Group06 Elec3city Proposal
Contents
Project Motivation
When it comes to the government’s push for efficient energy usage, most effort is expended on the efficiency of energy sources – e.g. using less carbon-intensive fuels (https://www.nea.gov.sg/our-services/climate-change-energy-efficiency/energy-efficiency/energy-efficient-singapore). However, hitherto, there has been scant statistical analysis on possible causes of inexpedient energy usage by households, with consideration of their varied age structure and the geospatial variation of environmental conditions (e.g. temperature’s effect on energy consumption).
Our team sees geospatial analytical tools (such as R) as thus far largely unexploited in exploring the origins of geospatial variation in energy consumption and is thus using spatial interpolation techniques (such as kriging) to provide an app which allows for authorities in Singapore such as the National Environment Agency to understand with data-driven evidence the origins of variation in Singapore household energy consumption so as to have more targeted efforts to reduce energy wastage.
Project Objective
Deliver a dynamic (interactive) application that provides authorities such as the National Environment Agency and Housing Development Board with the ability to:
- View monthly and yearly temperature geospatial variation in Singapore, and compare that to energy consumption at building level granularity
- View housing composition (e.g. age, income and race) geospatial variation, and compare that to energy consumption at a building level granularity
so as to make data-informed, targeted decisions to promote reduction of energy usage among varying types of households in Singapore, where hitherto there has been a blanket approach.
Data
Literature Review
In our due diligence for the project, the team looked at multiple research papers to inform and influence us in the best practices for analyzing geospatial variation in energy use, when it is to be compared against variables such as temperature and housing composition.
1. Appropriate use of Interpolation Methods in GIS - Mitas, L. and Mitasova, H. (2005) Spatial Interpolation, Chap. 34 Spatial InterpolationAim of literature: to enlighten reader of the appropriate interpolation method for different GIS themes.
Methodology:
1. Inverse Distance Weighted Interpolation (IDW) - rejected
- Con: Poor at "reproducing the local shape implied by data"
- Con: "produces local extrema at the data points"
2. Kriging - rejected
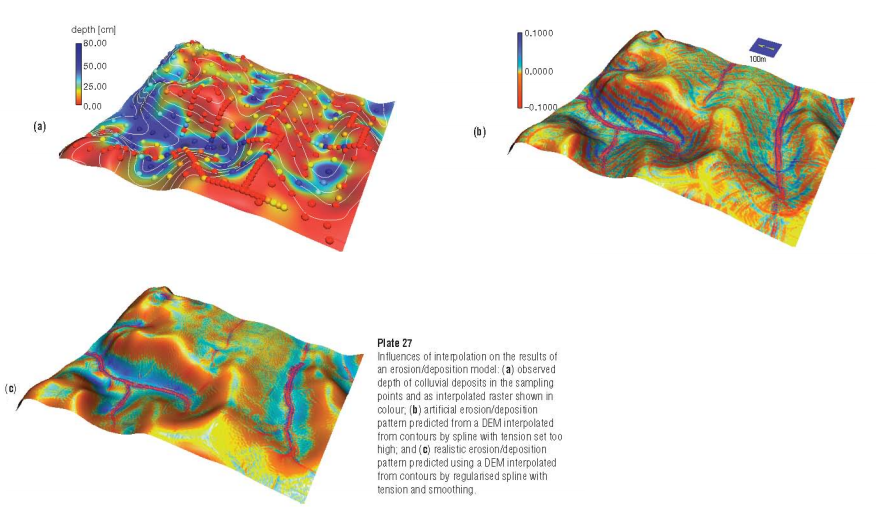
- Con: While good at predicting spatial distribution of uncertainty, it is less successful for applications where local geometry and smoothness are the key issues - Critical weakness for our interpolation of temperature data where granularity is at housing block level, thus Kriging is rejected.
3. Regularised spline with tension (RST) - adopted
Learning Points:
Areas for improvement:
Approach
Techniques:
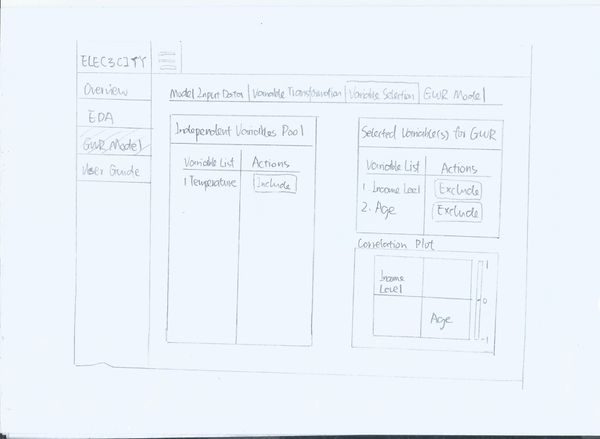
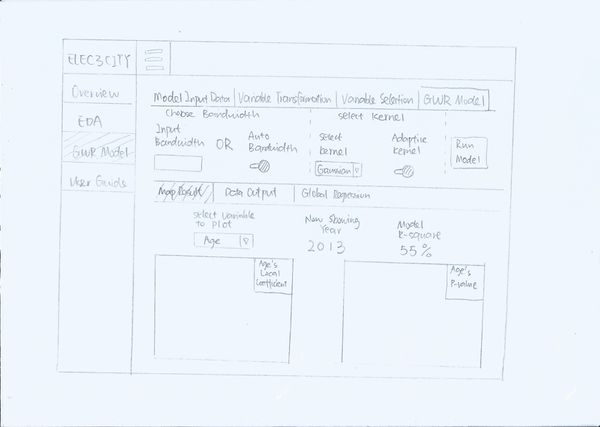
Web Application Design
Design Inspiration
The dashboard design is inspired by https://stanleyadion.shinyapps.io/AmazeingCrop
Initial Storyboard
Project Challenges
| Key Challenges | Description | Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Temperature Data Collection | We can only download the temperature data from Meteorological Service Singapore for one station and one month each time. There are more than 60 stations and 4 years of data to be downloaded for this project, which can be very time consuming. |
|
| 2. | Imperfect Temperature Data | Temperature information is only collected at the designated temperature stations. |
|
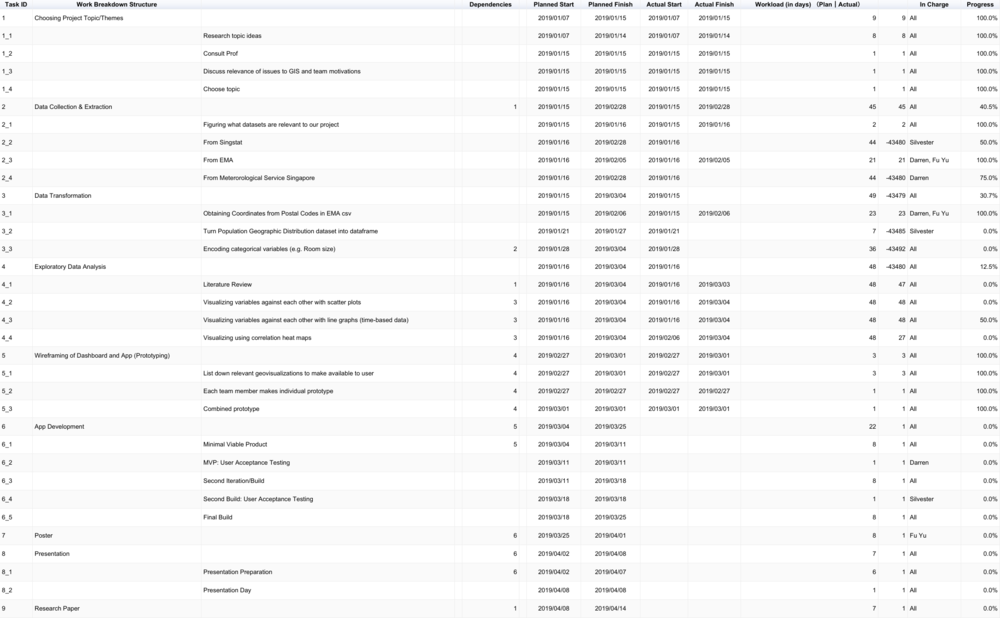
Project Timeline
Gantt Chart of Team's Timeline - FULL Updated Version
Snapshot of Gantt Chart (as of 3 March 2019)
|
No. |
Name |
Date |
Comments |
|
1. |
Insert your Name here |
Insert Date here |
Insert Comment here |
|
2. |
Insert your Name here |
Insert Date here |
Insert Comment here |
|
3. |
Insert your Name here |
Insert Date here |
Insert Comment here |