Difference between revisions of "XccessPoint Proposal"
m (Project Description and Motivation) |
(Literature Review part 1) |
||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <div style="font-size:150%; font-weight:bold;text-align: center; border-bottom:solid #044CA4;">Literature Review</div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p>Literature review of relevant research paper on spatial analysis of accessibilities are conducted to enhance our project methodology.</p> | ||
| + | <div style="width: 80%;> | ||
| + | <b>1.Site Suitability Evaluation for Ecotourism Using GIS & AHP: A Case Study of Surat Thani Province, Thailand</b></br></br> | ||
| + | <b>Study Objective:</b></br> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | This paper aims to identify and prioritize the potential ecotourism sites using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Analytical Hierarchy Process( AHP) in Surat Thani Province. The factors in consideration for suitability for the land ecosystems include landscape/naturalness, wildlife, topography, accessibility and community characteristics.</p> | ||
| + | </br> | ||
| + | <p>Visualization:</p> | ||
| + | <div style="width: 50%;> | ||
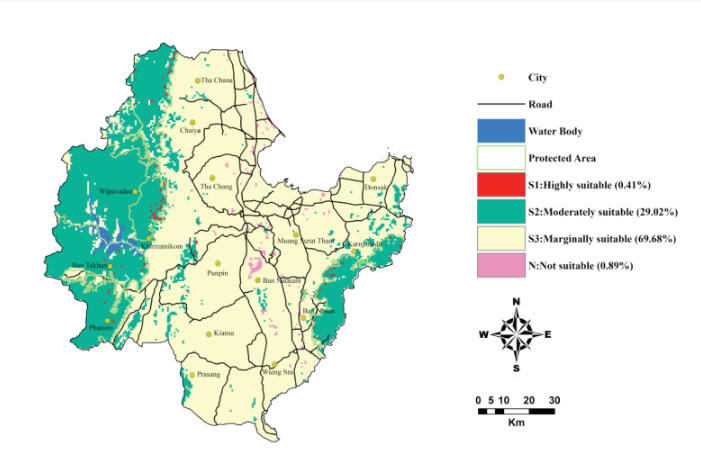
| + | [[File:Image1.png|frameless|Suitability Map for Ecotourism in Surat Thani Province in Thailand|800px]] | ||
| + | <p class='center'>Suitability Map for Ecotourism in Surat Thani Province in Thailand</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div style="width: 50%;> | ||
| + | [[File:Image2.png|frameless|Schematic Representation of the Methodology|800px]] | ||
| + | <p class='center'>Schematic Representation of the Methodology</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div style="width: 50%;> | ||
| + | [[File:Image3.png|frameless|AHP Matrix for Pairwise Comparisons and the Consistency Ratio Estimation|800px]] | ||
| + | <p class='center'>AHP Matrix for Pairwise Comparisons and the Consistency Ratio Estimation</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div style="width: 80%; margin-left: 20px;"> | ||
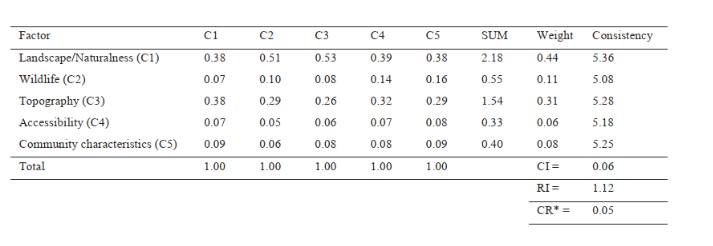
| + | <b>1.Determination of Weights using AHP</b> | ||
| + | <p>AHP is one extensively used Multi-Criteria Decision Making technique (developed by Saaty in 1980) used in structural decision making process for complex problems that involves multiple criteria across different hierarchical levels. Pairwise comparisons method is used to compare the criteria and allow for evaluation of relative significance of all parameters. Expert opinions were taken into consideration for the comparisons. Pairwise comparison uses a scale of 1 to 9 which 1 means having equal importance while 0 means having extreme importance. Reciprocal pairwise comparisons is used for opposite comparison of facilities. </p> | ||
| + | <b>2.Factoring in Decision Making Inconsistency</b> | ||
| + | <p>To ensure consistent judgement of decision makers, AHP efficiency criteria are measured by Consistency Relationship (CR = Consistency Index/Random Index). If CR is smaller than 0.10, degree of consistency will be fairly acceptable. Otherwise if it exceeds 0.10, inconsistencies exist in the evaluation process and we need to reject the pairwise comparisons and reiterate the process.</p> | ||
| + | <b>3.Land Suitability Assessment</b> | ||
| + | <p>The total suitability score “Si” for each land unit (i.e. each raster cell in the map) was calculated from the linear combination of suitability score obtained for each factor and criteria involved.</p> | ||
| + | [[File:Image4.png|frameless| Land Suitability Assessment Formula|100px]] | ||
| + | <p>where “n” is the number of factors, “Wi” is the multiplication of all associated weights in the hierarchy of “ith” factor ( as seen in Table 5) and “Ri” is a rating given for the defined class of the “ith” factor found on the assessed land unit</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <b>Learning Point:</b> | ||
| + | <p>- AHP will be an highly effective methodology for us to reduce the complexity in computing overall accessibility score by structurally factoring the pairwise comparisons of all facilities. Consistency Ratios need to be factor in too.</p> | ||
| + | <p>- Linear weighted combination of accessibility score could be adopted for our study</p> | ||
| + | <b>Caveat:</b> | ||
| + | <p>As this analysis is done on a proprietary software (ArcGIS 9.3), it is difficult for researchers to replicate the methodology of the research paper unless they have access to such software. As we aim to provide urban planners an open-source and easily reproducible application through R programming, there is a need to find similar packages for such methodology on R programming. </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
<div style="font-size:150%; font-weight:bold;text-align: center; border-bottom:solid #044CA4;">Application Prototype</div> | <div style="font-size:150%; font-weight:bold;text-align: center; border-bottom:solid #044CA4;">Application Prototype</div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
| − | |||
[[File:UI prototype-1.png|frameless|500px|]] | [[File:UI prototype-1.png|frameless|500px|]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 12 April 2019
| Home | The Team | Proposal | Poster | Application | Research Paper |
“This is what inequality looks like.” You Yenn Teo’s recent best seller book uncovers the heightened tension on social inequalities in Singapore. It has motivated to use to delve deeper into the current situations of inequality in Singapore. One way to understand the inequality is to examine the accessibility to many key essential facilities for an ordinary Singaporean living in Housing Development Board units. The aspect of accessibility to look into includes the distance to healthcare facilities (General Practitioner Clinics, Polyclinics and Hospitals), transportation infrastructure (MRT and Bus Stops) , schools, pre-school, police stations, and hawker centres for all HDBs in different planning subzones. We hope to develop an accessibility study tool for urban planners to better strategize the development of new facilities for achieving greater equality for an ordinary Singaporean. For instance, how would Land Transport Master Plan 2040 effectively improve the existing accessibilities to transport facilities.
Our team's objective is to analyse and determine how these facilities such as transportation, school and healthcare services would impact the accessibility level around HDB.
The government has been finding sustainable ways to tackle the increasing inequality and stratification in Singapore.With constant development and improvement of infrastructure around Singapore, the impact on accessibility has not really been research upon.
|
Dataset |
Description |
Data Type |
Source(s) |
|
Singapore Regions |
To facilitate urban planning, the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA) divides Singapore into 5 regions, namely Central, West, North, North-East and East Regions. |
SHP |
|
|
Singapore Planning Area |
Indicative polygon of planning area boundary. To facilitate urban planning, the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA) divides Singapore into 55 planning areas |
SHP |
|
|
Singapore Planning Subzone |
Indicative polygon of subzone boundary. The Planning Regions are divided into smaller Planning Areas. Each Planning Area is further divided into smaller subzones which are usually centred around a focal point such as neighbourhood centre or activity node. |
SHP |
|
|
HDB |
List of HDB location via postal code |
CSV |
|
|
School facilities |
List of education facilities in Singapore |
CSV,KML |
|
|
Government Markets Hawker Centres |
Contains Address of Hawker Centres in Singapore |
KML |
|
|
Heathcare Facilities |
Contains Address to Healthcare Facilities in Singapore |
Website Information |
|
|
LTA Mrt station |
The layer contains the locations of MRT station exits. |
KML |
|
|
Bus Stops |
All bus stops, bus interchanges, bus terminals in Singapore. |
CSV |
Literature review of relevant research paper on spatial analysis of accessibilities are conducted to enhance our project methodology.
1.Site Suitability Evaluation for Ecotourism Using GIS & AHP: A Case Study of Surat Thani Province, Thailand
Study Objective:
This paper aims to identify and prioritize the potential ecotourism sites using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Analytical Hierarchy Process( AHP) in Surat Thani Province. The factors in consideration for suitability for the land ecosystems include landscape/naturalness, wildlife, topography, accessibility and community characteristics.
Visualization:
1.Determination of Weights using AHP
AHP is one extensively used Multi-Criteria Decision Making technique (developed by Saaty in 1980) used in structural decision making process for complex problems that involves multiple criteria across different hierarchical levels. Pairwise comparisons method is used to compare the criteria and allow for evaluation of relative significance of all parameters. Expert opinions were taken into consideration for the comparisons. Pairwise comparison uses a scale of 1 to 9 which 1 means having equal importance while 0 means having extreme importance. Reciprocal pairwise comparisons is used for opposite comparison of facilities.
2.Factoring in Decision Making Inconsistency
To ensure consistent judgement of decision makers, AHP efficiency criteria are measured by Consistency Relationship (CR = Consistency Index/Random Index). If CR is smaller than 0.10, degree of consistency will be fairly acceptable. Otherwise if it exceeds 0.10, inconsistencies exist in the evaluation process and we need to reject the pairwise comparisons and reiterate the process.
3.Land Suitability Assessment
The total suitability score “Si” for each land unit (i.e. each raster cell in the map) was calculated from the linear combination of suitability score obtained for each factor and criteria involved.
where “n” is the number of factors, “Wi” is the multiplication of all associated weights in the hierarchy of “ith” factor ( as seen in Table 5) and “Ri” is a rating given for the defined class of the “ith” factor found on the assessed land unit
Learning Point:
- AHP will be an highly effective methodology for us to reduce the complexity in computing overall accessibility score by structurally factoring the pairwise comparisons of all facilities. Consistency Ratios need to be factor in too.
- Linear weighted combination of accessibility score could be adopted for our study
Caveat:
As this analysis is done on a proprietary software (ArcGIS 9.3), it is difficult for researchers to replicate the methodology of the research paper unless they have access to such software. As we aim to provide urban planners an open-source and easily reproducible application through R programming, there is a need to find similar packages for such methodology on R programming.
User Interface Prototype
- 1. Most of the datasets retrieved provided only addresses, not coordinates. Thus, first we had to geocode each point to get the coordinates.
- 2. Some datasets had CRS WGS84 while some had SVY21. Thus, we had to convert all to SVY21
- 3. Calculating the distance from each of the 8500 houses to each of the 5000 bus stops was computationally impossible. Thus, we had to use Raster to create a radius around each house and calculate distance from that house to the bus stops which lay within the radius to get the closest bus stop
- 4. Plotting 8000 points on a map was very cluttered and not insightful. Thus, we provided the user options to select regions/subzones/towns for better plots
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242450034_A_GIS-BASED_MULTI-CRITERIA_ANALYSIS_APPROACH_TO_ACCESSIBILITY_ANALYSIS_FOR_HOUSING_DEVELOPMENT_IN_SINGAPORE/download
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221354375_GIS-Based_Spatial_Distribution_and_Evolvement_Analysis_of_Urban_Affordable_Housing_A_Case_Study/download
Feel free to leave a comment