Difference between revisions of "SMT201 AY2019-20G1 Ex1 Kning Kit Siang"
Kskning.2018 (talk | contribs) |
Kskning.2018 (talk | contribs) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
* '''Aged population (+65) in 2010 and 2018.''' | * '''Aged population (+65) in 2010 and 2018.''' | ||
| − | [[File: Aged Population of Singapore in 2010 .png|center|800px]] | + | [[File:Aged Population of Singapore in 2010.png|center|800px]] |
| + | Based on the choropleth map above, majority of the ageing residents in Singapore live in Bedok, followed by Ang Mo Kio, Hougang and Bukit Merah, during the year 2010. Furthermore, the aged population of Singapore are more concentrated in the east region of Singapore compared to the other regions. Certain areas have low aged population as these areas may be used for other sectors such as industrial sector and tourist destinations. A few examples which can be observed from the map are the area of Western Water Catchment, Tuas and Changi. | ||
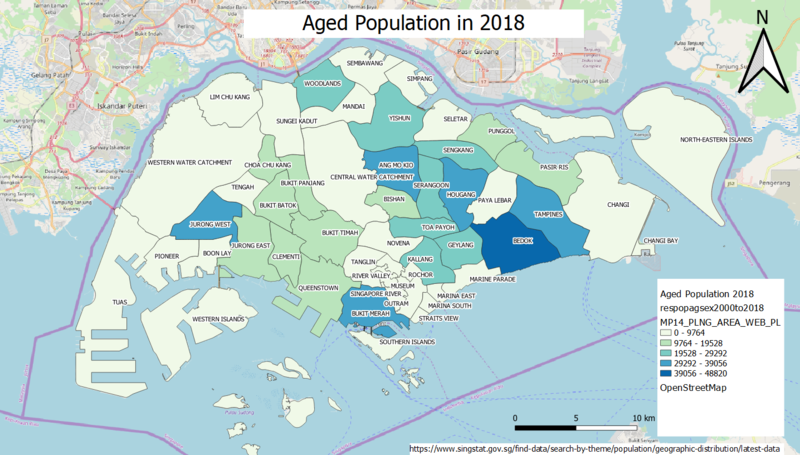
[[File:Aged Population of Singapore in 2018.png|center|800px]] | [[File:Aged Population of Singapore in 2018.png|center|800px]] | ||
| + | However, in 2018, the aged population in certain areas of Singapore has increased. For example, Sengkang and Serangoon have lower aged population in 2010 than in 2018. The aged population in Jurong West, Tampines and Queenstown have also increased. On the other hand, Bedok remains to be the area with the highest aged population in Singapore and the east region of Singapore also remains as having higher aged population compared to the other regions. | ||
* '''Proportional of aged population in 2010 and 2018.''' | * '''Proportional of aged population in 2010 and 2018.''' | ||
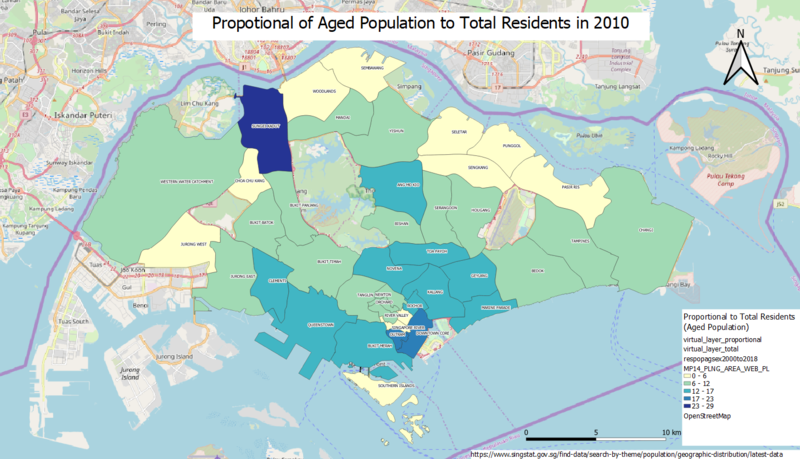
| − | [[File:Proportional of Aged Population to Total Residents in 2010.png|center|800px]] | + | [[File:Proportional of Aged Population to Total Residents in 2010 New.png|center|800px]] |
| + | When the aged population of every area is proportionate to the total residents of all age groups in every area respectively, the area of Sungei Kadut has the highest proportion of aged population. Areas within the central region of Singapore also have higher proportional of aged population to total residents compared to the other regions of Singapore. As a conclusion, the proportional of aged population to total residents are moderate in 2010. | ||
| − | [[File:Proportional of Aged Population to Total Residents in 2018.png|center|800px]] | + | [[File:Proportional of Aged Population to Total Residents in 2018 New.png|center|800px]] |
| + | In the year 2018, the proportional of aged population to total residents has increased. Many of the regions in Singapore have faced an increase in the proportion of aged population. Besides, most of the areas in the central region of Singapore and the areas around this region have higher proportion of aged population compared to 2010. | ||
* '''Percentage change of aged population between 2010 and 2018.''' | * '''Percentage change of aged population between 2010 and 2018.''' | ||
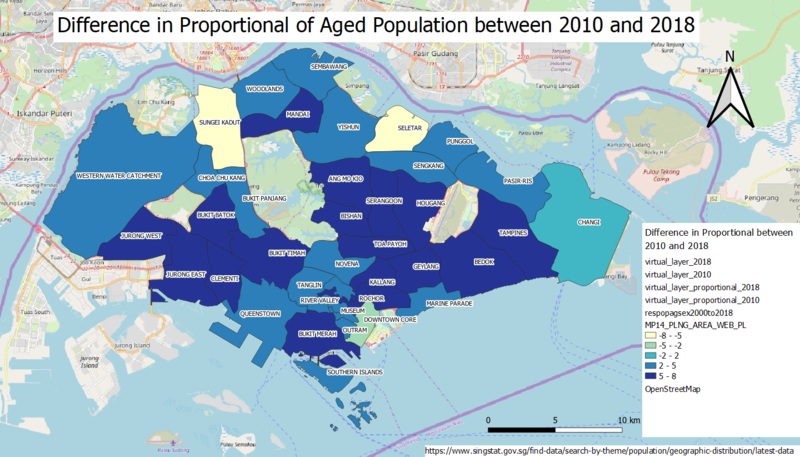
[[File:Difference in Proportional of Aged Population between 2010 and 2018.png|center|800px]] | [[File:Difference in Proportional of Aged Population between 2010 and 2018.png|center|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Based on the choropleth map above, many of the areas in Singapore faced a high increase in the proportional of aged population to total residents from the year 2010 to the year 2018. This has caused most of the regions of Singapore to face a rapid growth in ageing, especially the central region and the east region. This shows that Singapore could be facing an ageing population issue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Explain the reasoning behind your classification choices, how you derived the new variables and handled missing values, and any other relevant judgments and assumptions. Please limit this discussion to a maximum of not more than 500 words.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | For all the choropleth maps created, graduated technique has been used as the main classification choice in order to classify the areas of Singapore with the most number of aged population, highest number of proportional of aged population to total residents and largest difference of proportional of aged population to total residents between the year 2010 and 2018. As most of these variables are quantitative and use numerical values, it is more suitable to use graduated technique to represent the ranges and continuous values for building the digital map. Furthermore, as the data used, which is the statistics of age group and gender by planning area/subzone, included years from 2000 to 2018, the task of selecting specific data is required to only include the data which are needed, that is the age group and gender data for year 2010 and year 2018. QGIS 3.8 stores these data in the form of database which allows it to have SQL functions in order to select the required data. Therefore, SQL functions have been used to select the required data in the year 2010 and year 2018 as well as to create new variables/layers to help in finding the number of aged population in a particular planning area and calculating the proportional of aged population to total residents in every planning area. Missing values have been ignored as no available data could be found and little number of missing values would have less effect on the mapping of the data on the digital map. Moreover, an assumption for missing values has been made which is, as most of the areas with the missing values are more likely to be a non-residential area, the missing values can be considered to be ignored. | ||
Latest revision as of 22:52, 15 September 2019
Part 1: Thematic Mapping
- Using school information from data.gov.sg, prepare a thematic map showing the distribution of public education institution by school types such as primary, secondary, etc.
To prepare a thematic map showing the distribution of public education institution, a comma-separated values (CSV) file, containing the data of the education institution, has been used with MMQGIS in order to geocode the data in the file into a geospatial layer which can be interpreted by QGIS 3.8. The projection system used is SVY21/Singapore TM EPSG:3414 as the data analysed is located in the area of Singapore. Furthermore, a categorized technique has been used as a classification method because the different types of schools which are public education institution of Singapore have qualitative characteristics and can be distinguished by categorizing them. Different symbols, which mostly are related to education, have been used as well to represent the different types of schools to display the locations of the education institution on the digital map and show which region would most of the education institution located in.
- Using road GIS data of LTA, prepare a thematic map showing the hierarchy of road network system of Singapore such as expressway, major road, minor road, etc.
The road network system of Singapore consists of expressways, major roads and minor roads. A new class, known as RD_CLASS, has been added to the attribute table of the RoadSectionLine layer as a representation of the feature of each road, whether each road is an expressway, a major road or a minor road. This helps in categorizing each road on the digital map clearly on the different roads which have been constructed in every region of Singapore. Different colours have been used as well to easily distinguished the feature of each road on the digital map which provides better visualisation of the hierarchy of road network system of Singapore.
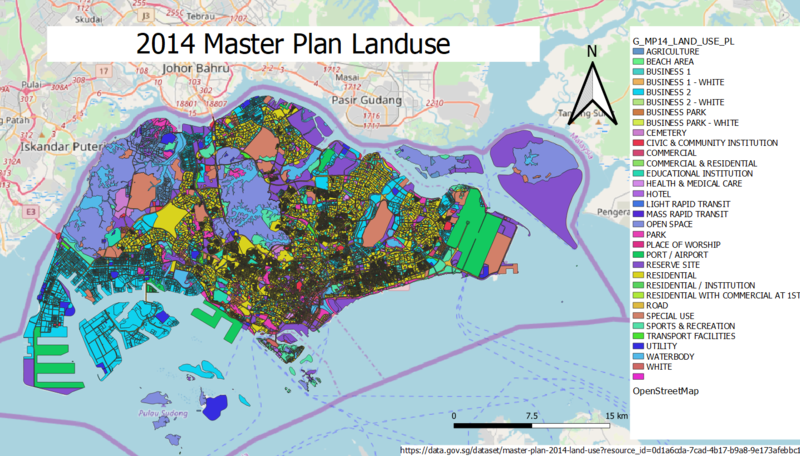
- Using master plan landuse GIS data from data.gov.sg, prepare a thematic map showing 2014 Master Plan Landuse.
A 2014 Master Plan Landuse shapefile has been used to create a thematic map showing 2014 Master Plan Landuse of Singapore. This shapefile is compatible with QGIS 3.8 which helps with the mapping of the landuse of Singapore for various purposes and the development of the country. As every area of the land has been used for its own purpose, these areas can be distinguished easily and classified by using the categorized technique. By using the categorized technique, different colours have been used distinctively to represent every uses and facility which are allocated on different region of Singapore. This helps to give a clear visualisation of what purpose which every part of the land in Singapore has been used for.
Part 2: Choropleth Mapping
- Using planning subzone GIS data from data.gov.sg and Singapore residents by age group and gender, prepare the following choropleth maps:
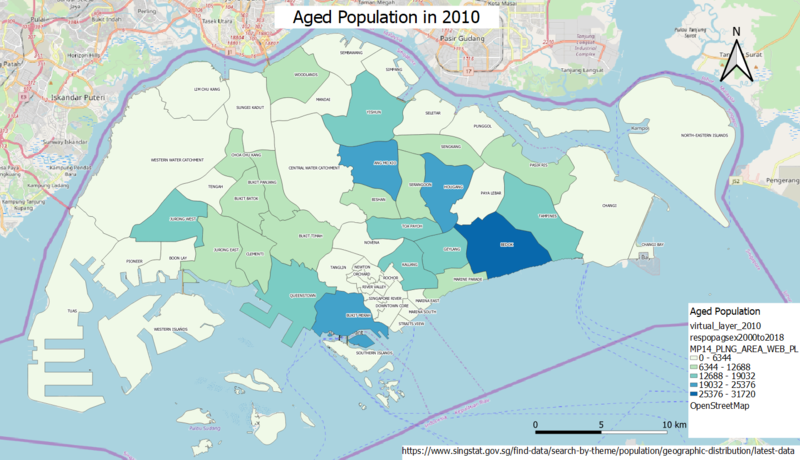
- Aged population (+65) in 2010 and 2018.
Based on the choropleth map above, majority of the ageing residents in Singapore live in Bedok, followed by Ang Mo Kio, Hougang and Bukit Merah, during the year 2010. Furthermore, the aged population of Singapore are more concentrated in the east region of Singapore compared to the other regions. Certain areas have low aged population as these areas may be used for other sectors such as industrial sector and tourist destinations. A few examples which can be observed from the map are the area of Western Water Catchment, Tuas and Changi.
However, in 2018, the aged population in certain areas of Singapore has increased. For example, Sengkang and Serangoon have lower aged population in 2010 than in 2018. The aged population in Jurong West, Tampines and Queenstown have also increased. On the other hand, Bedok remains to be the area with the highest aged population in Singapore and the east region of Singapore also remains as having higher aged population compared to the other regions.
- Proportional of aged population in 2010 and 2018.
When the aged population of every area is proportionate to the total residents of all age groups in every area respectively, the area of Sungei Kadut has the highest proportion of aged population. Areas within the central region of Singapore also have higher proportional of aged population to total residents compared to the other regions of Singapore. As a conclusion, the proportional of aged population to total residents are moderate in 2010.
In the year 2018, the proportional of aged population to total residents has increased. Many of the regions in Singapore have faced an increase in the proportion of aged population. Besides, most of the areas in the central region of Singapore and the areas around this region have higher proportion of aged population compared to 2010.
- Percentage change of aged population between 2010 and 2018.
Based on the choropleth map above, many of the areas in Singapore faced a high increase in the proportional of aged population to total residents from the year 2010 to the year 2018. This has caused most of the regions of Singapore to face a rapid growth in ageing, especially the central region and the east region. This shows that Singapore could be facing an ageing population issue.
- Explain the reasoning behind your classification choices, how you derived the new variables and handled missing values, and any other relevant judgments and assumptions. Please limit this discussion to a maximum of not more than 500 words.
For all the choropleth maps created, graduated technique has been used as the main classification choice in order to classify the areas of Singapore with the most number of aged population, highest number of proportional of aged population to total residents and largest difference of proportional of aged population to total residents between the year 2010 and 2018. As most of these variables are quantitative and use numerical values, it is more suitable to use graduated technique to represent the ranges and continuous values for building the digital map. Furthermore, as the data used, which is the statistics of age group and gender by planning area/subzone, included years from 2000 to 2018, the task of selecting specific data is required to only include the data which are needed, that is the age group and gender data for year 2010 and year 2018. QGIS 3.8 stores these data in the form of database which allows it to have SQL functions in order to select the required data. Therefore, SQL functions have been used to select the required data in the year 2010 and year 2018 as well as to create new variables/layers to help in finding the number of aged population in a particular planning area and calculating the proportional of aged population to total residents in every planning area. Missing values have been ignored as no available data could be found and little number of missing values would have less effect on the mapping of the data on the digital map. Moreover, an assumption for missing values has been made which is, as most of the areas with the missing values are more likely to be a non-residential area, the missing values can be considered to be ignored.