Difference between revisions of "Group14 Report"
Kalaisr.2017 (talk | contribs) |
Kalaisr.2017 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | [1] | + | [1] http://www.globalissues.org/issue/73/arms-trade-a-major-cause-of-suffering <br /> |
| − | [2] | + | [2] https://www.sipri.org/research/armament-and-disarmament/arms-transfers-and-military-spending/international-arms-transfers/<br /> |
| − | [3] | + | [3] http://visionofhumanity.org/app/uploads/2018/06/Global-Peace-Index-2018-2.pdf/ |
Revision as of 11:39, 14 August 2018
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
Overview
The arms trade is a global issue of concern because of its negative consequences related to armed conflict, wars, and human rights abuses [1]. It emerged as one of the main global issues in the post-Cold War era in addition to problems such as disease, poverty and gender inequality, as arms supplier countries recognized the effect of stockpiling weapon systems on the breakout of armed conflict. The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) conducts research on arms transfers between regions and states aimed at increasing the fundamental understanding of the impact of arms transfers and to support policymaking. SIPRI aims to contribute to greater transparency in the global arms trade to ensure responsible international arms transfers, hence helping to prevent violent conflict, alleviate tensions and warn about potentially destabilizing arms accumulations. Based on the latest publication by SIPRI in 2017, a rising trend is observed in the volume of international transfers of major weapons, with the highest volume of arm transfers recorded between 2013 to 2017, since 1990 [2].
The lack of significant improvement in managing the global arms trade, despite implemented global policies and publication of data, prompted our group to develop an alternative solution for the exploration and analysis of data published by SIPRI. Our group has developed an interactive application that allows users to visually explore and analyse the global arms trade. It is through this that we hope to offer an additional dimension of transparency and accountability that will invite greater scrutiny to this unabating global problem.
Past Works
A number of applications exist for the visualization of arms trade data and most of the visualisations are mainly static. SIPRI has produced an interactive web platform using data in their published database but the application was only focused on military expenditure instead of arms trade flows. There has also been no visualisations carried out based for countries with Low Global Peace Index ratings, as these countries are more vulnerable to import arms.
Our project aims to contribute an application featuring multiple visualizations of arms imports. The following sections describe our approach to the problem and how the application was designed and built.
|
|
Motivation and Objectives
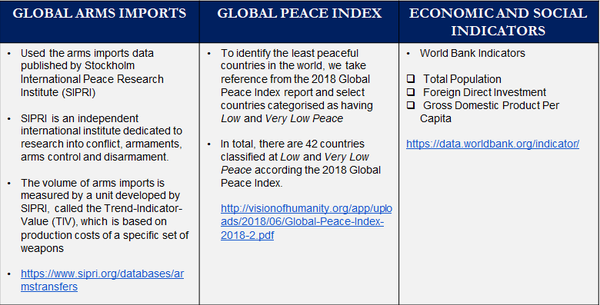
Based on the Global Peace Index 2018 published by the Institute for Economics and Peace, we have identified the countries with 'Low' and 'Very Low Peace' global peace index ratings. [3]
Our project aims to identify the trends and patterns in the international arms transfers at the regional and country levels for these Low Peace countries and explore the arms trade dependencies of these countries for the period 1993 to 2017. We also aim to explore the major importers and exporters of arms weapons and to find out the relationships between the global arm importers and exporters. Our team is motivated to design a dynamic and interactive dashboard to provide students and policymakers a better understanding and holistic view of the global arms trade for the Low Peace countries.
Data Sources
The table shows the data sources for our project. We use the Trend-Indicator-Value (TIV) published by SIPRI to visualise the trends and patterns of arms imports for the Low Peace Countries from 1993 to 2017.
|
|
Design Framework
1. Interface:
In this section, we will run through the dashboard visualizations. We used the flexdashboard package as we can easily create flexible and interactive dashboards with R. We included Shiny components for additional interactivity.
There are multiple tabs to our dashboard and each tab focuses on a specific type of visualisation. By having separate tabs, the user does not need to scroll up and down and can instead toggle freely between tabs to access the different visualisations. The dashboard consists of interactive plots so that users may gain insight on trends of the global arms imports for the low peace countries and explore the arms imports trade relationships between countries, by changing the filter options and by hovering and highlighting over the charts.
The purpose of this dashboard is to provide an application interface which facilitates an interactive analysis arms imports trend and arms trade over time and also arms dependencies of the low peace countries. The application also includes visualisation the relationship of arms imports with the social and economic indicators of the low peace countries.
In summary, the dashboard consists of the following 6 tabs for the visualisation of the above mentioned:
1. 2018 Global Peace Index
2. Top 100 Importers from 1993 to 2017
3. Visualization of Arms Dependencies
4. Visualization of Arms Trade Over Time
5. Visualization of Arms Import by FDI, GDP & Population Size, and
6. Visualization of Arms Trade Network.
|
|
2. Visualisations:
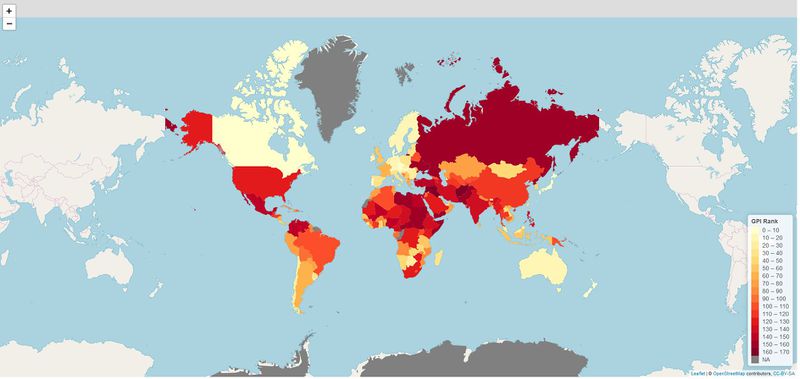
2018 Global Peace Index
We created a choropleth map to allow users to visualise geographically where the countries with low Global Peace Index (GPI) ratings are located. Countries are coloured by their Global Peace Index rankings with darker shades of red indicating a poor Global Peace ranking or countries considered to be least peaceful. Users can zoom in and out of the map and highlight the country of interest to see the country name and its Global Peace Index ranking. We used the leaflet package in R as it is highly interactive and customizable.
|
|
Visualizing the Arms Dependencies
We use a treemap and chord diagram to visualize the arms dependencies for the 42 Low Peace selected countries.
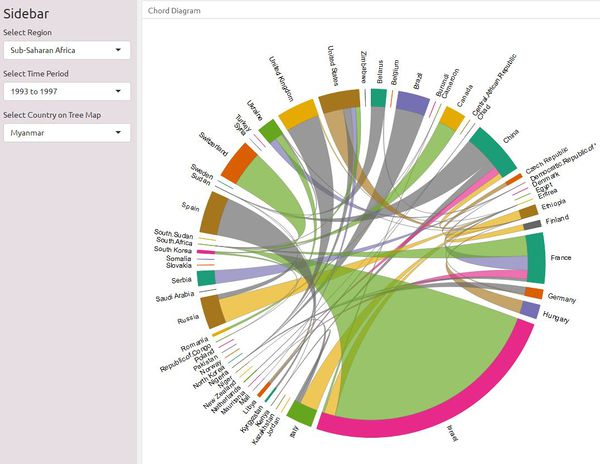
Chord Diagram
The chord diagram shows the source of arms imports flows for the selected 42 countries, in a given five-year period. It is created using the chorddiag package in R, which allows the creation of interactive chord diagrams using the JavaScript visualization library D3 from within R using the htmlwidgets interfacing framework.
The chord diagram created to visualize trade flows is shown below. Users can filter by region, as well as five-year time period, on the sidebar to explore the total volume of arms imports for countries in the selected region, and the supplier countries. Hovering over a band between two countries highlights the band and reveals the volume of arms imports to the importing country from its supplier.
|
|
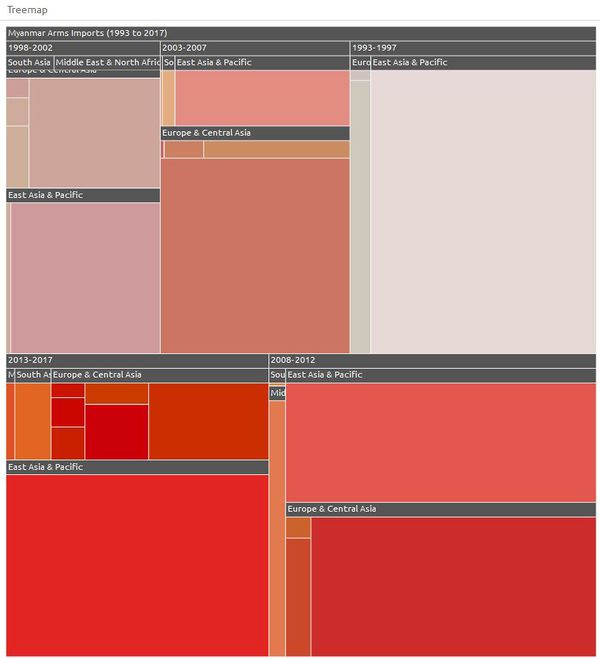
Treemap
The objective of the treemap is to show the regions and countries that specifically make up a selected country imports, over five-year periods. The hierarchy of the treemap is the five-year periods as the first hierarchy, followed by the region and then each specific country in the region. The total imports value is represented by the size of each treemap node as well as the colour.
Users can filter by country (one of the 42 countries) to visualize the country’s dependencies on supplier countries for arms in five-year periods from 1993 to 2017. Users can click on a region in the treemap to find out individual countries for the supplier region.
The treemap is created using the treemap package and the functionality of the treemap is combined with the interactivity of the d3.js treemaps though the d3treeR htmlwidget.
|
|
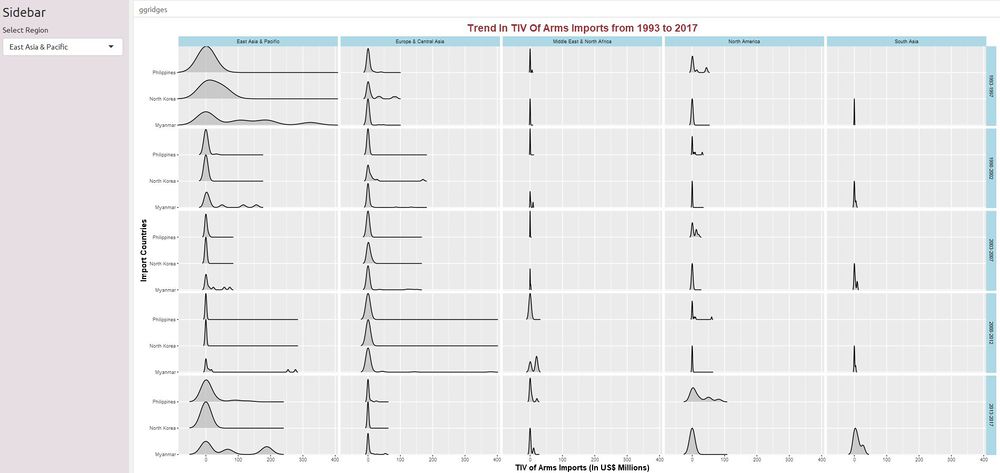
Visualizing the Arms Trade Flows Over Time
The ridgeline plots were incorporated to visualize changes in arms imports of the 42 countries over time. The ggplot2 and ggridge packages were used to create the ridgeline plot.The ggridge plot is useful as it can compare the trends in the arms imports of several countries together. Users can filter by region to explore the distribution of import values for countries in the selected region over time.
The facet_grid function is used to form a matrix of panels consisting of the export regions and the five-year time period. With the facetted diagram, users can explore the distribution of import values for countries of the selected region by five-year time periods and by export regions.
|
|
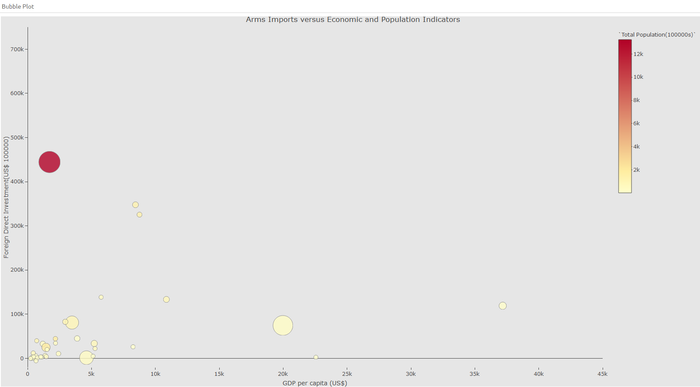
Visualizing the relationship between arms imports, foreign direct investment and GDP per capita
The bubble plot visualises the relationship between arms imports, FDI, GDP per capita and population of the 42 low peace countries. Users can use the slider to choose different years to explore how the arms imports change with the social and economic indicators for the selected country.
To create the bubble plot, we use the plotly package as it is an interactive, browser-based charting library built on the open source JavaScript graphing library plotly.js.
|
|
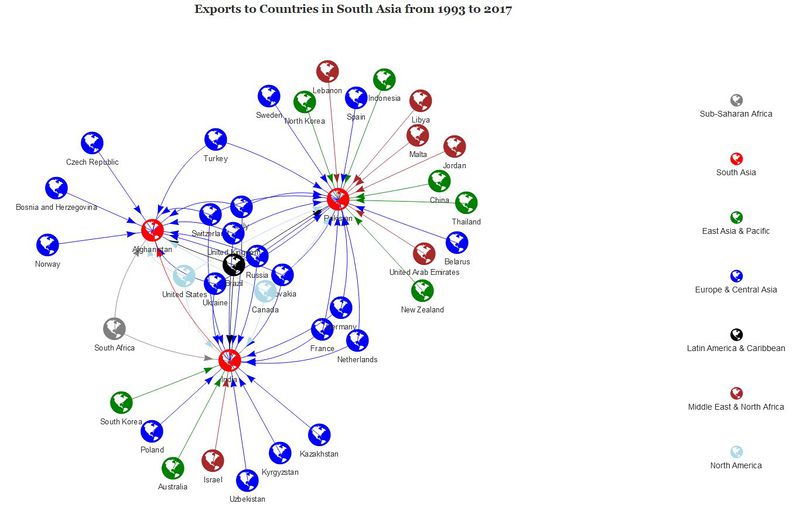
Visualizing the Arms Trade Network
The network diagram was created to visualise the links between the 42 importing countries and their suppliers as shown below. The network diagram is used as an additional dimension to arms import trade flows on top of the bilateral trade flows visualized using the chord diagram.
Users can filter by importing region and by five-year time periods to see for the selected importing region, which are the supplier countries. Hovering over a particular country of the selected importing region and time period results in highlighting of countries supplying arms to that particular country.
We use the Visnetwork package as it highly customizable and interactive.
|
|
Discussion
Through our application, we were able to identify the trends in the arms imports of the Low Peace countries from 1993 to 2017 and we were able to explore the arms trade dependencies of these countries. We showed how the arms imports of countries changes with different suppliers (export regions) over time and the relationship of a selected country imports with its social and economic indicators.
==Future Work==
1. The application currently focuses on countries with Low and Very Low Peace index. It could to be enhanced to include more countries from the SIPRI arms imports database to provide a better coverage of the global arms imports trade.
2. We could also include the military spending available in SIPRI database to explore the relationship between military spending and arms trade.
3. We could also extend our analysis to visualise the relationship between energy dependency and arms trade.
References
[1] http://www.globalissues.org/issue/73/arms-trade-a-major-cause-of-suffering
[2] https://www.sipri.org/research/armament-and-disarmament/arms-transfers-and-military-spending/international-arms-transfers/
[3] http://visionofhumanity.org/app/uploads/2018/06/Global-Peace-Index-2018-2.pdf/