Difference between revisions of "Group2 ProjectDeliverables"
| Line 216: | Line 216: | ||
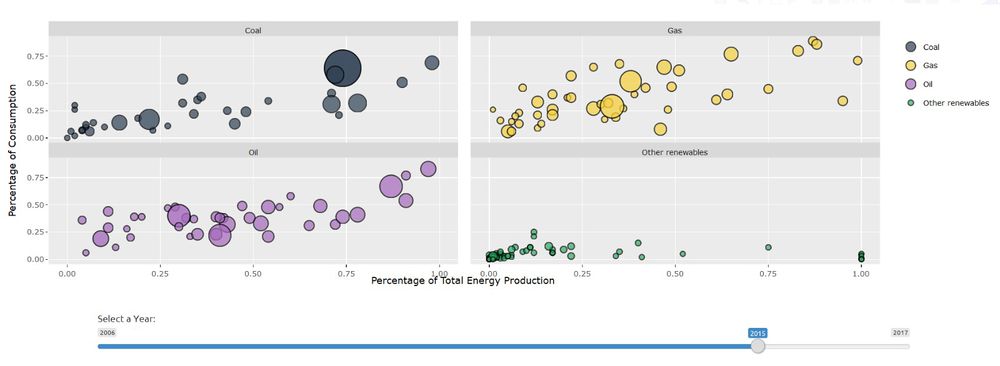
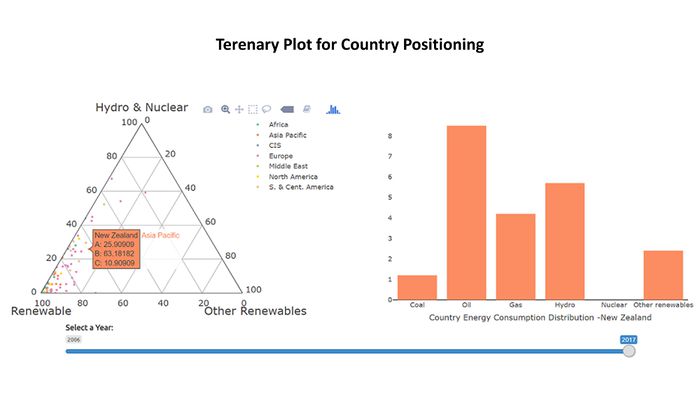
The ternary plot shows us that the major energy source for Norway in terms of consumption is Hydro energy, which is a good indication. However, if we look at India, the major energy consumption is for Coal and Oil which are non-renewable sources of energy. US primarily consumes Oil, followed by Gas.<br><br> | The ternary plot shows us that the major energy source for Norway in terms of consumption is Hydro energy, which is a good indication. However, if we look at India, the major energy consumption is for Coal and Oil which are non-renewable sources of energy. US primarily consumes Oil, followed by Gas.<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | China, over the years has tried to increase the percent contribution from renewable, hydro and nuclear energy sources as opposed to non-renewable energy sources.<br><br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:04, 12 August 2018
World Energy Production & Consumption: A Visual Study
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
Motivation
Energy growth drives the well-being and prosperity across the globe. Growing demand for energy has to be met in a safe and environmentally conscious manner. Rapidly changing energy dynamics determine the course of our economic development, geopolitics, technological breakthroughs, massive investments and trade flows.
|
Objective
Data visualization is often an after-thought for many of the practitioners who are collecting and analyzing data. And yet, without clear and compelling communication, analysis will never drive insights and action. Visualization can itself be used effectively in the process of insights discovery. Static visualization and reports do not allow for direct interaction with data, enhanced assimilation of information, quick access to relevant insights and drill-down analysis.
|
About The Data Source
Critique of the Existing Visualizations
Visualizations available on the energy outlook reports consists of basic graph types such as bar, line and pie charts which are static in nature and do not facilitate any discovery apart from what they are made to deliver. A sample visualization is presented below:
|
Dashboard Design
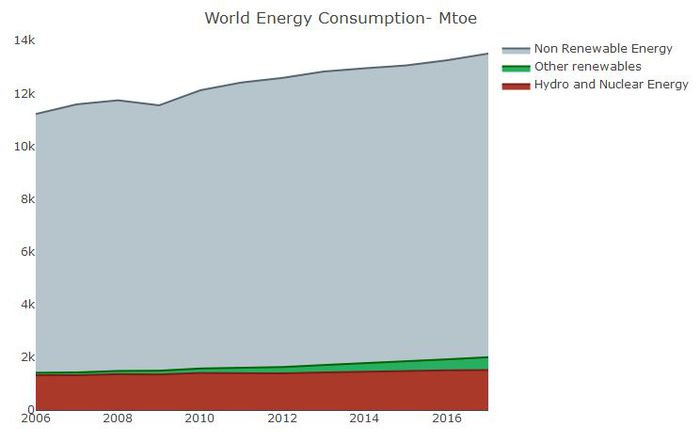
Global trend in Energy consumption for years 2006-2017 across energy types: Stacked Area Chart
|
Some Useful Insights
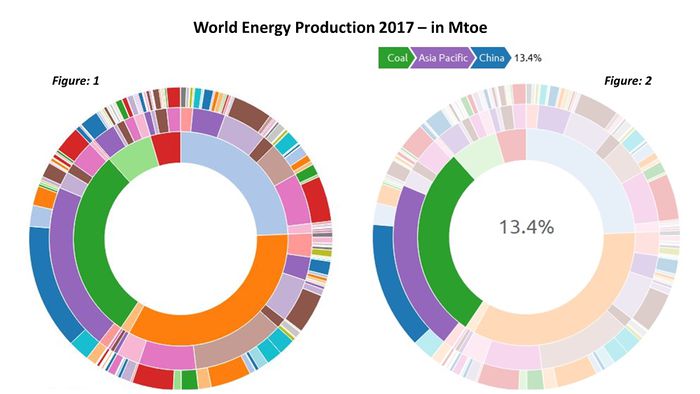
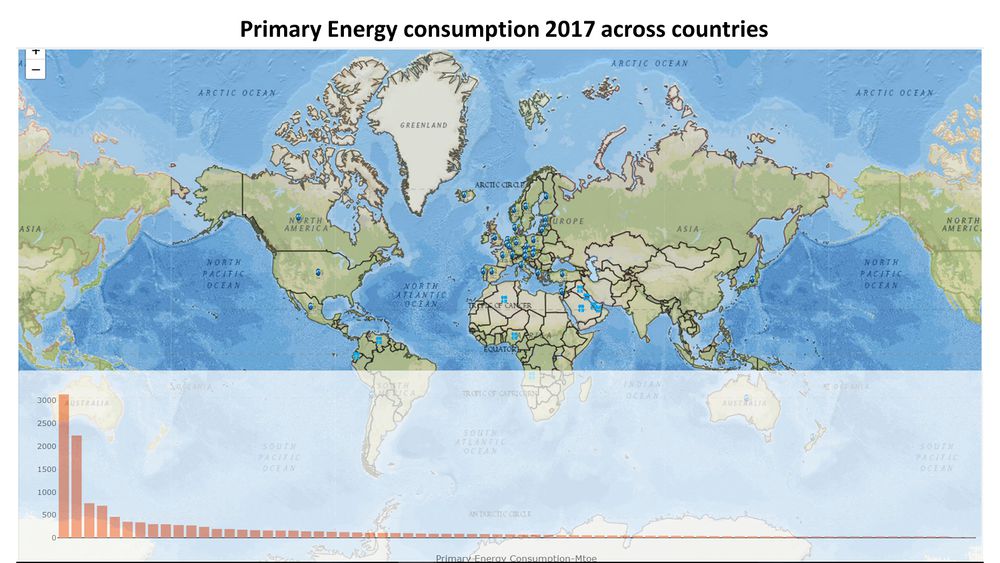
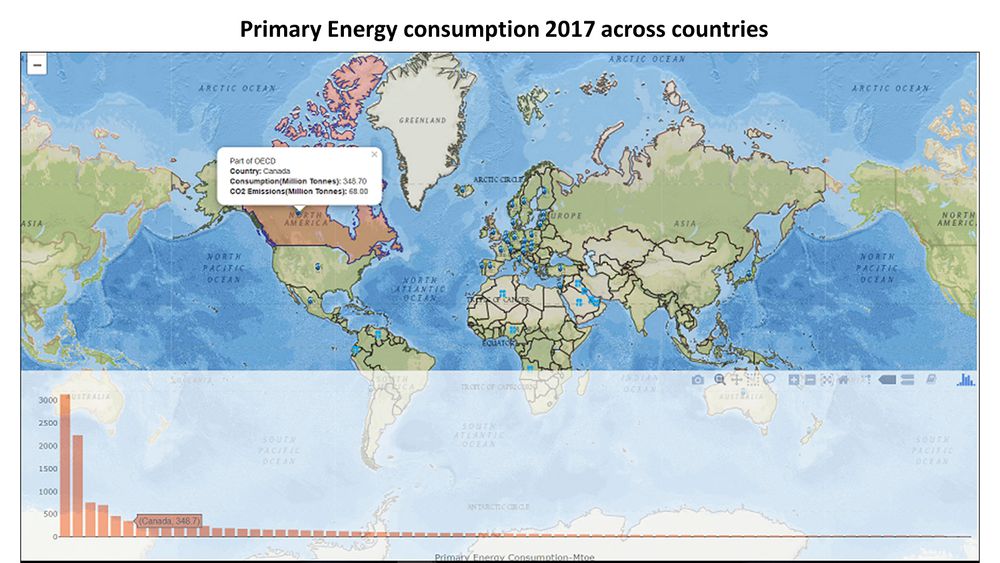
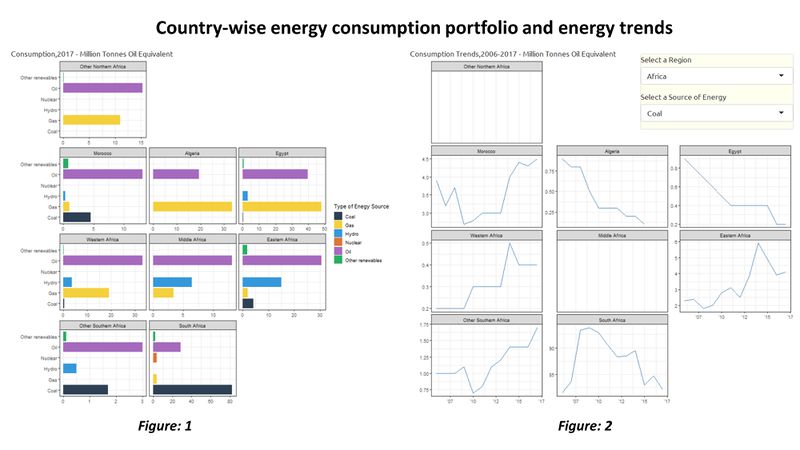
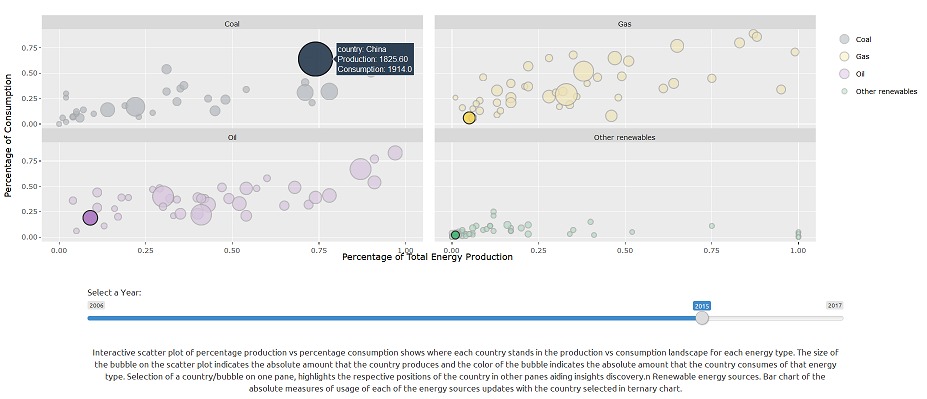
The Geofacet plot reveals that Japan is reducing their nuclear power production drastically after 2011 nuclear power plant leak, Fukushima Daiichi due to tsunami and earth quake Japan’s core focus has shifted from nuclear to other renewables. Last 5 years growth is remarkable, it has replaced about 33% of its nuclear consumption through other renewables Taiwan which is at higher risk for tsunami and earthquakes is following similar the same trend and has made significant reduction in their nuclear consumption. In 2016, winning government has stated phasing out nuclear power generation in their agenda With the reduction in the prices of Oil, the consumption from 2013 to 2017 has gone up for Oil across all countries. This can be visualized using the time-series pattern in the Geofacet graph for Oil For Finland, Iceland & Sweden, it is observed that a major proportion of energy consumption is from other renewable sources of energy From the Sunburst plot we can see that China produces 13.4% of the total energy of the world using Coal; Saudi Arabia produces 4.31% of the total energy of the World using Oil China, US & India are the top 3 countries in the Primary Energy Consumption in 2017 From the Geofacet plots we can see that China has been trying to reduce it's Coal consumption after 2012. If we look at Africa, Algeria has been able to reduce it's Coal consumption significantly over the years. The ternary plot shows us that the major energy source for Norway in terms of consumption is Hydro energy, which is a good indication. However, if we look at India, the major energy consumption is for Coal and Oil which are non-renewable sources of energy. US primarily consumes Oil, followed by Gas. China, over the years has tried to increase the percent contribution from renewable, hydro and nuclear energy sources as opposed to non-renewable energy sources. |
Conclusion/Future Work
The original dataset has several other metrics like prices of each energy source, reserves in each country, electricity generation, trade movements etc. These variables also must be included for analysing energy dynamics and the world energy outlook.
|
R Packages Used
We have used the following R packages to come up with our visualizations: |
References
[1] Shneiderman, B. (2005) “The eyes have it: A task by data type taxonomy for information visualization” IEEE Conference on Visual Languages (VL96), pp. 336-343 |