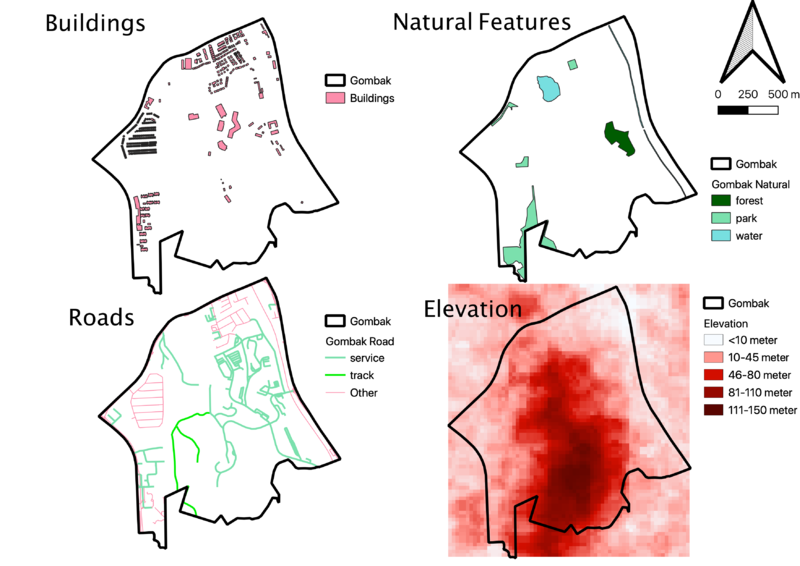
Overview of Gombak Subzone
Buildings (Health Risk Factor)
Buildings in Gombak subzone are mostly located around the boundary with some located in the central. It is densely populated in the northern part of Gombak subzone since there are quite a number of buildings situated. Therefore, southern part of Gombak subzone seems to be more appropriate to build the quarantine centre in order to satisfy the health risk factor.
Natural Features (Natural Conservation Factor)
Natural features in Gombak subzone seems to be spread across the whole area. In the east side there are forest and water bodies. North side have situated water body and 2 parks. Following by 2 parks located in western to south-west of Gombak Subzone. Looking at the spread, central and south-east of Gombak Subzone will be the appropriate place to build the quarantine centre.
Roads (Accessibility Factor)
Road’s spread in Gombak subzone are quite comprehensive of the area except on the southern part which are not covered by any part of roads. Eastern part of Gombak subzone is the most accessible as they has the most number of roads. Therefore, looking at the accessibility factor, building the quarantine centre in eastern part of Gombak subzone will be the most accessible.
Elevation (Economic Factor)
There are high elevation covered from central to southern of Gombak subzone. While around the boundary, there are less elevation especially on the northern part. Thus, looking at the economic factor, it is more appropriate to build the quarantine central at the northern part of Gombak subzone.
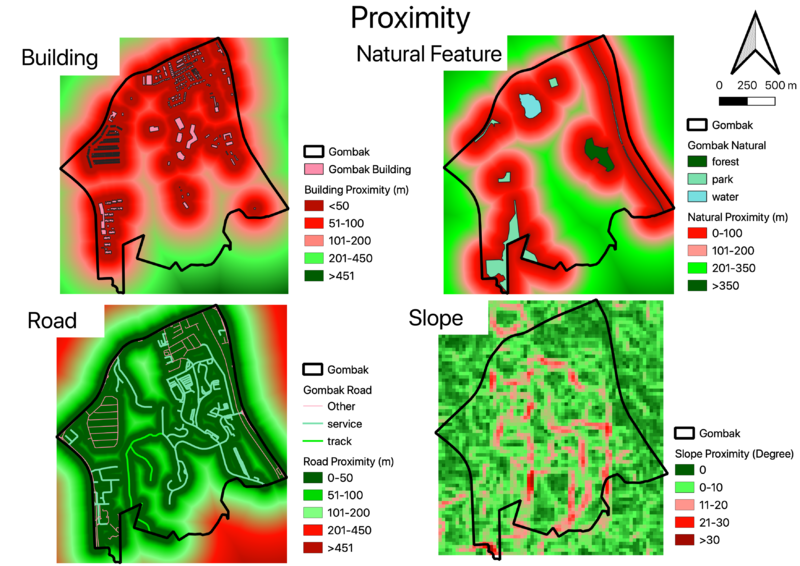
Proximity of the Four Factors
Building Proximity (Health Risk Factor)
The green color depicts suitable area while red color otherwise. The furthest distance from the buildings is 816.36 meters. The southern part and some part of the central are the suitable lot for building a quarantine centre.
Natural Features Proximity (Natural Conservation Factor)
The green color depicts suitable area while red color otherwise. The furthest distance from the natural conservation is 847.27 meters. The southern, central, and some part of west are the suitable lot for building a quarantine centre.
Road Proximity (Accessibility Factor)
The green color depicts accessible area while red color otherwise. The furthest distance from the road is 717.03 meter. I have chosen below 200 meter as a cut off for accessible area since walk time for 200 meter should take around 5 minutes. Most area of Gombak are quite accessible by roads except the southern part as said above. Therefore, looking at the road proximity, all area is suitable to build the quarantine centre except southern area.
Slope Proximity (Economy Factor)
The green color depicts flatter area while red color otherwise. The steepest area has a degree of 36.43. Despite high coverage of elevated area, it seems that Gombak subzone as a rather flatten steep. It is suitable to build the quarantine centre on the green area of the map.