Difference between revisions of "Group01 Report"
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
Circular visualization is commonly used in Genomics and related omics fields due to its efficiency in revealing associations in high dimensional genomic data. Other used case includes visualizing human movement related to Global Migration where movement can be plotted using Chord diagram function within the circular plot. In fact, this project where the team is undertaking will possibly be the first known project to use circular plot to represent the multi-dimensional data of the World Development Indicators. | Circular visualization is commonly used in Genomics and related omics fields due to its efficiency in revealing associations in high dimensional genomic data. Other used case includes visualizing human movement related to Global Migration where movement can be plotted using Chord diagram function within the circular plot. In fact, this project where the team is undertaking will possibly be the first known project to use circular plot to represent the multi-dimensional data of the World Development Indicators. | ||
| + | |||
====Data structure and display==== | ====Data structure and display==== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 67: | ||
*For the inner-most track, Circlize also allows chord diagram to rendered to visualize movement as well as dendrogram to be rendered for clustering purposes. | *For the inner-most track, Circlize also allows chord diagram to rendered to visualize movement as well as dendrogram to be rendered for clustering purposes. | ||
| − | [[File:grp01_circlize03.png| | + | [[File:grp01_circlize03.png|270px]][[File:grp01_circlize02.png|270px]][[File:grp01_circlize05.png|270px]] |
==Visual Representation== | ==Visual Representation== | ||
| Line 84: | Line 85: | ||
| − | == | + | ==CASE STUDY: Ministry of Health== |
| − | + | ||
| + | '''User:''' Data analyst from Ministry of Health | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Objective:''' Understanding Health of people living in Singapore and how it is compared globally | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''World Bank Data Visualization: Country Trends''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Grp01_Casestudy01.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We start from '''Country Trends''' model and filtered health data for Singapore from 2007 to 2015. We analyze the series one by one and find abnormal trend against our expectation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The series with unexpected or abnormal trends are: | ||
| + | * '''SP.DYN.TFRT.IN''' : Fertility rate, total (births per woman) | ||
| + | * '''SP.DYN.CDRT.IN''' : Death rate, crude (per 1,000 people) | ||
| + | * '''SP.DYN.CBRT.IN''' : Birth rate, crude (per 1,000 people) | ||
| + | * '''SH.ANM.CHLD.ZS''' : Prevalence of anemia among children (% of children under 5) | ||
| + | * '''SH.ANM.NPRG.ZS''' : Prevalence of anemia among non-pregnant women (% of women ages 15-49) | ||
| + | * '''SH.ANM.ALLW.ZS:''' Prevalence of anemia among children (% of children under 5) | ||
| + | * '''SH.PRG.ANEM''': Prevalence of anemia among pregnant women (%) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''World Bank Data Visualization: Compare Series''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Grp01_Casestudy02.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | After finding the series need to spot on, we use '''Compare Series''' model to compare Singapore against other countries with same set of series. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, we pick ''Fertility rate, total (births per woman)'', ''Death rate, crude (per 1,000 people)'' and ''Birth rate, crude (per 1,000 people)'' for 2015. Singapore is one of the countries that have low fertility rate, low to medium death rate and low birth rate. Similar countries and areas are United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Macau, Korea, Liechtenstein, and Hong Kong. They generally are small counties or regions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we read the circle with clockwise direction, first segment are counties with high fertility rate, death rate and birth rate with the darkest green. Following segments also have high rates, but slight lower than 1st segment. Most of them are from Africa. 3rd segment are mostly counties from middle east and Asia with medium fertility rate, death rate and birth rate. The 4th segment are counties with low fertility rate and birth rate but high death rate. Most of them are from developed countries. Last segment contains countries from America and Asia with low to medium fertility rate, death rate and birth rate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Singapore is a developed country. It faces problems that other developed countries also face, which is the low fertility rate/birth rate. However, Singapore didn’t encounter a high death rate as other developed countries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''World Bank Data Visualization: Series Trends''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Series:''' ''Birth rate, crude (per 1,000 people)''<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Grp01_Casestudy03.png|800px]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Series:''' ''Singapore vs. USA vs. Iran (birth rate)''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Grp01_Casestudy04.png|800px]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | To further investigate Singapore’s birth rate and death rate, we use ‘''Series Trend’'' model. As fertility rate and birth rate are closely related, we didn’t check fertility rate in this example. | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the above birth rate circlize chart, Singapore is in the biggest segment which contains half of the counties. Singapore has a fluctuating but generally downward trend of birth rate. If we randomly pick other countries such as United State and Iran, they also have a downward trend of birth rate. In conclusion, half of the world have the same downward trend, it is not Singapore alone. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Series:''' ''Death rate, crude (per 1,000 people)''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Grp01_Casestudy05.png|800px]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Series:''' ''Singapore vs. USA vs. Congo (death rate)''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Grp01_Casestudy06.png|800px]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | As for death rate, there’s no big cluster that contains most of the countries which means death rate trend are quite different among countries. Even the cluster Singapore belongs to doesn’t show a generic trend. However, we can find some Africa or developing countries are improving their death rate since it is easier to control the high death rate, e.g. Congo. As for some developed countries, they have fluctuating trend but lower death rate such as USA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In conclusion to the insights discovered: | ||
| + | * Singapore government need to improve their birth rate which is a common problem across the developed countries. | ||
| + | * Singapore death rate is generally increasing. However, this should not be causing any alarmed as the overall death rate is still considered low. | ||
==Limitation and Future Works== | ==Limitation and Future Works== | ||
| Line 102: | Line 169: | ||
*The data model could be enhanced to automatically include new series indicators that World Bank might add from time to time. | *The data model could be enhanced to automatically include new series indicators that World Bank might add from time to time. | ||
*The application can also be enhanced to allow for country grouping filtering such as region, Incomes Levels, Lending Groups, etc. classified under the World Bank database. | *The application can also be enhanced to allow for country grouping filtering such as region, Incomes Levels, Lending Groups, etc. classified under the World Bank database. | ||
| + | *Allow for different visualization for in depth analysis instead of the current fixed box plot and line chart representation. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:20, 3 December 2017
WORLD DEVELOPMENT INDICATORS: A NEW VISUAL PERSPECTIVE
A web-based analytics application to visualize countries development across the globe
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
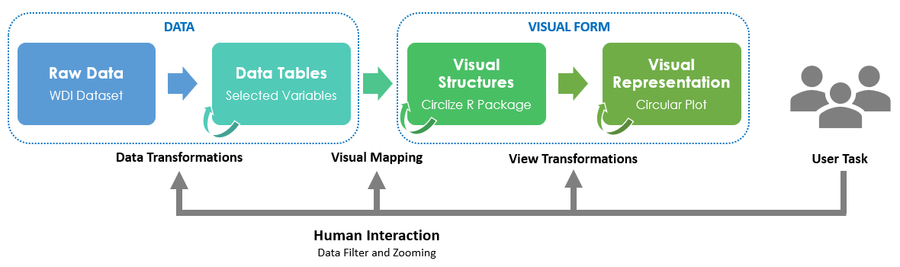
Visual Design Framework
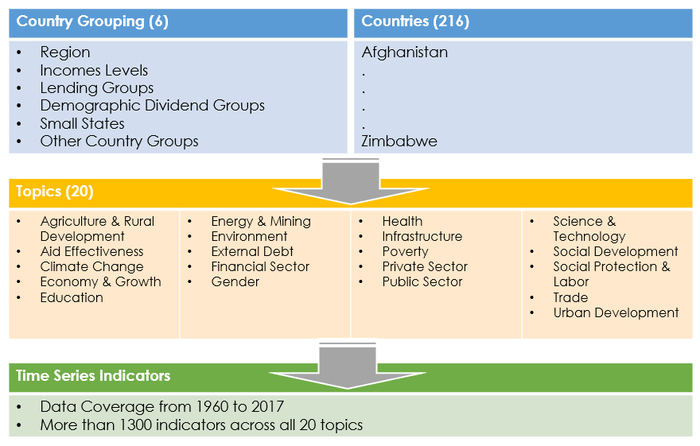
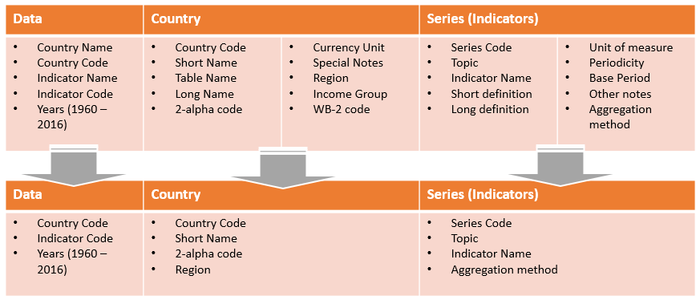
Raw Data
Data Tables
Visual Structure
Circlize in R
For development of the visual application, R will be used as the base code with the focus on using Circlize package to create the graphical visualization for WDI data.
The reason for selecting the Circlize package is that Circular layout is an efficient way for the visualization of massive amounts of information. This package provides an implementation of circular layout generation in R and provide the flexibility the use low-level and high-level graphics functions as defined by the team for specific purposes. Together with the seamless connection between the powerful computational and visual environment in R, it gives the team more convenience and freedom to design figures for better understanding complex patterns behind multiple dimensional data.
Circular visualization is commonly used in Genomics and related omics fields due to its efficiency in revealing associations in high dimensional genomic data. Other used case includes visualizing human movement related to Global Migration where movement can be plotted using Chord diagram function within the circular plot. In fact, this project where the team is undertaking will possibly be the first known project to use circular plot to represent the multi-dimensional data of the World Development Indicators.
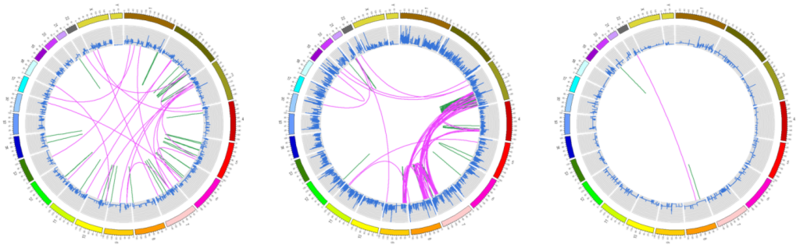
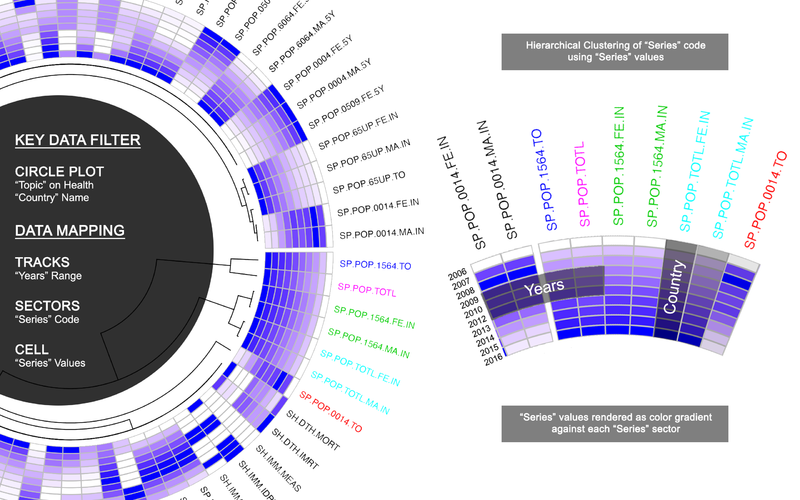
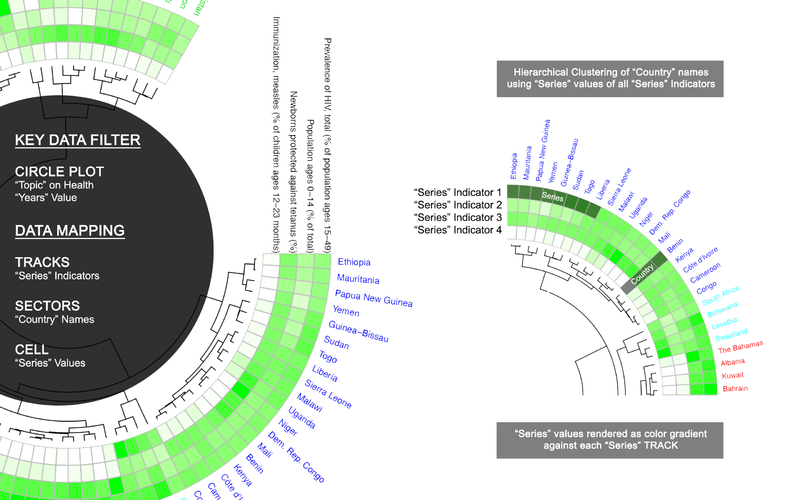
Data structure and display
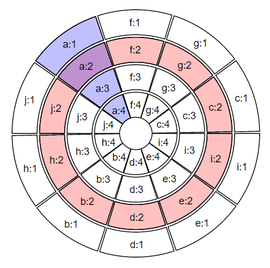
- A circular layout is composed of sectors, tracks and cells.
- As illustrated in the figure below, the pink circle is known as track, the blue section represents a sector and the intersection of a sector and a track is called a cell.
- Within each cell circlize allows the data to be displayed in the form of line graph, bar chart, histogram, scatterplot, heatmap, etc.
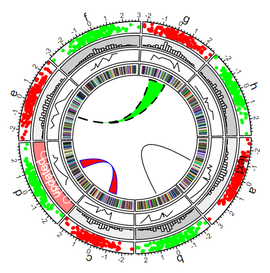
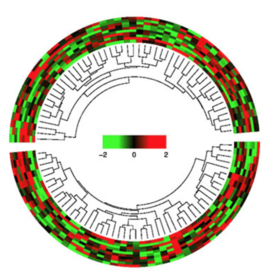
- For the inner-most track, Circlize also allows chord diagram to rendered to visualize movement as well as dendrogram to be rendered for clustering purposes.
Visual Representation
WDI data will be mapped into 3 circular plot in for 3 different type of visual representation as illustrated below:
Circular Plot (SeriesTrend)
Circular Plot (Country Trend)
Circular Plot (Series Comparison)
CASE STUDY: Ministry of Health
User: Data analyst from Ministry of Health
Objective: Understanding Health of people living in Singapore and how it is compared globally
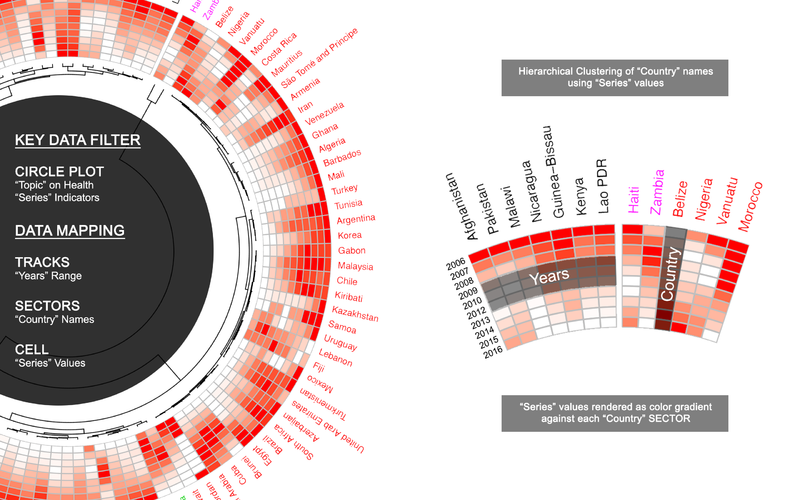
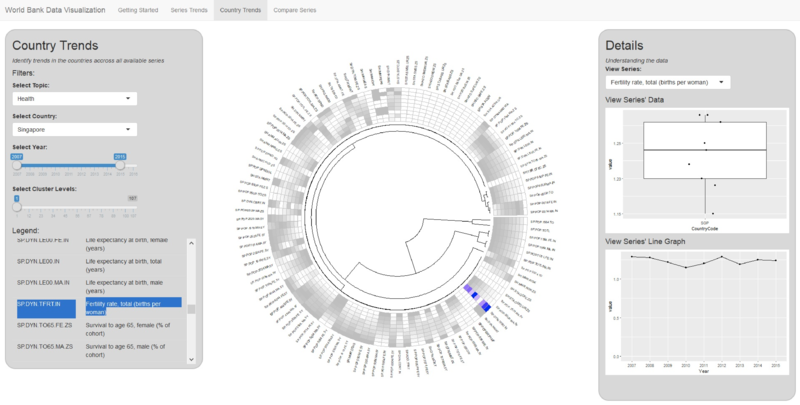
World Bank Data Visualization: Country Trends
We start from Country Trends model and filtered health data for Singapore from 2007 to 2015. We analyze the series one by one and find abnormal trend against our expectation.
The series with unexpected or abnormal trends are:
- SP.DYN.TFRT.IN : Fertility rate, total (births per woman)
- SP.DYN.CDRT.IN : Death rate, crude (per 1,000 people)
- SP.DYN.CBRT.IN : Birth rate, crude (per 1,000 people)
- SH.ANM.CHLD.ZS : Prevalence of anemia among children (% of children under 5)
- SH.ANM.NPRG.ZS : Prevalence of anemia among non-pregnant women (% of women ages 15-49)
- SH.ANM.ALLW.ZS: Prevalence of anemia among children (% of children under 5)
- SH.PRG.ANEM: Prevalence of anemia among pregnant women (%)
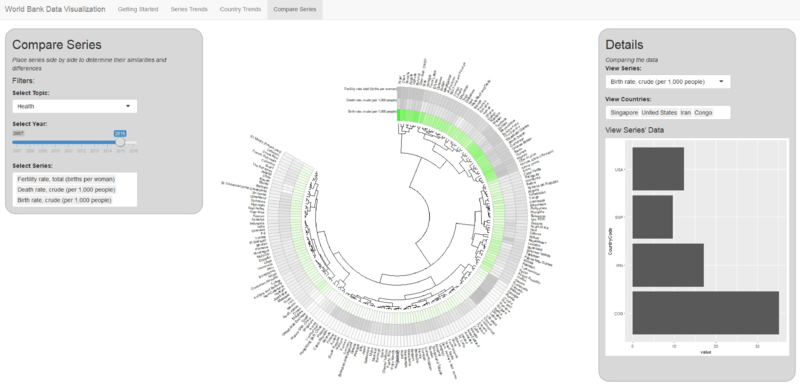
World Bank Data Visualization: Compare Series
After finding the series need to spot on, we use Compare Series model to compare Singapore against other countries with same set of series.
For example, we pick Fertility rate, total (births per woman), Death rate, crude (per 1,000 people) and Birth rate, crude (per 1,000 people) for 2015. Singapore is one of the countries that have low fertility rate, low to medium death rate and low birth rate. Similar countries and areas are United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Macau, Korea, Liechtenstein, and Hong Kong. They generally are small counties or regions.
If we read the circle with clockwise direction, first segment are counties with high fertility rate, death rate and birth rate with the darkest green. Following segments also have high rates, but slight lower than 1st segment. Most of them are from Africa. 3rd segment are mostly counties from middle east and Asia with medium fertility rate, death rate and birth rate. The 4th segment are counties with low fertility rate and birth rate but high death rate. Most of them are from developed countries. Last segment contains countries from America and Asia with low to medium fertility rate, death rate and birth rate.
Singapore is a developed country. It faces problems that other developed countries also face, which is the low fertility rate/birth rate. However, Singapore didn’t encounter a high death rate as other developed countries.
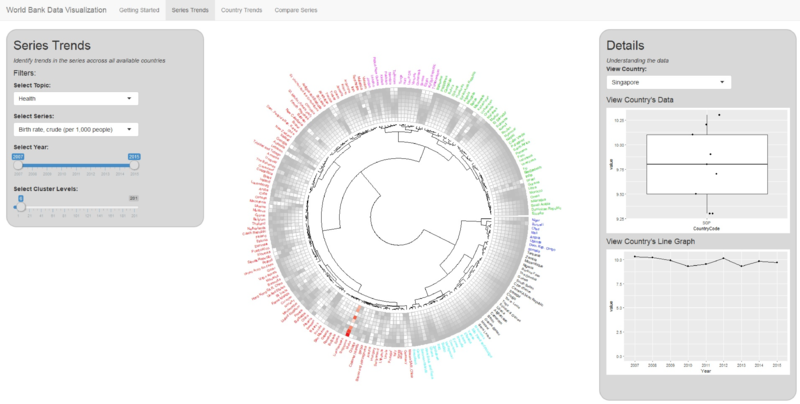
World Bank Data Visualization: Series Trends
Series: Birth rate, crude (per 1,000 people)
Series: Singapore vs. USA vs. Iran (birth rate)
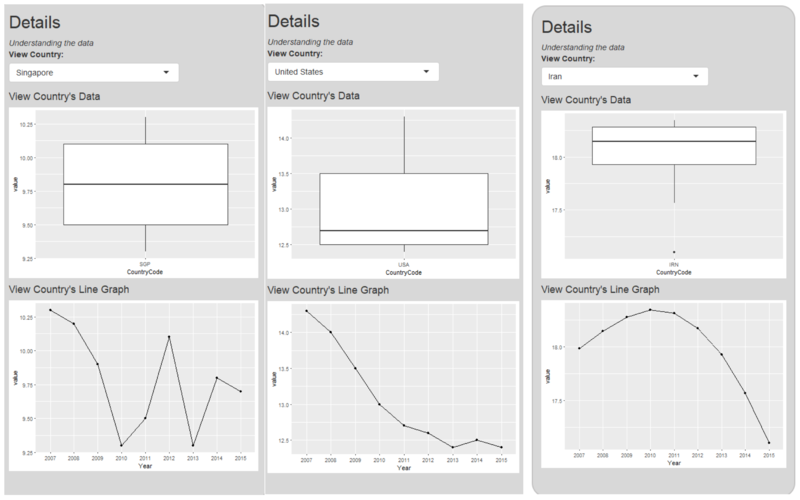
To further investigate Singapore’s birth rate and death rate, we use ‘Series Trend’ model. As fertility rate and birth rate are closely related, we didn’t check fertility rate in this example.
From the above birth rate circlize chart, Singapore is in the biggest segment which contains half of the counties. Singapore has a fluctuating but generally downward trend of birth rate. If we randomly pick other countries such as United State and Iran, they also have a downward trend of birth rate. In conclusion, half of the world have the same downward trend, it is not Singapore alone.
Series: Death rate, crude (per 1,000 people)
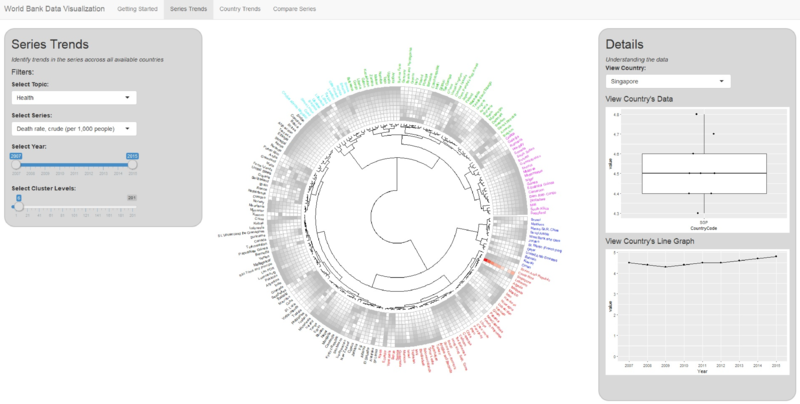
Series: Singapore vs. USA vs. Congo (death rate)
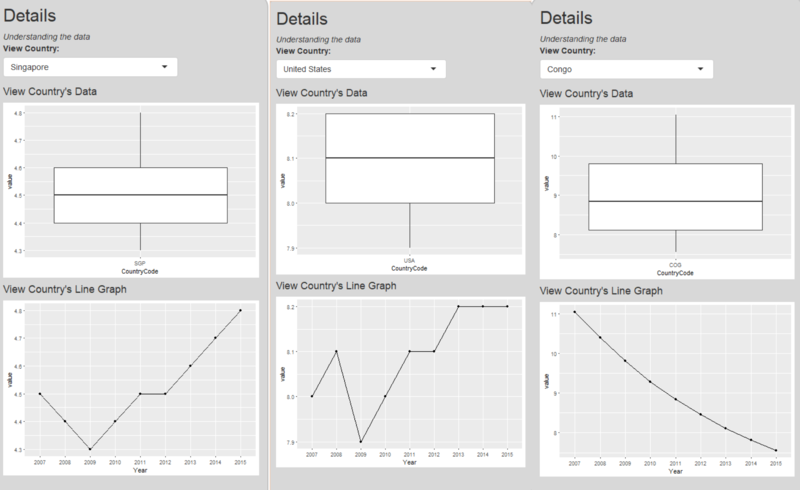
As for death rate, there’s no big cluster that contains most of the countries which means death rate trend are quite different among countries. Even the cluster Singapore belongs to doesn’t show a generic trend. However, we can find some Africa or developing countries are improving their death rate since it is easier to control the high death rate, e.g. Congo. As for some developed countries, they have fluctuating trend but lower death rate such as USA.
In conclusion to the insights discovered:
- Singapore government need to improve their birth rate which is a common problem across the developed countries.
- Singapore death rate is generally increasing. However, this should not be causing any alarmed as the overall death rate is still considered low.
Limitation and Future Works
Limitation of the current application
The World Development Indicators visualization application are currently having the following limitations.
- Due to the incumbent restriction of the Shiny package, maximum file size allowed to be uploaded is 30MB which does not allow the application to load the full 56 years of data into the application unless manual remove of data is performed after downloading it from World Bank Data. Additionally, the application is also designed to only accept .csv file.
- Circular Plot is restricted by it’s 360 degrees view it is not advisable to selected too many data variables to be display all at once.
- The data range of the selected series indicator must not have any "blank" values, else the application will automatically exclude it from the final visual representation.
- The application currently only support trends analysis through the heatmap colour gradient representation. There is no other visual representation of the absolute values in other graphical form.
- As hierarchical clustering will be performed, the No. of Cluster cannot be less than the No. of Sector values selected to allow clustering to happen.
Future improvement of the application
The World Development Indicators visualization application has a lot of potential to be extended and enhanced further.
- The data file upload function could be replaced with an automated API call to read future data uploaded by World Bank data to allow for real-time analysis and exploration.
- The data model could be enhanced to automatically include new series indicators that World Bank might add from time to time.
- The application can also be enhanced to allow for country grouping filtering such as region, Incomes Levels, Lending Groups, etc. classified under the World Bank database.
- Allow for different visualization for in depth analysis instead of the current fixed box plot and line chart representation.