Difference between revisions of "IS428 AY2018-19T1 Chen Yuge"
Yg.chen.2015 (talk | contribs) (Created page with " == Problem & Motivation == As one of the most polluted countries in Europe, Bulgaria is facing a high level of pollution. It is ranked eighth in the European Environment Agen...") |
Yg.chen.2015 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Problem & Motivation == | == Problem & Motivation == | ||
As one of the most polluted countries in Europe, Bulgaria is facing a high level of pollution. It is ranked eighth in the European Environment Agency’s 2017 report on air quality in Europe in terms of most premature deaths caused by PM2.5[1]. Our goal in this report is to find the pollution condition in the capital of Bulgaria– Sofia city. <br> | As one of the most polluted countries in Europe, Bulgaria is facing a high level of pollution. It is ranked eighth in the European Environment Agency’s 2017 report on air quality in Europe in terms of most premature deaths caused by PM2.5[1]. Our goal in this report is to find the pollution condition in the capital of Bulgaria– Sofia city. <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
In this report, I will use 3 Air Quality indicators—Official Air Quality Concentration, PM2.5 and PM10 to analyze the air quality in Sofia city. PM2.5 is a pollutant stemming from fuel combustion, heating, transportation, waste incineration, agriculture and other anthropogenic sources. According to studies, it is highly correlated with cancer rate, with a 36% increase in lung cancer per 10 μg/m3 as it can penetrate deeper into the lungs[2]. Worldwide exposure to PM2.5 contributed to 4.1 million deaths from heart disease and stroke, lung cancer, chronic lung disease, and respiratory infections. PM10 is particulate matter 10 micrometers or less in diameter, which has slight larger dimension than PM2.5 but same level of danger. | In this report, I will use 3 Air Quality indicators—Official Air Quality Concentration, PM2.5 and PM10 to analyze the air quality in Sofia city. PM2.5 is a pollutant stemming from fuel combustion, heating, transportation, waste incineration, agriculture and other anthropogenic sources. According to studies, it is highly correlated with cancer rate, with a 36% increase in lung cancer per 10 μg/m3 as it can penetrate deeper into the lungs[2]. Worldwide exposure to PM2.5 contributed to 4.1 million deaths from heart disease and stroke, lung cancer, chronic lung disease, and respiratory infections. PM10 is particulate matter 10 micrometers or less in diameter, which has slight larger dimension than PM2.5 but same level of danger. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
By using the above-mentioned indicators, the goal is to visualize the air quality situation as well as the factors affecting the air quality. The factors which will be analyzed in this report are:<br> | By using the above-mentioned indicators, the goal is to visualize the air quality situation as well as the factors affecting the air quality. The factors which will be analyzed in this report are:<br> | ||
- Local energy sources<br> | - Local energy sources<br> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
== Data Analysis & Transformation == | == Data Analysis & Transformation == | ||
===Data Analysis and Cleaning === | ===Data Analysis and Cleaning === | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====Air Tube data==== |
| − | + | <br> | |
After doing a quick plotting of the raw data, I found that there are outliers (or misreading) in the Air Tube Dataset: | After doing a quick plotting of the raw data, I found that there are outliers (or misreading) in the Air Tube Dataset: | ||
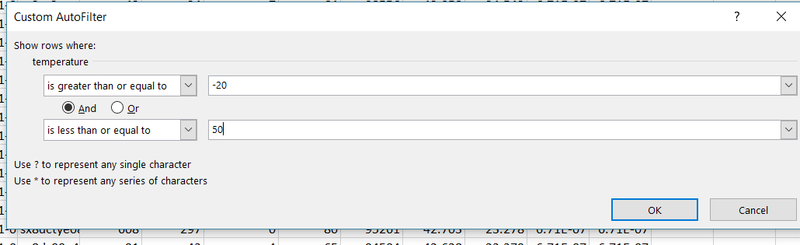
| − | + | Temperature: remove temperature less than -20 and larger than 50<br> | |
| − | [[File:Cap.png| | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #536a87;color:#fbfcfd;width: 20%;" | Column Name | ||
| + | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #536a87;color:#fbfcfd;width: 40%" | Action | ||
| + | ! style="font-weight: bold;background: #536a87;color:#fbfcfd;" | Screenshot | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <center>'''Temperature''' <br/> | ||
| + | || <center>remove temperature less than -20 and larger than 50</center> | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | [[File:Cap.png|800px|center]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <center>'''Filter each floor/zone using a single selection drop down list''' <br>[[File:Drop down list GwendolineTanWanXin.png|200px|center]]</center> | ||
| + | || <center>To allow analysts to concentrate on the data collected from each level with the use of a single selection. | ||
| + | <br/>Use of a drop down list also allow analysts to easily choose the building level that they are interested to analyse.</center> | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | # Configure the filter selection to be a single selection drop down list | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <center>'''Change and zoom of floor plans based on each floor filter''' <br>[[File:Dynamic Floor Plan GwendolineTanWanXin.png|200px|center]]</center> | ||
| + | || <center>To allow for easy reference of mapping each building data elements with each zone. <br/> | ||
| + | When a user filters from one floor to another, the floor plan also changes to provide for quick and easy reference. Due to the space constraint, each floor plan has to be zoomed for users to identify and see the zone areas clearly.</center> | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | # Create calculated fields for the x and y axis. | ||
| + | # Put the 2 calculated fields into the worksheet view. | ||
| + | # To hide the mark, set the colour as transparent. | ||
| + | # Navigate to Maps > Background Images. Add the floor plans into the background images and configure it according to the filter condition. | ||
| + | # Put the “floor” attribute as a filter. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Cap.png|800px|center]] | ||
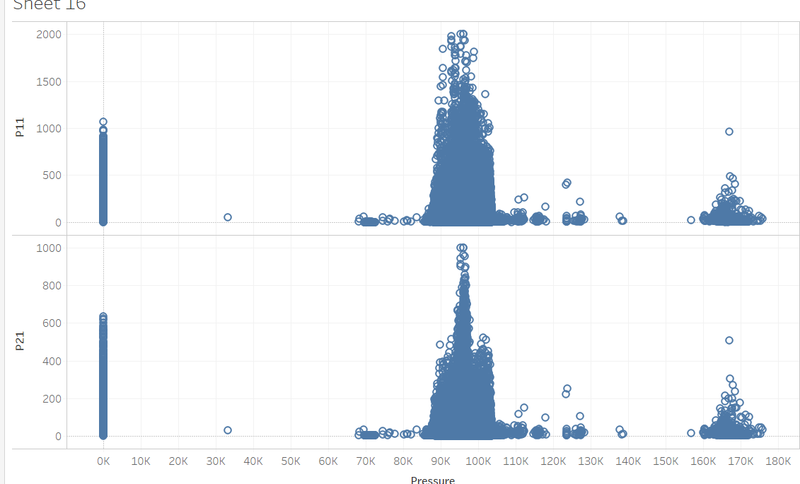
| + | Pressure: remove pressures valued 0<br><br> | ||
| + | [[File:Cap2.png|800px|center]]</p> | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 11 November 2018
Contents
Problem & Motivation
As one of the most polluted countries in Europe, Bulgaria is facing a high level of pollution. It is ranked eighth in the European Environment Agency’s 2017 report on air quality in Europe in terms of most premature deaths caused by PM2.5[1]. Our goal in this report is to find the pollution condition in the capital of Bulgaria– Sofia city.
In this report, I will use 3 Air Quality indicators—Official Air Quality Concentration, PM2.5 and PM10 to analyze the air quality in Sofia city. PM2.5 is a pollutant stemming from fuel combustion, heating, transportation, waste incineration, agriculture and other anthropogenic sources. According to studies, it is highly correlated with cancer rate, with a 36% increase in lung cancer per 10 μg/m3 as it can penetrate deeper into the lungs[2]. Worldwide exposure to PM2.5 contributed to 4.1 million deaths from heart disease and stroke, lung cancer, chronic lung disease, and respiratory infections. PM10 is particulate matter 10 micrometers or less in diameter, which has slight larger dimension than PM2.5 but same level of danger.
By using the above-mentioned indicators, the goal is to visualize the air quality situation as well as the factors affecting the air quality. The factors which will be analyzed in this report are:
- Local energy sources
- Meteorology such as temperature, pressure, rainfall, humidity, wind etc
- Human Behavior such as driving, room heating
- Behaviors of Neighbors of Sofia city.
Data Analysis & Transformation
Data Analysis and Cleaning
Air Tube data
After doing a quick plotting of the raw data, I found that there are outliers (or misreading) in the Air Tube Dataset:
Temperature: remove temperature less than -20 and larger than 50
| Column Name | Action | Screenshot |
|---|---|---|
Use of a drop down list also allow analysts to easily choose the building level that they are interested to analyse. |
| |
When a user filters from one floor to another, the floor plan also changes to provide for quick and easy reference. Due to the space constraint, each floor plan has to be zoomed for users to identify and see the zone areas clearly. |
|
Pressure: remove pressures valued 0