Difference between revisions of "IS428 2016-17 Term1 Assign1 Manas Mohapatra"
Manasm.2012 (talk | contribs) |
Manasm.2012 (talk | contribs) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Abstract== | ==Abstract== | ||
| + | [[File:Housing classification.png|800px|frameless|center]] | ||
| + | <p>At the first tier all properties have been divided into Residential, Industrial, Commercial. I've decided to focus on Residential only, as the topic of properties gets quite complex when zoomed in, and I'd prefer to analyse the depth over breadth to get a better understanding of the topic. Thus upon zooming into the private residential properties, there are 3 kinds: Public , Private, Hybrid. The focus of the project is Private properties, hence I will be focusing on the classification of Private properties. </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Executive Condominiums were mentioned separately in the report under Private properties. Upon further research I came to know that Executive Condominium, or EC, are a type of housing in Singapore. First built in 1994, EC is a hybrid of public and private housing. They resemble private condominiums and are enclosed within a gated compound with security, amenities like swimming pools, clubhouses, playgrounds and so forth. They are also built and sold by private developers, but at a price lower than private homes because their land prices are subsidised by the Government. Additionally, buyers can take Central Provident Fund (CPF) grants to pay for an EC bought from a developer. Despite being a HDB project, EC is not eligible for Home Protection Scheme.ECs are subjected to Mortgage Servicing Ratio, which mandates that repayments of loans are capped at 30% of buyer's gross monthly income.Hence an EC is subject to some regulations that apply to HDB flats. Executive Condominium: A new type of housing introduced by the government in 1995 to meet the housing aspirations of the growing number of graduates and young professionals. It is a strata-titled apartment built by the private sector and has facilities comparable to a private condominium. However, there are some restrictions attached to it in the initial years such as eligibility conditions (similar to those for HDB flats) and a minimum occupation period before the flat can be sold.Thus I will be excluding Executive Condominiums from the analysis, as they fall under Public-Private Hybrid, whilst this analysis is purely on private properties</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <p>One of the most basic classifications of Private residential properties is:</p> | ||
| + | <p>1. Landed Property: This refers to detached houses, semi-detached houses, terrace houses, townhouses, strata bungalows and cluster housing.</p> | ||
| + | <p>2. Non-Landed Property: This refers to apartments and condominium housing.</p> | ||
| + | Moreover, Singapore is often divided into 3 geographical regions to analyse land properties as shown in the map below | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:SingaporeRegionMap.png|800px|frameless|center]] | ||
==Problem & Motivation== | ==Problem & Motivation== | ||
| + | To analyse: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Rental: The gross rent per month including service charge but excluding Goods and Services Tax (GST).</p> | ||
| + | <p>Price: The price agreed between the purchaser and the vendor for property and land. It excludes stamp duties, agency fees, legal and other professional fees.</p> | ||
| + | <p>Property Price Index: The ratio of the current price per square metre compared to that in the 4th Quarter of 1998. It is used to monitor the movement of private properties in Singapore.</p> | ||
| + | Important Points to note: | ||
| + | <p>2015 – tough year for pvt property market</p> | ||
| + | <p>2 years of price decline, oversupply of private </p> | ||
| + | <p>Govt. cooling measure. Oversupply of private residential property</p> | ||
| + | <p>Total supply = Vacant units + New units</p> | ||
| + | <p>To consider: unsold supply</p> | ||
| + | <p>Demand remains soft</p> | ||
| + | <p>Production cost increasing – high land price bids</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>The price-to-rent ratio is a well-established economic principle used for real estate valuation. It is typically calculated as the ratio of home prices to annualized rent in a given location. At its most basic level, the price-to-rent ratio is a benchmark for understanding whether is it better to rent or buy a property.</p> | ||
| + | <p>Secondary market: Subsale: The sale of a unit by one who has signed an agreement to purchase the unit from a developer or a subsequent purchaser before the issuance of the Certificate of Statutory Completion and the Subsidiary Strata Certificates of Title or the Certificates of Title for all the units in the development. Resale: The sale of a unit by a developer or subsequent purchaser after the issuance of the Certificate of Statutory Completion and the Subsidiary Strata Certificates of Title or the Certificates of Title for all the units in the development.</p> | ||
| + | |||
==Approaches== | ==Approaches== | ||
==Tools utilized== | ==Tools utilized== | ||
| − | Tableau 10.0 </ | + | <p>1. Tableau 10.0 </p> |
| − | + | <p>2. OCR Scanner</p> | |
==Result== | ==Result== | ||
| − | + | [[File:Supply.png|800px|frameless|center]] | |
| + | [[File:Price-rental.png|800px|frameless|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | One major result from the Tableau visualizations is that the Price of a private property is on average higher that its rental. Thus one can obsserve that the sales in Secondary market is higher than the sales in the Primary market (or from developers) | ||
Latest revision as of 17:34, 17 September 2016
Abstract
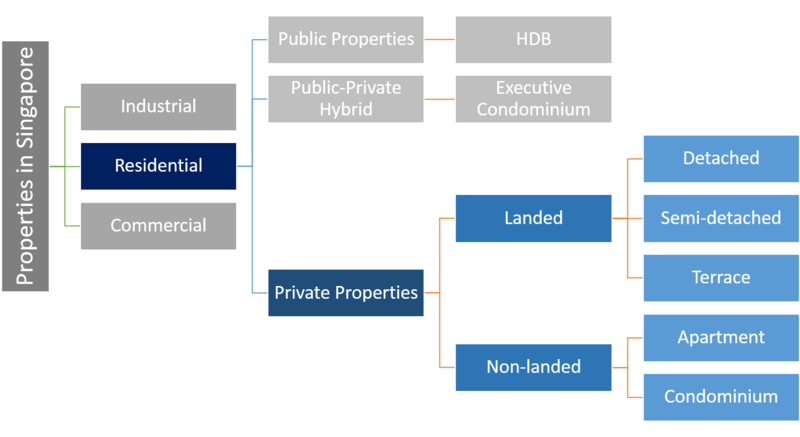
At the first tier all properties have been divided into Residential, Industrial, Commercial. I've decided to focus on Residential only, as the topic of properties gets quite complex when zoomed in, and I'd prefer to analyse the depth over breadth to get a better understanding of the topic. Thus upon zooming into the private residential properties, there are 3 kinds: Public , Private, Hybrid. The focus of the project is Private properties, hence I will be focusing on the classification of Private properties.
Executive Condominiums were mentioned separately in the report under Private properties. Upon further research I came to know that Executive Condominium, or EC, are a type of housing in Singapore. First built in 1994, EC is a hybrid of public and private housing. They resemble private condominiums and are enclosed within a gated compound with security, amenities like swimming pools, clubhouses, playgrounds and so forth. They are also built and sold by private developers, but at a price lower than private homes because their land prices are subsidised by the Government. Additionally, buyers can take Central Provident Fund (CPF) grants to pay for an EC bought from a developer. Despite being a HDB project, EC is not eligible for Home Protection Scheme.ECs are subjected to Mortgage Servicing Ratio, which mandates that repayments of loans are capped at 30% of buyer's gross monthly income.Hence an EC is subject to some regulations that apply to HDB flats. Executive Condominium: A new type of housing introduced by the government in 1995 to meet the housing aspirations of the growing number of graduates and young professionals. It is a strata-titled apartment built by the private sector and has facilities comparable to a private condominium. However, there are some restrictions attached to it in the initial years such as eligibility conditions (similar to those for HDB flats) and a minimum occupation period before the flat can be sold.Thus I will be excluding Executive Condominiums from the analysis, as they fall under Public-Private Hybrid, whilst this analysis is purely on private properties
One of the most basic classifications of Private residential properties is:
1. Landed Property: This refers to detached houses, semi-detached houses, terrace houses, townhouses, strata bungalows and cluster housing.
2. Non-Landed Property: This refers to apartments and condominium housing.
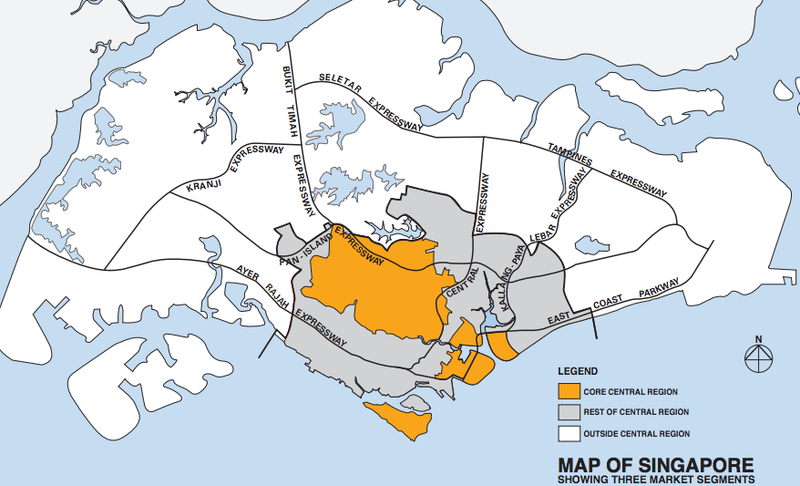
Moreover, Singapore is often divided into 3 geographical regions to analyse land properties as shown in the map below
Problem & Motivation
To analyse:
Rental: The gross rent per month including service charge but excluding Goods and Services Tax (GST).
Price: The price agreed between the purchaser and the vendor for property and land. It excludes stamp duties, agency fees, legal and other professional fees.
Property Price Index: The ratio of the current price per square metre compared to that in the 4th Quarter of 1998. It is used to monitor the movement of private properties in Singapore.
Important Points to note:
2015 – tough year for pvt property market
2 years of price decline, oversupply of private
Govt. cooling measure. Oversupply of private residential property
Total supply = Vacant units + New units
To consider: unsold supply
Demand remains soft
Production cost increasing – high land price bids
The price-to-rent ratio is a well-established economic principle used for real estate valuation. It is typically calculated as the ratio of home prices to annualized rent in a given location. At its most basic level, the price-to-rent ratio is a benchmark for understanding whether is it better to rent or buy a property.
Secondary market: Subsale: The sale of a unit by one who has signed an agreement to purchase the unit from a developer or a subsequent purchaser before the issuance of the Certificate of Statutory Completion and the Subsidiary Strata Certificates of Title or the Certificates of Title for all the units in the development. Resale: The sale of a unit by a developer or subsequent purchaser after the issuance of the Certificate of Statutory Completion and the Subsidiary Strata Certificates of Title or the Certificates of Title for all the units in the development.
Approaches
Tools utilized
1. Tableau 10.0
2. OCR Scanner
Result
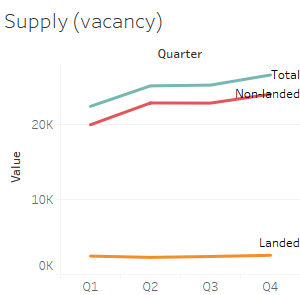
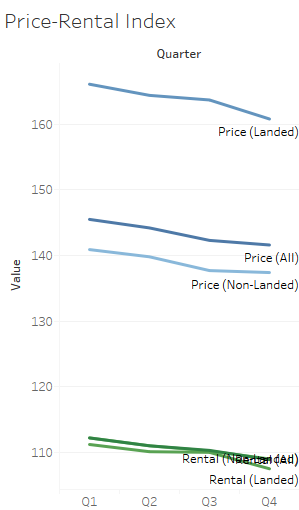
One major result from the Tableau visualizations is that the Price of a private property is on average higher that its rental. Thus one can obsserve that the sales in Secondary market is higher than the sales in the Primary market (or from developers)