Course information
|
|
|
|
|
|
Synopsis
In this globalising and competitive business environment, the value of location as a business measure is fast becoming an important consideration for organisation. Geospatial Analytics with its capability to visualise, analyse and model business information spatially is emerging as a location intelligence tool. Today, many kinds of industries are employing geospatial analytics as an integral part of their business processes. Examples of the use of geospatial analytics in business are:
- Market Analysis
Which is the company’s market share in different geographical areas? Where are the customers located? What are the characteristics of customers in different geographical locations? Are there potential customers and where do they live?
- Site Selection
Where are the shops or branches of the company located today? Where are the competitors located? What would be the surrounding market area for a new location? What are the socio-economic characteristics of the people living in this market area? Will the establishment of a new shop interfere with the existing shop owned by the company? Are the land prices in different areas suitable for building a new shop?
- Sales territories
Which the company’s present division into sales territories? What kind of customers live in these districts and how much is sold? Is there a need for more salesmen in any district? Could redistricting lead to more efficient sales organisation and less travelling time for the salesmen?
- Distribution and travel costs
How can the distribution system be made more efficient? In what way does the transport system influence the distribution and how does it restrict or facilitate expansion in the region? Can the number of journeys made by company staff be reduced by applying route planning software? Are there any alternatives to our present distribution system?
- Analysis of the global environment and new export markets
What is the general economic and spatial pattern in the region? How good is the infrastructure? How is the population distributed geographically? Which other companies are present in the region and where are they located? Is this region a potential export market for the company’s products?
This course provides students with an introduction to practical applications of geospatial analytics in business operations. Emphasis will be placed on:
- locating, acquiring and integrating business data with geographical data,
- understand the principles and methodologies of the georefencing, geocoding and geospatial data management processes,
- become familiar with conventional geographical information science and technologies, mapping science and cartographic design principles and geospatial analytics, and
- explore the technologies and possibilities of geospatial web application systems.
Basic Modules
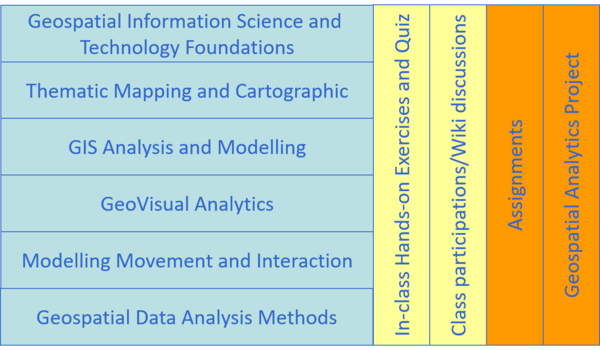
This course comprises ten integrated components as shown below:
Grading Summary
The grading distribution of this course are as follows:
- Class Participation 10%
- Quiz (4 @ 5% each ) 20%
- Assignment 25%
- Geospatial Analytics Application Project 45%
There will be no mid-term test or final examination for this course.