Difference between revisions of "SMT201 AY2019-20T1 EX2 Wang Youjin"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[File:Basemap allinone.PNG| | + | [[File:Basemap allinone.PNG|900px|center]] |
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center;line-height:normal'><span | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Aggregated View=== | ===Aggregated View=== | ||
| − | [[File:1.4.PNG| | + | [[File:1.4.PNG|900px|center]]<br> |
Description | Description | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 9 November 2019
Contents
Part 1: Base Map Views
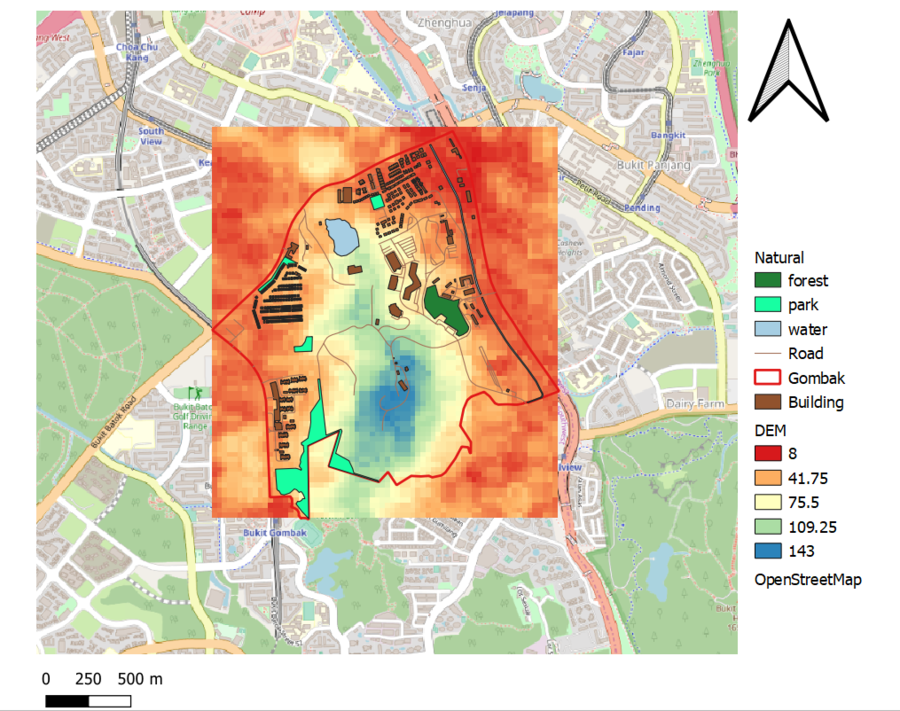
In order to identify a location suitable for building a National Communicable Disease Quarantine Centre given in the task question, we have to first look at the important aspects for consideration in targeted Gombak planning subzone by building the base map views 1) Gombak Road 2) Gombak Building 3) Gombak Natural Features 4) Digital Elevation together with targeted study area - Bukit Gombak:
Map with 4 viewsGombak Study Area with Buildings, Roads, Natural Feature and Elevation in 1 View
Gombak Target Road
|
Aggregated ViewDescription Digital Elevation Layer
|
Write-up
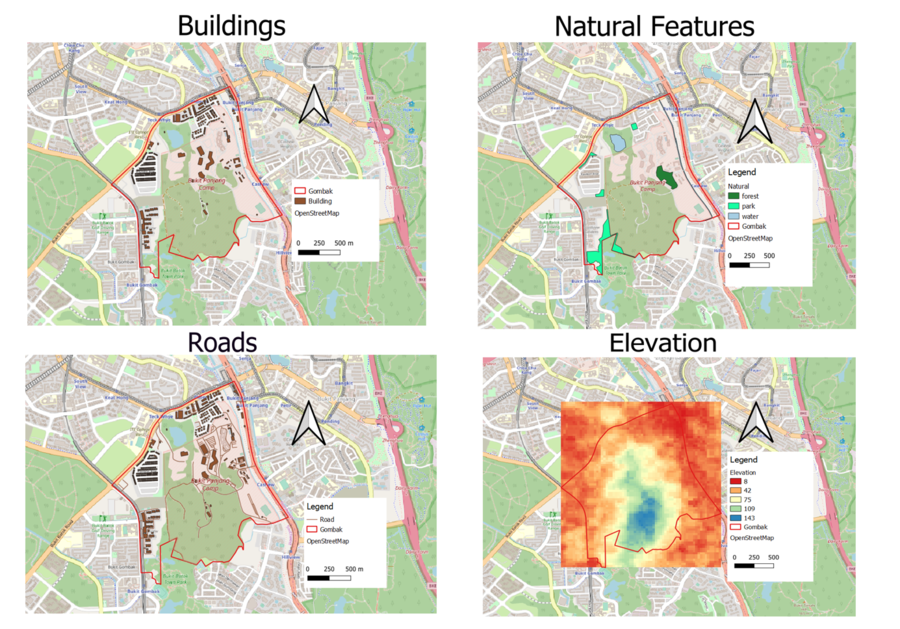
1.Roads(only service & tracks)In view of the Accessibility Factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be close to local roads to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage, we are using roads layer as one of the base map. The data has been cleaned up as required to show only categorized service roads using thicker strokes and tracks using thinner strokes. There are 199 service roads and only 2 tracks. From observation,the service roads spread across of the target area and are more concentrated in the north east didtrict.
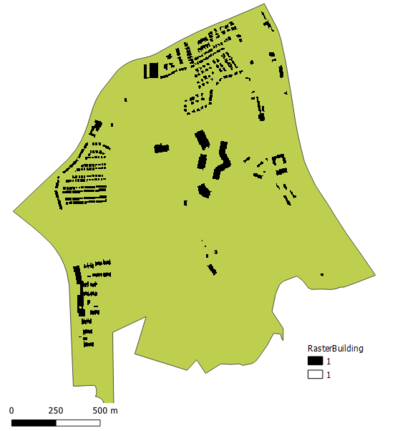
2. BuildingIn view of the Health Risk factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site to be away from population to prevent the diseases from spreading to the public. By using categorize visualization of the building types, we can see there are 7 types including clinic, construction site, garage, place of worship, public space, residential area, and train station. However, 95%(505) of the building data are not known of its type which make it hard to present a clear understanding of the building type by categorizing it.
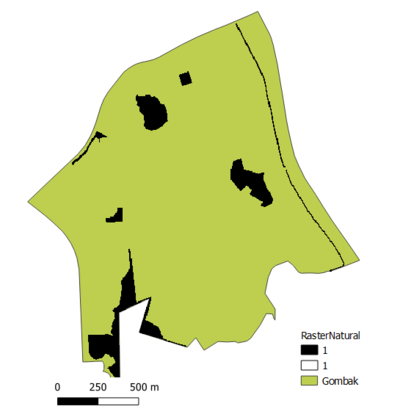
3.Natural FeaturesIn view of the Natural Conservation factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should be also be away from natural features, such as forests, parks and water bodies. From the OSM data, we can see there are 1 forest, 4 parks and 3 water bodies in the target area. Since these features are special regions and are reserved - we will use special color scheme to identify them 1)forest is in grey green, 2)parks is in light green 3)water bodies is in light blue.
4. Digital ElevationIn view of the Economic factor that we need to consider that requires the selected site should avoid steep slopes to reduce the development costs for cut-and-fill construction techniques. The lowest elevation is 8 meters above sea level, depicted in grey/white.The highest elevation with 145 meters above sea level, depicted in dark black. |
Part 2: Factor Layers:Proximity and Slope Map Views
Next, we did a proximity analysis to show the closeness of all features in target area to the identified features of interest. As shown in the screenshot below, the darker parts the maps below depict higher closeness to the features of interest.
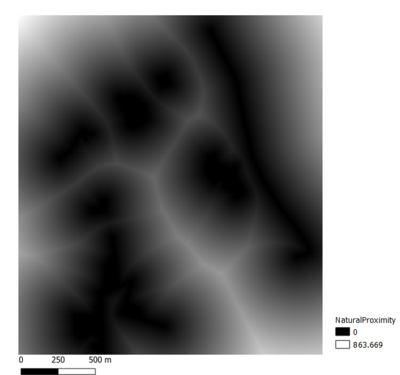
Four views showing the proximity map to 1)target roads layer, 2) buildings layer,3) target natural features layer and 4) slope layer that are created in Part 1.
| 1. View with 4 Proximity maps
|
|
Rasterized Building Layer
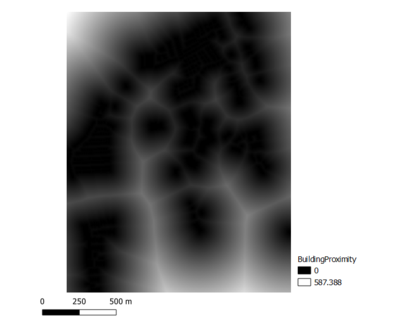
Proximity to Building
Rasterized Natural Features Map
Proximity to Natural features
|
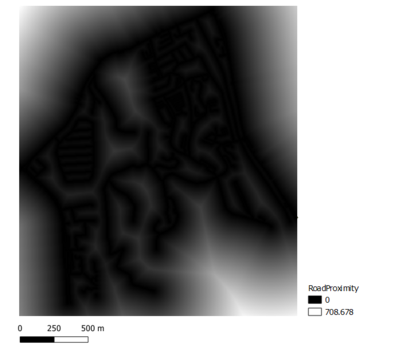
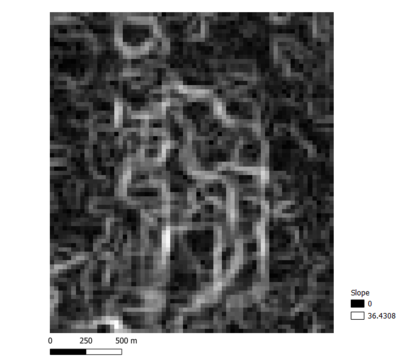
WRITE UP1. Proximity to RoadsDarker values means the roads network are closer to the feature in the targeted are, which means it's more suitable of developing a building. According to the number generated - the distance from a 5 meters by 5 meters land lot to the nearest road within Gombak is 0 meters, and the furthest distance is 452.60 meters. 2.Proximity to BuildingsLand lots with lighter values have higher suitability to be chosen to build the quarantine center because these locations are further away from the population. The distance from a 5 meters by 5 meters land lot to the nearest building that is located within Gombak is 0 meters, and the furthest distance is 561.81 meters. 3.Proximity to NatureLand lots that are further away from natural features have lighter values in the map, and they have higher suitability to be chosen to build the quarantine center. The distance from a 5 meters by 5 meters land lot to the nearest forest, park or water body is 0 meters, and the furthest distance is 517.93 meters. All land lots with distance to the nearest natural feature of at least 200 meters are shown in white in the map above. 4.Slope AnalysisSlopes are calculated using proximity to elevation. Land lots with darker values have flatter surfaces, and thus they have higher suitability to build the quarantine center. The minimum steepness of a 30 meters by 30 meters land lot is 0 degrees, which indicates flat land; while the maximum steepness is approximately 37.45 degrees. As seen from the map, most of the land lots in Gombak are flat, despite the rather uneven elevation in the region.
Slope
|
Part 3: Factor Layers with Criterion Scores
With the proximity analysis done on the 4 selected features of interest, next we need to quantify the suitability. We will use the Max- Min method to standardise the proximity analysis results:
Standardised Results = [Proximity to Features - Min(Proximity to Features)] / [Max(Proximity to Features) - Min(Proximity to Features)]
Results -
With the standardised scores, we can move on and calculate the criterion scores.
| Factor Layer | Criterion Scores |
|---|---|
| 1. Economic Factor |
he selected site should avoid steep slope. This is because construction at steep slope tends to involve a lot of cut-and-fill and will lend to relatively higher development cost.
School types
Description
|
| 2. Accessibility Factor |
The selected site should be close to existing local roads, namely: service roads and tracks. This is to ensure easy transportation of building materials during the construction stage [[File:|600px|center]] Road Network
|
| 3. Health Risk Factor |
The selected site should be away from population i.e. housing areas and offices in order to avoid disease spreading to the nearby population Land Use
|
| 4.Natural Conservation Factor |
The selected site should be away from forested land, park and water [[File:|600px|center]] Road Network
|
Part 4: Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) input matrix
An Analytical Hierarchical Process input matrix and result report and a short description of not more than 150 words discussing the analysis results.
| Factor Layer | Criterion Scores |
|---|---|
| input matric |
Description
School types
Description
|
Part 5: Suitability land lot
A map layout with the suitability land lot(s) and a short description of not more than 200 words commenting on each of the suitable land lot identified.
| Conclusion | Map Layout |
|---|---|
| Land Lot |
Description
School types
Description
|