Difference between revisions of "Task 3: Other Factors Affecting Air Quality"
Yqchia.2017 (talk | contribs) |
Yqchia.2017 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
Local meteorology factors such as temperature, pressure, rainfall, humidity, wind are represented in the “METEO” dataset provided.<br/> | Local meteorology factors such as temperature, pressure, rainfall, humidity, wind are represented in the “METEO” dataset provided.<br/> | ||
| − | To better understand the interaction between various meteorology factors, we have built a Tableau | + | To better understand the interaction between various meteorology factors, we have built a Tableau Dashboard to visualize changes in humidity, temperature and precipitation across years, months and days. <br/> |
[[File:METEO dashboard1.jpg|900px|frameless|left]] | [[File:METEO dashboard1.jpg|900px|frameless|left]] | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
| − | '''Winters in Sofia City have high humidity and lower temperature''' | + | '''Winters in Sofia City have high humidity and lower temperature'''<br/> |
Average humidity level in winter (December) can go above 100% as compared to 60-70% range during summer seasons (June). This could be a plausible reason for higher pollutant concentration in December and January compared to other months. <br/> | Average humidity level in winter (December) can go above 100% as compared to 60-70% range during summer seasons (June). This could be a plausible reason for higher pollutant concentration in December and January compared to other months. <br/> | ||
Nonetheless, the phenomenon can also be explained by social and health reasons e.g. more household consume thermal power to heat up their homes during winter season.<br/> | Nonetheless, the phenomenon can also be explained by social and health reasons e.g. more household consume thermal power to heat up their homes during winter season.<br/> | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Precipitation shows seasonal trend across months collective but not days'''<br/> |
| − | Interestingly, there is no significant changes in volume or frequency of precipitation across the month. | + | Interestingly, there is no significant changes in volume or frequency of precipitation across the days of the month regardless of season. While instinctively rainfall might be perceived as having a "washdown" effect on the pollutants hovering in the air, for the case of Sofia City, it is not a significant factor for consideration when explaining pollutant concentration in air.<br/> |
=== Potential factor 2: Presence of local thermal power plant === | === Potential factor 2: Presence of local thermal power plant === | ||
Revision as of 02:50, 19 November 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Understanding other factors affecting air quality in Sofia
Contents
Overview
According to Unmask My City, a global initiative dedicated to improving air quality and reducing emissions in cities, Bulgaria’s sources of air pollution includes household burning of fossil fuels or biomass, and transport. Specifically, coal plants are responsible for most of Bulgaria’s PM10 and fine particle pollution PM2.5 (particles 2.5 microns or smaller) e.g. sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions.
For this task, we will examine the possible industrial reasons attributing to the air pollution situation in Sofia e.g. presence of thermal power plants, transboundary pollution etc. We also attempt to undercover the relationship between natural factors such as local meteorology and topography, and their impact on the trends highlighted in earlier tasks.
Potential factor 1: Meteorology in Sofia City
Local meteorology factors such as temperature, pressure, rainfall, humidity, wind are represented in the “METEO” dataset provided.
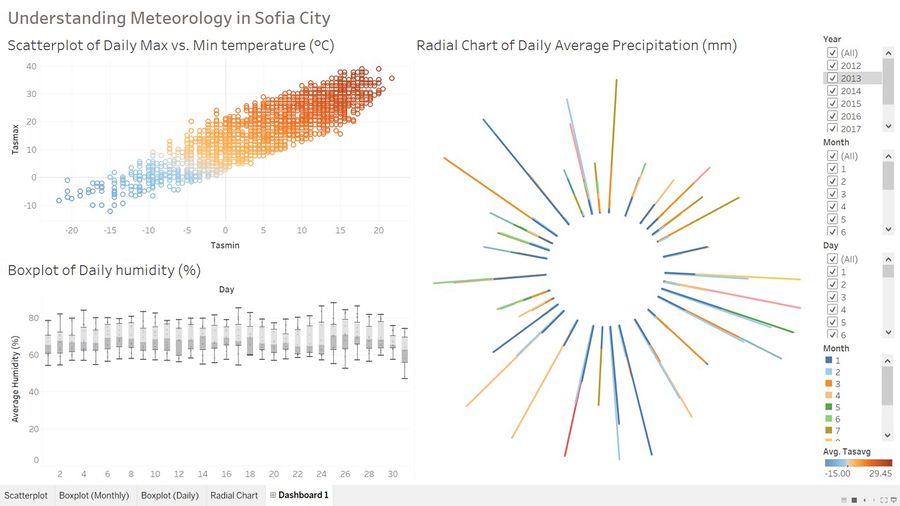
To better understand the interaction between various meteorology factors, we have built a Tableau Dashboard to visualize changes in humidity, temperature and precipitation across years, months and days.
Winters in Sofia City have high humidity and lower temperature
Average humidity level in winter (December) can go above 100% as compared to 60-70% range during summer seasons (June). This could be a plausible reason for higher pollutant concentration in December and January compared to other months.
Nonetheless, the phenomenon can also be explained by social and health reasons e.g. more household consume thermal power to heat up their homes during winter season.
Precipitation shows seasonal trend across months collective but not days
Interestingly, there is no significant changes in volume or frequency of precipitation across the days of the month regardless of season. While instinctively rainfall might be perceived as having a "washdown" effect on the pollutants hovering in the air, for the case of Sofia City, it is not a significant factor for consideration when explaining pollutant concentration in air.
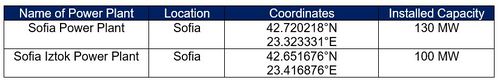
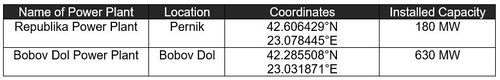
Potential factor 2: Presence of local thermal power plant
A thermal power station is a power station in which heat energy is converted to electric power. In most of the places in the world the turbine is steam-driven. Water is heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. This process is fueled by burning coals which releases sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter (PM), and heavy metals.