IS428 AY2018-19T1 Ye Min Oo
To be a Visual Detective
The assignments require you to put the concepts, methods, and techniques you had learned in class to solve a real-world problem using visual analytics techniques. Students should also use the assignments to gain hands-on experience in using the data visualization toolkits I had shared with you to complete the assignment.
Contents
Overview
Air pollution is an important risk factor for health in Europe and worldwide. A recent review of the global burden of disease showed that it is one of the top ten risk factors for health globally. Worldwide an estimated 7 million people died prematurely because of pollution; in the European Union (EU) 400,000 people suffer a premature death. The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) predicts that in 2050 outdoor air pollution will be the top cause of environmentally related deaths worldwide. In addition, air pollution has also been classified as a leading environmental cause of cancer.
Air quality in Bulgaria is a big concern: measurements show that citizens all over the country breathe in air that is considered harmful to health. For example, concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 are much higher than what the EU and the World Health Organization (WHO) have set to protect health.
Bulgaria had the highest PM2.5 concentrations of all EU-28 member states in urban areas over a three-year average. For PM10, Bulgaria is also leading on the top polluted countries with 77 μg/m3on the daily mean concentration (EU limit value is 50 μg/m3).
According to the WHO, 60 percent of the urban population in Bulgaria is exposed to dangerous (unhealthy) levels of particulate matter (PM10).
Data Preparation
| No | Issues | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | Air Tube data and EEA data show date and time as one data. So, it is hard to visualize the data based on year, month, or date. | Using “LEFT” and “RIGHT” formulas from tableau, separated the date and time data into three different categories (“By Date”, “By Hour”, and “By Year”) for better visualization.
For combined.csv LEFT(RIGHT([Datetime End],15),8) - Hour, LEFT([Datetime End],7) - Month, LEFT([Datetime End],10) - Date, LEFT([Datetime End],4) - Year For AirTube.csv LEft(RIGHT([Time],9),8) - Hour, LEFT([Time],4) - Year |
| #2 | EEA data.zip has timeseries data from 2013 to 2018 for 5 stations. However, the files are not consolidated. Each file represents a time series data of a particular year for a station. | Using R Studio, combined all the csv files into “combine.csv” which now contains 5 years of data for 5 stations. Moreover, the 5 stations data for each year is also grouped by year for better understanding of data. (Example: 2013 data will be grouped into “combined2013.csv”). |
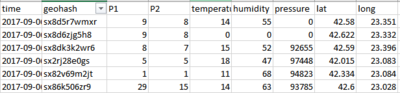
| #3 | Air Tube data has two files and each of them has a geohash data column. It was difficult to plot the location on Tableau. | Using R Studio, “geohash” data is geocoded and converted to latitude and longitude data. |
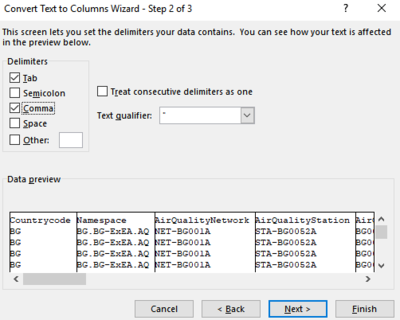
| #4 | All given data files are in csv format and each column value is separated by comma. Although the data are organized and prepared, it will be difficult when plotting certain charts or graphs. | Using Excel, all commas were delimited by comma for better analysis and understanding of data. |
Task 1: Spatio-temporal Analysis of Official Air Quality
The table below are the findings from the dataset.
| No | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
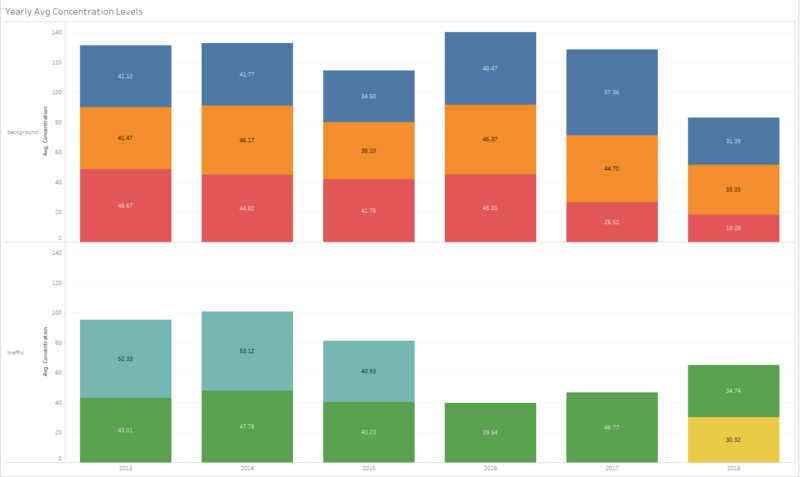
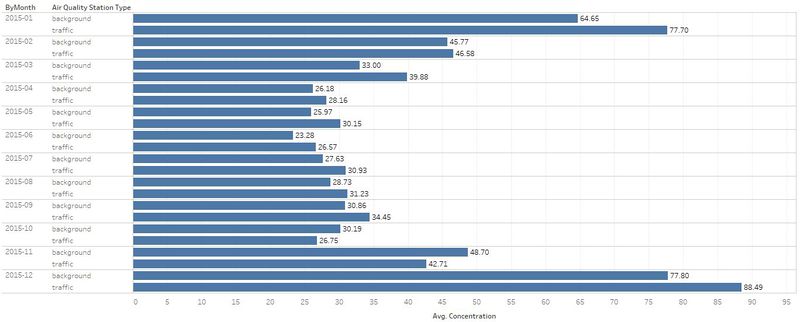
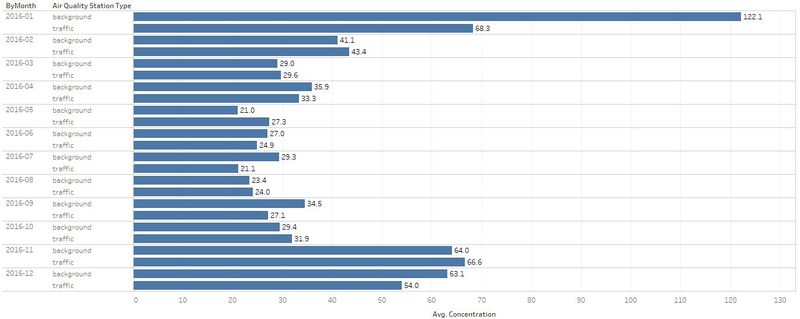
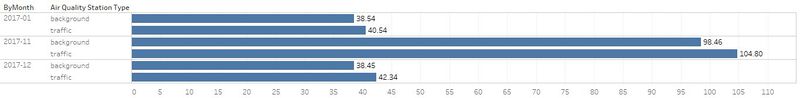
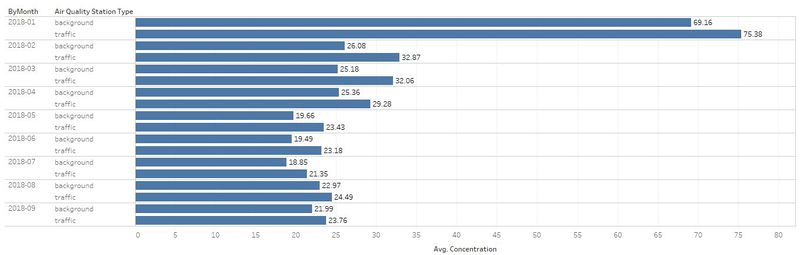
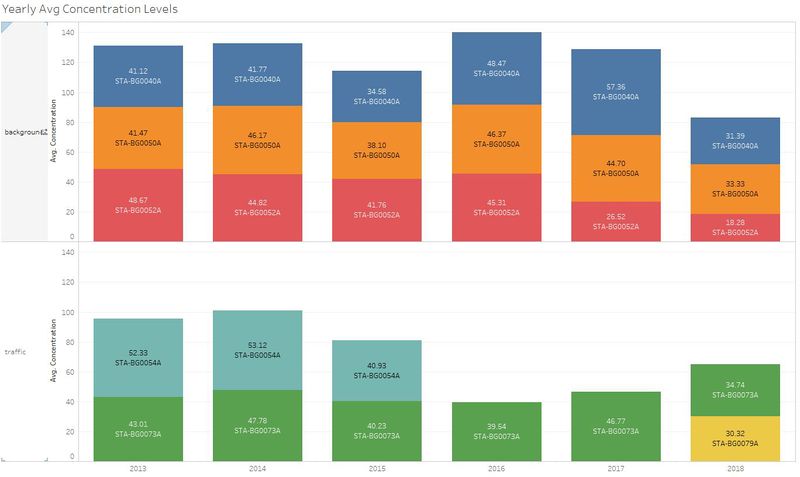
| #1 | Comparison of air concentration levels from 2013 to 2018. | |
| #2 | Typical Day air concentration level in the city. The concentration levels are withing the healthy range. | |
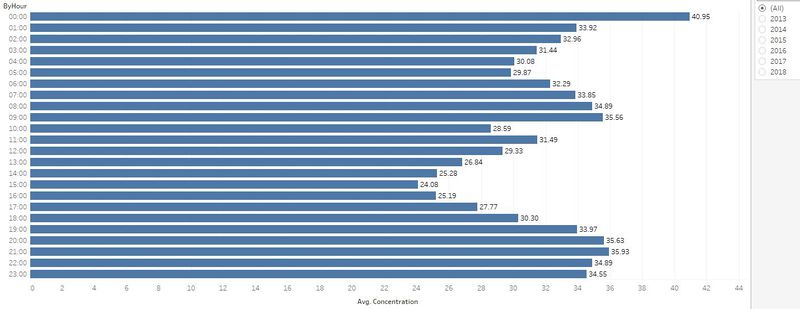
| #3 | The air concentration levels are higher in the mornings and evenings and tends to go lower in the afternoons. | |
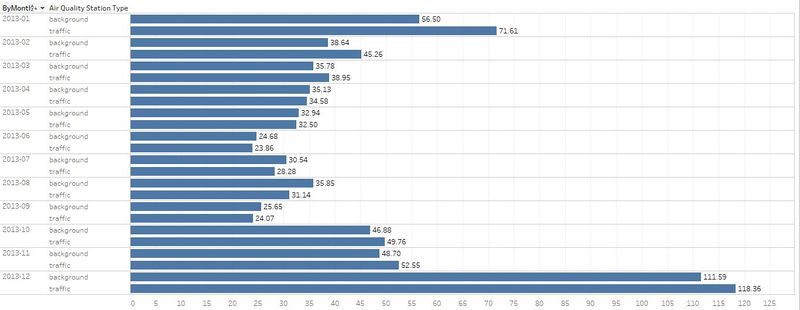
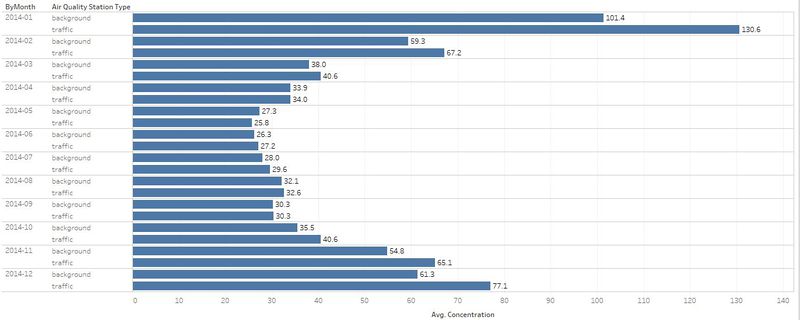
| #4 | The air concentration levels are highest during Janurary, November and December. |
Task 1: Tableau Public Link
Task 2: Spatio-temporal Analysis of Citizen Science Air Quality Measurements
Using appropriate data visualization, you are required will be asked to answer the following types of questions:
- Characterize the sensors’ coverage, performance, and operation. Are they well distributed over the entire city? Are they all working properly at all times? Can you detect any unexpected behaviors of the sensors by analyzing the readings they capture? Limit your response to no more than 4 images and 600 words.
- Now turn your attention to the air pollution measurements themselves. Which part of the city shows relatively higher readings than others? Are these differences time-dependent? Limit your response to no more than 6 images and 800 words.
The table below are the findings for sensors.
| No | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
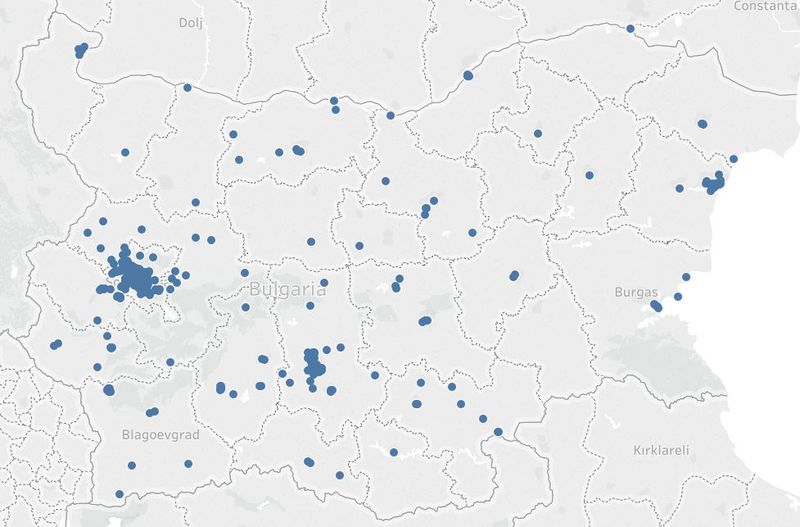
| #1 | The sensors are spreaded out across Bulgaria, but most of the sensors are located in Sofia-Grad. | |
| #2 | Not all sensors were working properly. BG0079A stopped working on 14/09/2018. BG0054A was either removed or stopped working from 2016 onwards. | BG0079A BG0054A |
The table below are the findings for air pollution measurements.
| No | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | The sensors are spreaded out across Bulgaria, but most of the sensors are located in Sofia-Grad. | |
| #2 | Not all sensors were working properly. BG0079A stopped working on 14/09/2018. BG0054A was either removed or stopped working from 2016 onwards. | BG0079A BG0054A |
| #3 | The air concentration levels are higher in the mornings and evenings and tends to go lower in the afternoons. | |
| #4 | The air concentration levels are highest during Janurary, November and December. |
Task 3
Urban air pollution is a complex issue. There are many factors affecting the air quality of a city. Some of the possible causes are:
- Local energy sources. For example, according to Unmask My City, a global initiative by doctors, nurses, public health practitioners, and allied health professionals dedicated to improving air quality and reducing emissions in our cities, Bulgaria’s main sources of PM10, and fine particle pollution PM2.5 (particles 2.5 microns or smaller) are household burning of fossil fuels or biomass, and transport.
- Local meteorology such as temperature, pressure, rainfall, humidity, wind etc
- Local topography
- Complex interactions between local topography and meteorological characteristics.
- Transboundary pollution, for example, the haze that intruded into Singapore from our neighbors.
In this third task, you are required to reveal the relationships between the factors mentioned above and the air quality measure detected in Task 1 and Task 2. Limit your response to no more than 5 images and 600 words.
The Data Sets
Four major data sets in zipped file format are provided for this assignment, they are:
- Official air quality measurements (5 stations in the city)(EEA Data.zip) – as per EU guidelines on air quality monitoring see the data description HERE…
- Citizen science air quality measurements (Air Tube.zip), incl. temperature, humidity, and pressure (many stations) and topography (gridded data).
- Meteorological measurements (1 station)(METEO-data.zip): Temperature; Humidity; Wind speed; Pressure; Rainfall; Visibility
- Topography data (TOPO-DATA)
They can be download by click on this link.
Visualisation Software Used
- Tableau
- JMP Pro
- Qlik Sense
- Microsoft Power BI
Reference
Suggestions
Kindly help comment below for further improvements.