From Visual Analytics and Applications
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
|
| Line 136: |
Line 136: |
| | <br><br> | | <br><br> |
| | <b>Country-wise Energy Consumption Portfolio and energy trends: Geofacets</b> | | <b>Country-wise Energy Consumption Portfolio and energy trends: Geofacets</b> |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | Geofacets are used to visualize data for each geographical entity, with the resulting set of visualizations being laid out in a grid that mimics the original geographic topology as closely as possible for the region. Each geofacet visualization for a selected region consists of a horizontal bar chart for energy consumption portfolio for all the countries in the region. |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | Figure 1 in the visualization below shows Country-wise Energy Consumption Portfolio which allows viewers to compare energy consumption distribution across types within a country as well as across countries in the region. |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | [[File:Group2_geofacet.jpg|1000px|centre]] |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | Another geofacet graph which has an additional option to select the energy type is used to display the trends in consumption of the energy type across countries of the region. |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | Figure 2 in the visualization above shows evolution of Energy usage per country over time for each energy type. (time-series in geofacet) |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | <i>Critique</i>: Given the custom aggregations of countries in the report as well as the unavailability of data for few countries , geofacets were the best choice however comparisons across countries form different regions is not direct. Choropleth and Tile maps limit analysis to one variable which is color encoded to aid analysis. Quantifying intensity of color is difficult and choropleths are known to favour large geographic entities over smaller ones. |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | <i>Disadvantages</i>: A geofacet grid is only meaningful if the person already has an understanding of the underlying original geography. Also, this form of visualization takes more space and representing some of the geographical entities on grid layout can be challenging. |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | <i>Tools used</i>:”geofacet” in R, Geo Grid Designer app for creating grids for each region. |
| | <br><br> | | <br><br> |
| | <b>Production vs Consumption landscape for each energy type: Interactive Scatter Plot</b> | | <b>Production vs Consumption landscape for each energy type: Interactive Scatter Plot</b> |
Revision as of 15:17, 9 August 2018
World Energy Production & Consumption: A Visual Study
Motivation
Energy growth drives the well-being and prosperity across the globe. Growing demand for energy has to be met in a safe and environmentally conscious manner. Rapidly changing energy dynamics determine the course of our economic development, geopolitics, technological breakthroughs, massive investments and trade flows.
The main objective of this project is to study the dynamics of regional energy production and consumption of the different countries of the world to identify the dominant as well as weaker player in the world energy market
Though reports from various organizations such as EIA, IEA, OPEC, BP are available, most of the visualizations are static and do not aid exploration, limiting the scope of further drilling down to the areas of particular interests. Hence, we've decided to take up rich data-set provided by BP & explore the information related to energy production and consumption across countries, which might otherwise be hidden in the existing static visualizations.
|
Objective
Static visualization and reports do not allow for direct interaction with data, enhanced assimilation of information, quick access to relevant insights and drill-down analysis. By using interactive, visual data analytics techniques we will be bringing the above-mentioned capabilities to the interface.
We will be using the world energy datasets from BP along with the CO2 emissions to come up with more detailed visualizations including some level of interactivity to enable users to drill down in the world energy data & reveal specific insights.
|
About The Data Source
BP plc, formerly British Petroleum, is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. It is the world's sixth-largest oil and gas company, the sixth-largest energy company by market capitalization and the company with the world's twelfth-largest revenue (turnover). It is a vertically integrated company operating in all areas of the oil and gas industry, including exploration and production, refining, distribution and marketing, petrochemicals, power generation and trading. It also has renewable energy interests in biofuels and wind power.
For 66 years, the BP Statistical Review of World Energy has provided high-quality objective and globally consistent data on world energy markets. The review is one of the most widely respected and authoritative publications in the field of energy economics, used for reference by the media, academia, world governments and energy companies. A new edition is published every June.
For the purpose of this project, we are using the BP Statistical Review of World Energy data.
The dataset consists of energy consumption and production data from around 1965 for 2017 for more than 90 countries spanning across regions Africa, Europe, APAC, CIS, Middle-East , North America, S. & C. America. Energy resources are categorized as Primary Energy(Oil, Coal, Gas, Hydro, Nuclear); Other Renewable resources(Solar, Wind, Biofuels, Geothermal etc.).
Below figure shows the different data we have for Oil in the dataset:

A closer look at the tab Oil: Production - Tonnes (from 1965) reveals the below information regarding Oil production across different countries of the world:
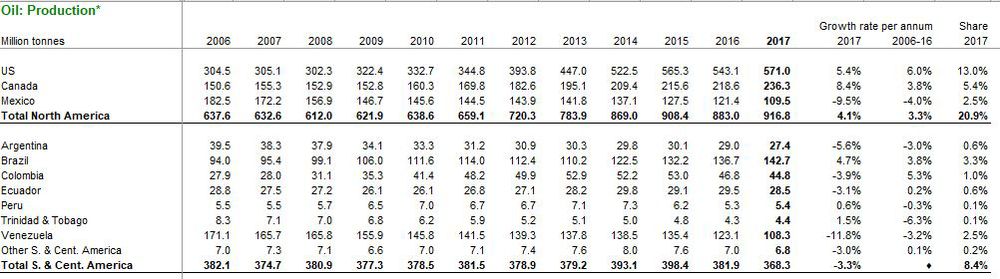
Similarly, we have different datasets each for the different forms of energy like Natural Gas, Coal, Nuclear Energy, Biofuels etc.
|
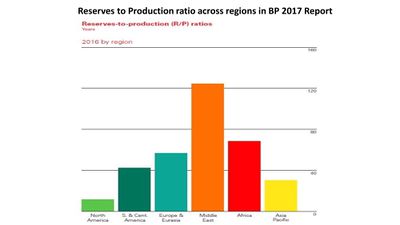
Critique of the Existing Visualizations
We noticed that all the existing visualizations in the BP Statistical Review report are static in nature which limits the usage of the plots and restricts information retrieval. Below image shows a sample visualization from the report:
As shown above, the visualization does not allow user to dig deeper into the dataset. Hence, to enhance usability of the the data, we have come up with interactive plots in order to gain deeper insights.
|
Dashboard Design
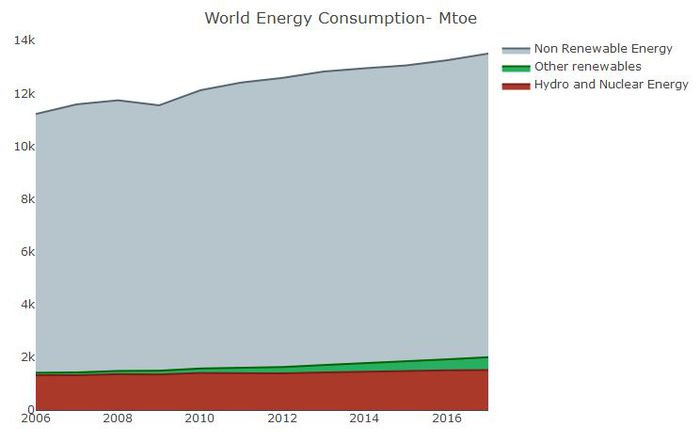
Global trend in Energy consumption for years 2006-2017 across energy types: Stacked Area Chart
A Stacked area chart gives us a good understanding of the rate at which world energy consumption is changing with time along with the trends for individual components.
Tools Used: Plotly
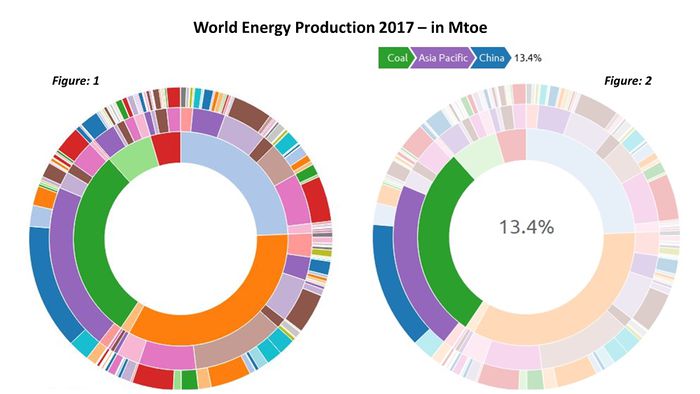
Country-wise percentage consumption across various energy types: Sunburst Plot
Usage: World energy profile consists of Non renewable energy sources such as coal, oil and gas as well as renewable sources like hydro energy, nuclear energy and other renewables like solar, wind, biogas etc. Sunburst Chart allows the user to interactively drill down and understand the percentage contribution of a region to World energy Production detailed for each energy type.
Critique: Sunburst is a form of a radial chart which breaks out general categories into subsets to better understand the components that make up or contribute to the whole. This form a visualisation is similar to a treemap however it is easier to see multiple layers of data with sunburst, while the treemap is better for comparing categories within the same hierarchical layer.
Disadvantages: Deeper slices exaggerate their size, and look visually larger. This type of visualization requires the quantitative comparison of angles, instead of lengths, which is difficult for the human eye.
Tools used: SunburstR
Figure above shows the Sunburst visualization of the World Energy consumption. Figure 1 in the visualization represents the country-wise percentage consumption across various energy types. The sunburst plot is interactive and can be used to dig deeper to understand the percentage consumption of the energy type to the country level. For example,as revealed in Figure 2, China uses 13.4% of the total coal of the world. Similarly, we can explore different energy type consumption.
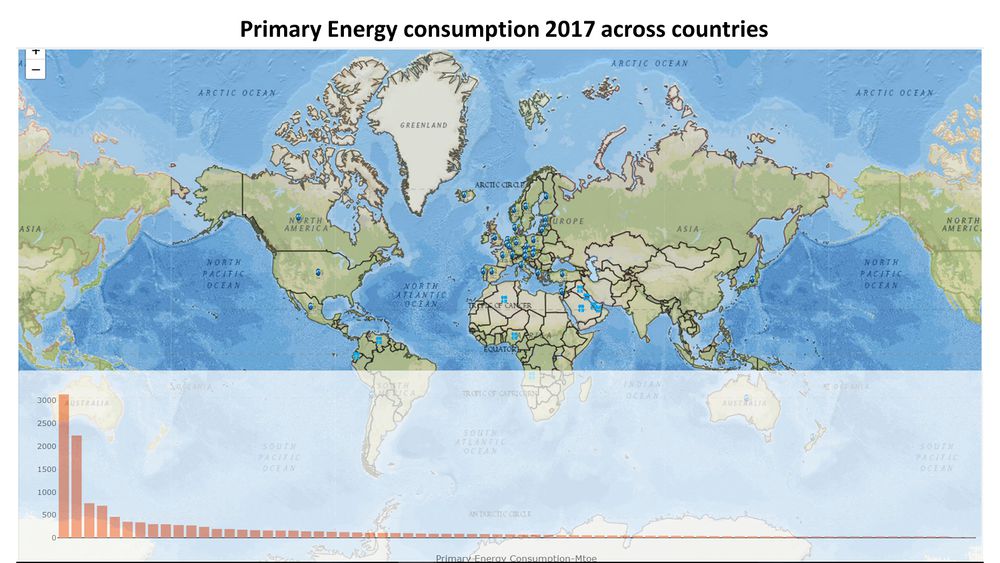
Primary Energy consumption for 2017 across the World: Interactive World Map
To further explore the primary energy consumption across the world and to understand who are the major energy primary energy consumers of the world and their respective CO2 emissions, we have implemented an interactive world map with a bar graph, as shown in the figure below. When the user clicks on the bars, the corresponding country is highlighted in the map and a tool-tip displays the Energy consumption in Mtoe, along with the CO2 emissions and whether the country belongs to OECD/OPAC. Alternatively, the user can click on any country of interest on the map to get the information on the primary energy consumption and CO2 emissions for the particular country
Critique: This method was chosen to make the exploration interesting. Choropleth Map was not considered as countries are custom aggregated in the report and for some countries values are not listed.
Tools Used: Plotly
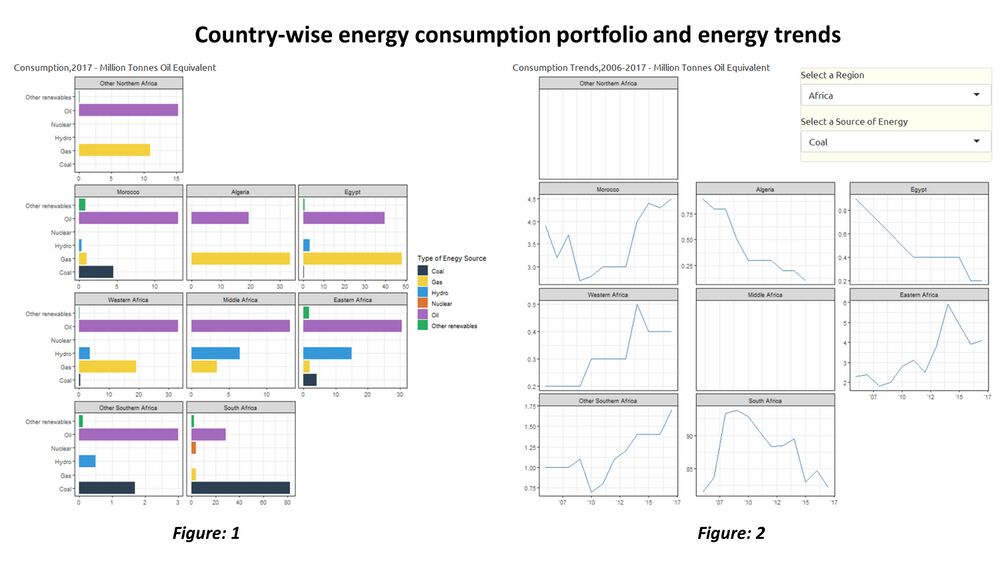
Country-wise Energy Consumption Portfolio and energy trends: Geofacets
Geofacets are used to visualize data for each geographical entity, with the resulting set of visualizations being laid out in a grid that mimics the original geographic topology as closely as possible for the region. Each geofacet visualization for a selected region consists of a horizontal bar chart for energy consumption portfolio for all the countries in the region.
Figure 1 in the visualization below shows Country-wise Energy Consumption Portfolio which allows viewers to compare energy consumption distribution across types within a country as well as across countries in the region.
Another geofacet graph which has an additional option to select the energy type is used to display the trends in consumption of the energy type across countries of the region.
Figure 2 in the visualization above shows evolution of Energy usage per country over time for each energy type. (time-series in geofacet)
Critique: Given the custom aggregations of countries in the report as well as the unavailability of data for few countries , geofacets were the best choice however comparisons across countries form different regions is not direct. Choropleth and Tile maps limit analysis to one variable which is color encoded to aid analysis. Quantifying intensity of color is difficult and choropleths are known to favour large geographic entities over smaller ones.
Disadvantages: A geofacet grid is only meaningful if the person already has an understanding of the underlying original geography. Also, this form of visualization takes more space and representing some of the geographical entities on grid layout can be challenging.
Tools used:”geofacet” in R, Geo Grid Designer app for creating grids for each region.
Production vs Consumption landscape for each energy type: Interactive Scatter Plot
Relative positioning of countries in terms of usage per energy type: Ternary Plot
|
R Packages Used
We have used the following R packages to come up with our visualizations:
dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. It is a fast, consistent tool for working with data frame like objects, both in memory and out of memory.
tidyr:It's designed specifically for data tidying (not general reshaping or aggregating) and works well with 'dplyr' data pipelines
reshape:Casts a molten data frame into the reshaped or aggregated form you want
readr :The goal of 'readr' is to provide a fast and friendly way to read rectangular data (like 'csv', 'tsv', and 'fwf'). It is designed to flexibly parse many types of data found in the wild, while still cleanly failing when data unexpectedly changes
ggplot:A system for 'declaratively' creating graphics. You provide the data, tell 'ggplot2' how to map variables to aesthetics, what graphical primitives to use,
and it takes care of the details
Plotly:Easily translate 'ggplot2' graphs to an interactive web-based version and/or create custom web-based visualizations directly from R
SunburstR:Make interactive 'd3.js' sequence sunburst diagrams in R with the convenience and infrastructure of an 'htmlwidget'.
Crosstalk:Provides building blocks for allowing HTML widgets to communicate with each other, with Shiny or without (i.e. static .html files)
Geofacet:Provides geofaceting functionality for 'ggplot2'. Geofaceting arranges a sequence of plots of data for different geographical entities into a grid that preserves some of the geographical orientation
|
References